Understanding Personality In Order To Improve Communication
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Sociology |
| ✅ Wordcount: 4282 words | ✅ Published: 08 Sep 2017 |
New Britain Oils is a Palm Oil manufacturer who specialises in fully sustainable Palm Oil. The organisation is a subsidiary of New Britain Palm Oil Limited which has been around since the 1980’s.
The organisation consists of a number of site across the globe with the main plantations growing in Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands covering 82,000 hectares and employing over 10,000 workers. There are only two refinery, one in Papua New Guinea and the second is in Liverpool. Liverpool is the only site outside of Australasia and had an opening employment count of 26 in 2010, this number currently stands at 78 in 2016.
The Liverpool Refinery opened in 2010 starting with bulk oil supply into 28 tonne road tankers. In 2012 the Packing Facility was opened, this plant converts some of the bulk oil into industrial margarine and other bakery fats. Since opening in 2010 New Britain Oils is now the number one supplier of sustainable Palm Oil in the UK.
With the rapid growth of the Liverpool site came an increase in employees and inevitably the dynamic of the working environment changed with it. Some employees left the organisation, who have since been replaced, and new departments have been created to cope with the growth of the business. Consequently this instability has affected the productivity in some areas. This issue could’ve been exacerbated by the management teams’ failure to recognise this variation and react accordingly. Bringing in new workers will bring in differing psychological preferences and according to Jung (1971) preferences influence our choice of careers, ways of thinking, relationships, and work habits. Richard L. Hughes et al. (2015) stated that our preferences play a role in the characteristic and unique ways we behave from day to day. Consequently, could increasing the management awareness of their teams individual preferences promote better relationships, through improved communication, within the organisation?
Mary Uhl-Bien and George B. Graen (1995) discovered that higher quality Leader-Member Exchange relationships have very positive outcomes for leaders, followers, work units, and the organisation in general, the same research also found that the development of Leader-Member Exchange relationships is influenced by characteristics and behaviours of leaders and members.
This assignment will first outline what can affect the effectiveness of a leader and why increasing the value of relationships could increase the effectiveness of a leader. Using existing research it will look at why communication is a crucial tool for a leader and how an understanding of how differing personality types interact, prefer to receive information and what drives their decision making, can enable leaders to communicate more effectively. A recognised psychological test will be used to gather data about the psychological preferences of some of the employees across different areas of the business with the objective being to identify potential differences in preferences. The overall aim of the research is to increase the management teams’ awareness of some of the differing personality types within their department and understand the differences between these types. The intention is to educate the management team and give them the opportunity to adapt their leadership style to promote better quality relationships through a better understanding of the individuals within their team.
Leadership
Leadership has been the subject of research for a long time. Burns (1978) stated that due to its importance in human groups, the concept of leadership is one of the organisational topics that have most intrigues researchers for centuries. As a result, attempts to define leadership have proved to be an ambiguous. Leadership as simply a complex form of social problem solving (Miller and Ross 1975), leadership is directing and coordinating the work of group members (McCall Jnr et al. 1988), leadership is creating conditions for a team to be effective (Reason and Mycielska 1982). Powell and Pirsico (rev. ed. 2003) defined leadership as the process of influencing an organized group toward accomplishing its goals. All of the definitions stated have a connection which is the reference to a group or team. This implies that leadership would not exist without individuals to lead.
The definitions detailed show the variation in concepts of leadership and this is reflected in the research. Some leadership researchers have focused on the leader-follower relationship and Geoff Thomas et al. (2013) stated that the reason we focus on the leader-follower relationship is because research shows that the quality of this relationship is reliably linked to follower well-being and performance.
Other researchers, such as John Adair, looked at how the situation can affect the way leaders act. Adair identified that leadership is affected by three things. The task, the team and the individual and leaders need to balance their time equally between the three areas and at certain times one of the areas will dominate, but over the long run a balance would be achieved (John Adair 1982). Figure 1. shows John Adair’s concept of action centred leadership. In different situations the circles will be overlapping different amounts showing which the dominant factor is.


