The China-US Trade War: Causes and Impacts
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: International Relations |
| ✅ Wordcount: 2253 words | ✅ Published: 03 Nov 2020 |
In the 21st century the effects of globalization on society include high amounts global trade and foreign direct investment. The results of globalization are clear in the past two decades when examining companies ‘outsourcing’ certain processes in production and increasing foreign direct investments in these countries. This upward trend in trade and foreign direct investment (FDIs) faced a massive barrier when the current President of the United States (POTUS), Donald Trump, implemented a “trade-war’ with a country home to majority of the offshoring production operations American companies employed: China. Potus argued that China’s practices in trade were unfair; whilst China argued that the U.S was attempting to limit their rise in economy. This lead to the U.S imposing trade tariffs amounting to over $360bn on Chinese goods, with China countering and imposing tariffs amounting over $110bn on American products (BBC, 2019).
The aim of this paper is to analyze the current trade dispute between China and the United States of America and argue its negative impact on global trade, foreign direct investment and international business, and positive impact on other countries, with focus on company’s manufacturing units. This paper will firstly explore the impact the China-US trade war has had on the upward globalization trend in the last half century. Secondly, the paper will assess the existence of ideological conflicts between China-US, with regards to free-market and state controlled economies. Thirdly, the paper will explore how a global brand such as, Samsung: a Korean tech-giant, would re-assess their FDI’s in manufacturing locations, with regards to the political and socio-economic effects of the China-US trade war. Lastly, the paper will discuss the impact of the current trade-war and its future affects on the global economy.
The ongoing China-US trade war has resulted in major consequences on a global scale. The upward trend of globalization in the last 20 years has been stagnated and has the potential to spiral downwards due to the tariffs and taxes implemented by both countries. Globalization as been on an upward trend and growing since the Industrial Revolution in the early 1900s. The era of the digital age has expanded the potential and growth of globalization exponentially, with decreasing barriers to entry through rapid advances in technology. The formation of the World Trade Organization in 1995 facilitated and regulated all international trade, supporting this growth in globalization. The current trade dispute between China-US has stagnated this growth and has the potential to not only put a stop to this upward trend, but also have the power to propel it downwards. China is only second to the European Union with regards to exports to the United States.
Due to the new trade tariff and taxes implanted by POTUS and Chinese President, Xi Jinpang’s (Xi) retaliation; a mass amount of American companies have shifted focus towards other countries to import goods, reducing imports from China to 12.2% (CNBC, 2019). Potus continued to undermine trade law with the “America First” trade policy. “The Free World must embrace its natural foundations…if you want freedom take pride in your country”(Trump, 2019). This quote is an extract from POTUS’ speech in the U.N defending the ‘America First ‘policy. To reduce the trade deficit with China, POTUS has used nationalism as a blanket for this policy to sell it to Americans, as a positive patriotic move, when in reality; this has the potential to disrupt world trade. Chief economist at Capital Economics, Niel Shering, explained that POTUS’s move to levy tariffs on Chinese imports could lead to the end of globalization, leading to macroeconomic implications towering over a tariff battle (CNBC, 2019).
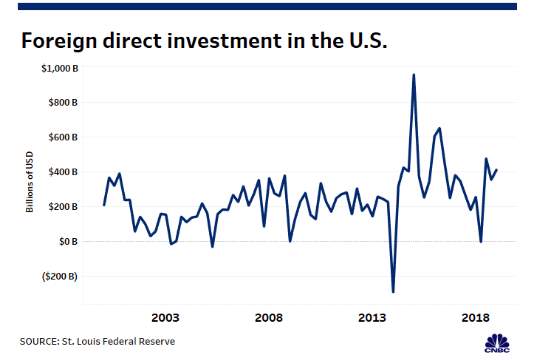
(Source: St.Louis Federal Reserve, 2019)
The graph above depicts a massive drop in FDI’s in the United States between 2014 and 2018, highlighting the effects the trade war with China has had. This negatively impacts American consumers, because this decrease suggests that investors are more wary, leading to big blows to the retail and manufacturing industries.
This leads to higher prices on everyday consumer goods such as clothing and electronics. Dan Hanson and Tom Orlik, explained that if markets slump as a result of the tariff expansion covering U-S China trades, by 2021 global GDP would be reduced by $600bn in 2021 (Bloomberg, 2019). Global GDP amounted to 84.93 trillion in 2018 (Statista, 2019), hence a $600bn hit is a massive counter effect caused by the China-US trade war.