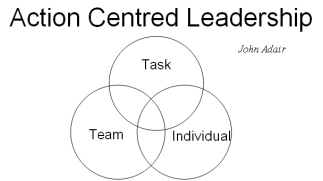 Figure 1. John Adair (1982)
Figure 1. John Adair (1982)
Researchers have studied the behaviours of the leader and what behaviours are associated with an effective leader. Leadership is earned and it is not granted by role or rite of passage (Lloyd l. Sederer 2012) and through our interactions humans sustain the effect of leadership and we interpret it even though we may not be aware that we do so (Kempster and Parry 2011). This means that leaders could be established by displaying a distinct set of behaviours which followers associate with a leadership role.
Research shows that there are behaviours that can be attributed to an effective leader. These are known as The Six C’s of Leadership Credibility (Bamford, 2016)
 Figure 2. David Bamford (2016)
Figure 2. David Bamford (2016)
Communication would fall under the ‘Character’ umbrella and plays a crucial fundamental role in every business. The quality of the communication can be affected by the relationship between two individuals and a key element of the quality of the relationship is the interaction between the personalities. Different personalities and give out information in different ways and how this information is interpreted can affect the quality of the communication. Leaders who have calm dispositions and do not attack or belittle others for bringing bad news are more likely to get complete and timely information from subordinates than are bosses who have explosive tempers and a reputation for killing the messenger (Hughes et al. 2015).
Personality
Many theories have been developed to explain what causes individuals to behave the way they behave and why they behave differently to other individuals. The term personality is among the most comprehensive of those in the psychologist’s vocabulary, clarification of its connotation to the satisfaction of a majority, even of psychologists, is difficult (John K. McCreary 1960). This view begins to explain the range of opinions as to what personality means to people. McCreary goes on to describe some the definitions as experimental, calling for criticism and inviting agreement. This belief is quite ambiguous as all definitions would fall under one of those three categories.
Robert Hogan (1991) had a different approach and he stated that the term personality is fairly ambiguous and has at least two quite different meanings rather than a definition. The first meaning implies that personality is the impression a person makes on others. The second meaning is less obvious and focusses more on the unseen processes within a person which explains why we behave the way we behave. These internal processes have been categorized as traits by some researchers. Personality traits as useful concepts for explaining why people act fairly consistently from one situation to the next (Hughes et al. 2015).
Traits are characteristics or habits which are specific to an individual. Traits can have one of two outcomes, such as extroversion and introversion however, individuals are not categorized into one these traits but rather they sit on a scale which may show a preference towards one of the two oppositions. If we attempt such scaling, we should remember that we are likely to constrain personalities unnaturally fitting them into one mould (Allport and Odbert 1936)
Gordon Allport and Henry Odbert were theorists the idea of traits and trait names. They explored two comprehensive dictionaries and identified 17,953 trait-names in the English language. They reduced the list down to 4500 adjectives. They reported that the unfamiliarity of a large proportion of the trait-names in our list proves that our practical vocabulary is inadequate to the task of representing the complex phenomena of human nature (Allport and Odbert 1936). They arrange the traits into a hierarchy of three:
- Cardinal Traits – the dominant trait
- Central Traits – general characteristics
- Secondary Traits – not obvious, such as attitudes
Raymond Cattell further explored the work completed by Allport and Odbert by taking the list of 4500 adjectives and reducing it down to 171 by removing all the synonyms. Cattell was the first to collect data regarding personality traits. The outcome of the data he collected allowed him to come up with 16 personality factors which he used to come up with an assessment called the 16PF. This was one of the first attempts to measure personality.
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator
Measuring personality is difficult because personality cannot be seen but some psychology researchers have devised tools that can be used to give results owing to an individuals’ psychological preferences. The most commonly used tool is the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI). This tool evolved over a period of 5 decades and was based on the work carried out by Swiss Psychologist Carl Jung who spent a lot of his career researching personalities within individuals.
Jung defined two opposing tendencies in personality: introversion and extroversion and while both tendencies are present in all individuals, one tends to dominate the other (Almerinda Forte 2005). Along with the two opposing tendencies for personality, Jung also identified four functions relating to personality which are thinking, feeling, sensing and intuiting.
Katharine Briggs and her daughter Isabel Myers both had an interest in individual differences which they brought together, including the work done by Carl Jung, which resulted in the development of the MBTI. The MBTI is a very popular tool used worldwide mainly for psychiatric patients but also the MBTI has been in extensive use in personal and management development since the early 1970’s (Leary et al. 2009).
The MBTI is based on the principle that the differences in behaviour from one person to another can be expressed in terms of preferences between the polarities (Amel Behaz and Mahieddine 2012) and the MBTI focuses on two primary human activities: how people gather information and how they make decisions (Richard J. Daisley, 2011). However, note that measurement is only possible if we blindly insist that people are comparable in respect to each ‘common’ trait (Allport and Odbert 1936)
Allen et al. (2002) adapted the Four-Part Framework developed by Susan Brock to demonstrate the difference between each of the oppositions. This is shown below:

Figure 3. Allen et al. (2002)
In completing the MBTI each of the individuals will demonstrate a preference for one of the two oppositions. For example the introvert/extrovert scale is based how the individual get their energy whilst the sensing/intuitive scale considers how people interpret data. The thinking/feeling scale looks at the factors people take into account when making decisions and the judging/perceiving scale considers the amount of information an individual needs before making a decision.
Yuval Cohen et al. (2013) described each of the bipolar oppositions in their paper based on personality types of project managers.
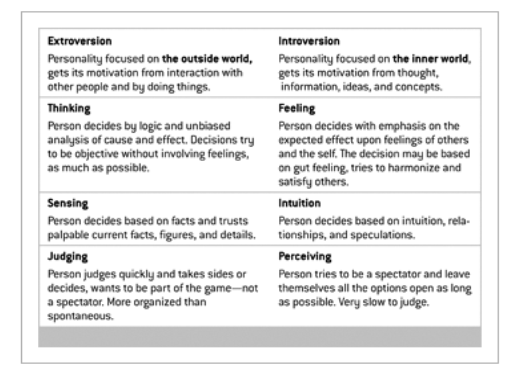
Figure 4. Yuval Cohen (2013)
The first opposition is the most commonly associated when thinking about differing personalities: Introversion or Extroversion. There are three main differences between introversion and extroversion. Energy creation is noted as the most important difference, but the response to stimulation and the approach to knowledge are also different (Heidi Eve-Cahoon 2003). Introverts are energized by the internal world of ideas, impressions, and emotions, whereas extroverts focus outside of themselves and are energized by activities, people, and things of the outside world (Heidi Eve-Cahoon 2003). Extroverts are often seen as possessing the desirable set of personality traits for success in today’s fast-paced world, on the other hand, introverts bring a whole host of desirable personality traits to the table, which need to be equally valued, nurtured, and utilized (Shelley J. Schmidt 2016).
 Samples for the United States suggest that 55 to 60 percent of all people are extroverts (Gardner and Martinko 1996). Fretwell et al. (2013) highlighted some data (Filbeck et al. 2005, Fox-Hines and Bowersoch 1995) relating to each of the four dimensions, which demonstrates the preferences of the U. S. population. This data agrees with other research that a greater percentage of individuals have an extroverted preference. Results of this study will demonstrate any direct correlation to the results of the U. S population.
Samples for the United States suggest that 55 to 60 percent of all people are extroverts (Gardner and Martinko 1996). Fretwell et al. (2013) highlighted some data (Filbeck et al. 2005, Fox-Hines and Bowersoch 1995) relating to each of the four dimensions, which demonstrates the preferences of the U. S. population. This data agrees with other research that a greater percentage of individuals have an extroverted preference. Results of this study will demonstrate any direct correlation to the results of the U. S population.
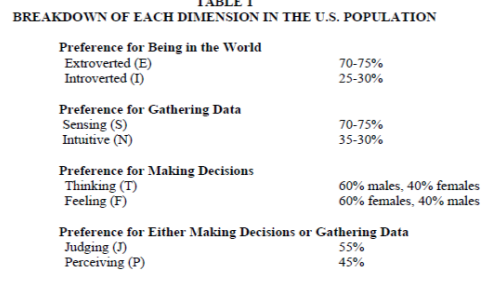
Figure 5. Fretwell et al, (2013)
A similar study was documented in Training and Coaching Today (2007) which showed the findings from a recent MBTI study of 1634 individuals in the UK.
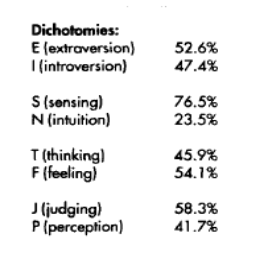
Figure 6. Training and Coaching Today (2007)
As New Britain Oils is situated in the UK, it is predictable that the results from this study will correlate to the results from the study of the UK individuals.
As there are four bipolar oppositions for MBTI, this means that there are sixteen possible results which could be given based on the responses to the questions and the scores obtained on the bipolar scale.
 Figure 7.
Figure 7.
One downside to having so many possible outcomes and factors involved is that it takes interest and effort to remember one’s type (William A. Lynagh 2006).
Psychology researchers and advocates of personality preferences maintain that no one type is better than the others because a team benefits from the presence of varied personality types (Cynthia Plonen 2015). The best way to think of it is that neither set of traits is better or more valuable than the other – rather, they are different, often complementary, and both are needed to make the world go round, so-to-speak (Shelly J. Schmidt, 2016), however many more leaders are ISTJs, ESTJs, and ENTJs than other types (Hughes et al. 2015). Gathering data from the management team will be able to demonstrate a positive or negative correlation to this statement.
Methodology
The data collection process involved 25 employees from a number of departments and all of the employees who completed the questionnaire did so voluntarily. Results were obtained from 100% of the employees in two departments along with 50% of employees from another department. Shift patterns limited one department but a representative sample of 65% was obtained to provide data. In addition, 57.14% of the management team were included in the study to determine the range of the personality preferences amongst the management team. Figure 7 shows the structure of the organisation.
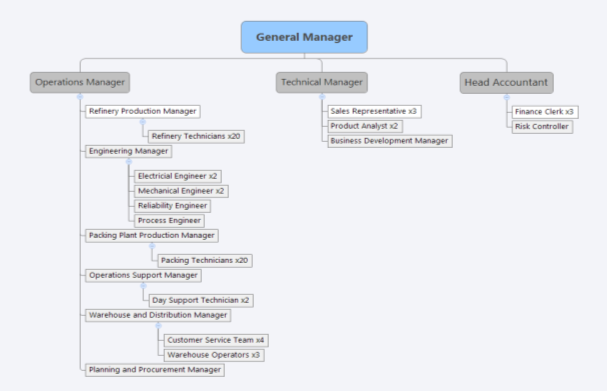
Figure 7.
Despite there being question marks over the integrity of personality measurement instruments, they are still widely used in organisations. A Humanmetrics Jung Typology Test, based on the MBTI, will be used to gather the data for this study. The questionnaire consists of 64 multiple choice questions which will result in a four letter type based on the Myers-Briggs 16 types.
The Humanmetrics Jung Typology Test was selected because the results will correlate directly to the MBTI theory and also this method is more accessible for employees and allows for more data to be collected.
The purpose of the questionnaire is to begin to develop an understanding of the personality types that exist within some departments of the organisation because personality questionnaires are ideal for describing personality (Luke D. Smillie 2008).
The MBTI has been used widely across a number of business sectors for decades. The instrument has been extensively tested for reliability and validity (James C. Lampe 2004) and the extensive research on the instrument since its development supports its reliability and validity (Moore et al. 2004). Over 2 million copies of the instrument are sold each year (Pittenger 1993) and the MBTI is the most widely used instrument for non-psychiatric populations (A. J. DeVito 1985).
Despite its depth of validation there are still many sceptics of the MBTI itself as a viable instrument and future research must use more rigorous designs before greater confidence can be placed in the results (Gardner and Martinko 1996). It has been speculated that subjects of the instrument can falsify their responses in an attempt to achieve different results. This wary approach, when questioning the validity of the responses, could be considered when the instrument is used as part of an organisations recruitment process as subjects could change their responses in an attempt to become more appealing to an employer.
The organisation has 78 employees and a sample of 32% were included in the study but statistical generalisation is difficult owing to the low number of cases (Bamford et al. 2003). Some correlations can be made between the existing literature and the results of the MBTI used in the organisation but this cannot be reflective of the organisation as a whole.
Findings
Key Findings
The key findings from the research showed that there are a range of personality types present within the organisation and out of the 16 possible personality types the individuals from the organisation fell into 9 of those types. Over 50% of the results from the individuals who took part in the study fell into 3 of the possible 16 personality types. All 3 of the common personality types included a preference for thinking rather than feeling and judging rather than perceiving. This means that 68% of the individuals included in the study prefer to be analytical, critical and make decisions objectively but those individuals only require a minimal amount of information to make decisions and as a result they can make poor decisions.
|
ISTP |
ISFP |
ISTJ |
ISFJ |
|
7 |
|||
|
ESTP |
ESFP |
ESTJ |
ESFJ |
|
1 |
5 |
3 |
|
|
INTP |
INFP |
INTJ |
INFJ |
|
1 |
|||
|
ENTP |
ENFP |
ENTJ |
ENFJ |
|
1 |
1 |
4 |
2 |
Figure 8.
Introvert/Extrovert Preference
As mentioned previously, one of the dimensions that then MBTI specifically looks at is where individuals prefers to focus their energy. This dimension has two bipolar oppositions, introversion and extroversion. The data gathered shows that 68% of the individuals who took part in the research had a greater preference for extroversion.
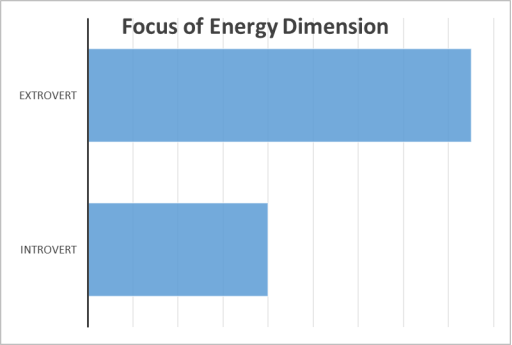
This means that more than half of the employees at the organisation prefer to work in larger groups, get their energy from people and activities. The management team could use this data to adapt their leadership style to suit some of the personality preferences within their team and using a collective approach to problem solving may prove to be more effective.
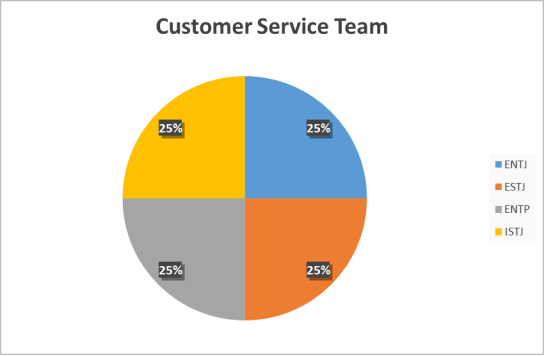
Customer Service Team Personality Types
75% of the customer service team have a preference for extroversion and this would fit well with their role and responsibilities as they obtain their energy from interacting with people. Having this preference could help them to build better relationships with customers and suppliers. 100% of the customer service team had a preference for thinking which means they are more concerned with operational considerations and are able to detach themselves from the decisions they make which is a good characteristic to have relative to their role.
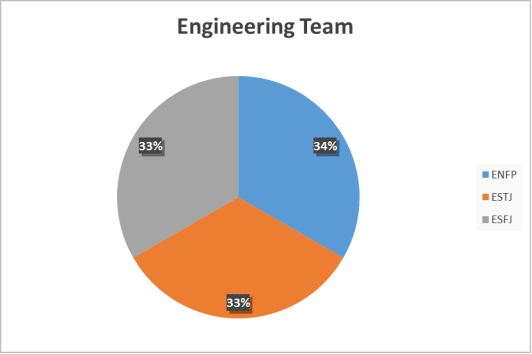
Engineering Team Personality Types
50% of the engineering department contributed to the research and 100% of the employees who contributed showed a preference to extroversion so using team meetings when tackling engineering issues would give the extroverts the forum to think out loud, share ideas with each other and has the potential to be very effective. The Engineering Manager showed a preference to introversion and so he would prefer to take the information gathered from the team meeting and spend some time thinking about in order to come up with the most effective solution. This approach to engineering issues has the potential to be very productive by considering the individuals preferences in order to maximise their input and provide the Engineering Manager with lots of information before making decisions.
Shift Workers Personality Types
The responses from the shift workers presented a large amount of variation, however, 69.23% of the shift workers, who completed the questionnaire, showed a preference for extroversion. This outcome is reasonably foreseeable in having a higher number of extroverts in this department as all of the individuals work on a shift consisting of four employees. Individuals with a preference for introversion would be less attracted to work which would include them working within shifts, although only having four employees on a shift would be more attractive than organisations with high numbers of employees on each shift.
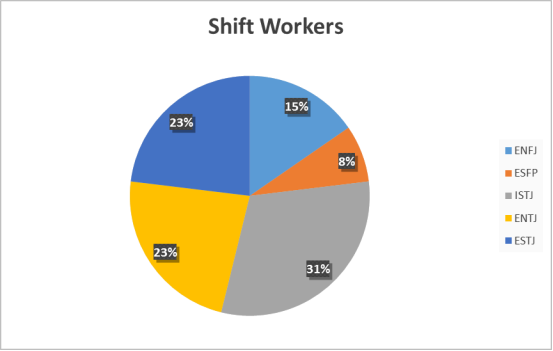
92.3% of the shift workers showed a preference for judging rather than perceiving and individuals with this preference only require a minimal amount of information before making a decision. Shift workers operate on a 24 hour rotation system therefore they work outside of normal hours and so they are expected to make quick decisions independently. Individuals who have a preference for perceiving like to intake as much information as possible before making a decision and so too many perceivers on one shift could delay decisions and corrective action which could result in reduced output from that shift.
Management Team Personality Types
57.14% of the organisations management team took part on the study. The data shows that the management team fall into three different personality types: ISTJ, ESTJ and INTJ.
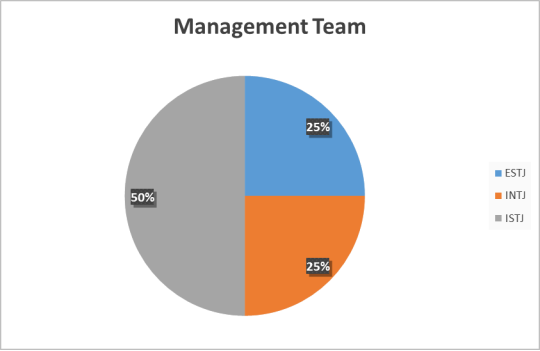
The results showed that 50% of the individuals who contributed had a personality type of ISTJ which displays characteristics which would typically be associated with someone who is in a senior position, such as being serious, practical and realistic. 75% of the management team, which would equate to 42.8% of the total management team, demonstrated a preference for introversion rather than extroversion and these members of the management team are responsible for technical, engineering and the safety department. All of these departments are smaller, in team size, than all of the other departments and each of these members of the management team have their own individual office and so it is foreseeable that they would have a preference for introversion. The extroverted individual from the management team is responsible for a large team consisting of 20 shift workers and their workspace is located in the production area and so having the extroverted preference is advantageous to their role. All of the members of the management team showed preferences for thinking and judging rather than feeling or perceiving respectively. This again is a predictable outcome given their position within the organisation as this indicates that they prefer to be analytical, approach decisions objectively and pay careful attention to any potential operational impacts.
Discussion
The first of the four dimensions provides data on the individuals’ preferences towards introversion or extroversion. Samples from the United States suggest that 55 to 60 percent of all people are extroverts (Gardner and Martinko, 1996). The data obtained from this study appear to validate this statement as 68% of the individuals showed a preference for extroversion. The data in the study by Fretwell et al. (2013) noted that 70 – 75% of individuals in the U. S. have a preference towards extroversion and that data would correlate more closely with the data obtained in this study. The study of the U. K. showed only 52.6% of the individuals have a preference towards extroversion which is contradictory to the results of this study.
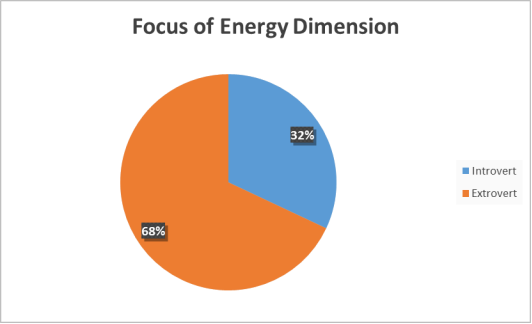
Consequently more than half of the employees, involved at the organisation have a personality focused on the outside world, get motivation from interaction with other people and by doing things (Yuval Cohen, 2013). The data could be used by the management team in order to improve productivity by using groups sessions allowing the individuals share ideas.
Comparison to Existing Research
The data previously mentioned in the study by Fretwell et al. (2013) and the data shown in Training and Coaching Today (2007) showed results for individuals in U. S. and U. K respectively and some of those results are closely correlated to the results of this study.
|
Dimension |
U.S. |
U.K. |
New Britain Oils |
||
|
Extrovert |
70-75% |
52.6% |
68% |
||
|
Introvert |
25-30% |
47.4% |
32% |
||
|
Sensing |
70-75% |
76.5% |
60% |
||
|
Intuition |
35-30% |
23.5% |
40% |
||
|
Thinking |
60% males |
40% females |
45.9% |
68% males |
36.6% females |
|
Feeling |
40% males |
60% females |
54.1% |
32% males |
33.3% females |
|
Judging |
55% |
58.3% |
88% |
||
|
Perceiving |
45% |
41.7% |
12% |
||
The similarity of results for the extrovert and introvert dimension has already been discussed but there are similarities with results for the other dimensions. The sensing and intuition dimension results are similar to the results from the studies of the U. S and U. K. albeit closer to the results from the U. S study, as there is a greater preference towards sensing. This means that the individuals prefer concrete details of a situation and rely on the five senses to observe facts or happenings (Fretwell et al. 2013)This also means that they tend to be practical, orderly, and down-to-earth decision makers (Hughes et al. 2015).
When comparing the thinking and feeling dimension, the results are more closely correlated with the results for the study of the U. S. population. 72% of the individuals, in this organisation, showed a preference to thinking, however in the study of the U. K. the majority of the individuals showed a preference to feeling. This means that individual from this organisation prefer to assume a more objective approach to decisions and show more consideration to operational factors. Individuals who show a greater preference towards thinking are associated with careers such as consultants, lawyers, executives and engineers. (www.similarminds.com).
The results for the final dimension show that overall the individuals from the organisation have a much greater preference for judging rather than perceiving. These results compare with the studies from the U. S. and U. K., in terms of the majority of the individuals showing a greater preference towards judging, however nearly 90% of this organisation shares this preference as were the other studies show just over 50%. This could impact the organisation because individuals with this preference tend to make up their minds quickly and as a result can make poor decisions (Hughes et al. 2015).
The management team in the organisation presented results which partially correlated with the work done by Hughes et al. (2015), who stated that more leaders are ISTJs, ESTJs, and ENTJs than other types. In this organisation, the management team demonstrated personality types matching ISTJ and ESTJ however there were no ENTJ personality types from the results collected.
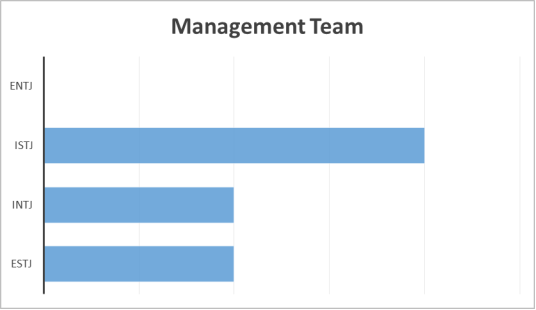
50% of the management team showed a personality type of ISTJ and this preference would be associated with behavioural characteristics such as being responsible, organised and punctu
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