Disruptive technologies in the past 20 years have had positive outcomes in society, with the inventions such as the smartphone and the Internet, which have facilitated global networking. These trade barriers have the potential to not only disrupt technology and global supply chains negatively, but also increase the price of consumer goods, due to import restrictions, leading to lower amounts of welfare and productivity on a global level. These alarmingly high numbers and consequences highlight the effects the China-US trade war is having on the upward trend of globalization in the past 20 years, which raises the question: can a state-controlled economy successfully conduct long-term business with a free democratic society?
A communistic government compared to a democratic ‘free-world’ will have clashing ideologies and values. Both countries have had stringent views on governing for a long period of time. One advocates serving the people of the country, when the other expects the people to serve the country. This was not an issue in the past as the US and China were mutually benefiting of each other, and kept governance practices separate to trade agreements. Thomas Friedman explained that historically China ‘s trades with the US simply ranged from the Chinese importing Boeing jets and soybeans, whilst the US imported clothing and toys (Friedman, YEAR observer artic).
President Xi in 2015 announced the plans for ‘Made in China’, with the goal to make China the leading manufacturer in high technology products. This can be seen as a potential threat to the US, due to the threats in loss of privacy these technologies have on the American society. Mutual trust is required in alliances with regards to technology. This is seen as a major threat due to the implications of a communist society being able to dig into a democratic society. Around the time of the G-20 summit in 2019, POTUS quoted:
“China has inroads too on this continent that demand our attention…China wants to be the dominant economic and military power of the world, spreading its authoritarian vision for society and its corrupt practices worldwide”
(NY Times, 2019)
The quote above highlights the potential dangers China has on the US with regards to advances in technology. Additional to this, economists suggest that China will have the largest economy in the world in the next 15-20 years. This is alarming to the ‘greatest country in the world’ as classified by POTUS; as a dominant free world society such as the US, historically has opposed to threats from Communist countries rising in power, as seen with ongoing historical conflicts with Russia.
Additionally, the US demanded that china abandon its state-owned enterprises and state-conrrolled economy as a part of the trade agreement, but Cina signaled no intent to adhere to this (SCMP, 2019). POTUS is using nationalism as a tool to support his views on imposed tariffs in trade with China. Due to this dispute, many companies are shifting focus to other countries to outsource their manufacturing units.
Over 50 companies have shifted focus with regards to manufacturing from China to other countries (CNBC, 2019). One of the largest companies to make the shift is the Korean tech-giant, Samsung. Staff writers at the Nikkei Asian Review explored the counter-effects of the China-US trade war, where 50 companies have moved their manufacturing processes out of China (Nikkei Asian Review, 2019). One of these companies included one of the largest multinational technological conglomerates in the world: Samsung. According to Reuters, the two manufacturing plants in China: Tianjin and Huizhou, together made over 108 million smartphones, but the Korean tech-giant has decided to shift focus to India, where they initially planned to invest $750 million in 2017 (WSJ, 2017) and went onto increasing investments in 2019 by investing an additional $353 million with the aim to turn its India operations into a ‘hub for components business’ (ET, 2019). Samsung announced in 2018 that their largest mobile phone factory to date would be in Noida, India (FT, 2019). This highlights the increase of FDI’s in India being a counter-effect of the China-US Trade War.
Indian Prime Minister, Narendra Modi, and Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, are working together to introduce a simpler incentives and reducing corporate tax rates to 15% in order to make India a more attractive manufacturing hub than China to such giant conglomerates The Indian minister of electronics and IT stated “we are one of the big countries which can provide an alternative” when referring to the China-US trade war, whilst meeting the leaders of 50 different phone companies (WSJ, 2019).
The Indian government is providing such attractive numbers to make up for the reputation damage they faced when Nokia was forced to shutdown in 2014, due to the Finish tech-company being subjected over $500 million in taxes, when they had setup a large manufacturing plant in 2007 and employed over 30,000 employees by 2013 (WSJ, 2019). The company has ventured past manufacturing entities placed for the production of batteries and smartphone displays, by setting up venture capital arm where they facilitate the funding of start-ups revolving around electronics and software.
Prime Minister Modi, learnt from historical mistakes with Nokia, and implemented a new channel to make manufacturing in India attractive to companies around the world. He initiated the ‘Make in India’ movement facilitating innovation and investment with regards to manufacturing in India., with the creation of new sectors, a new mindset, new infrastructure and new processes. Obsolete frameworks have been replaced with transparent systems facilitating investment, innovation, and the protection of intellectual property with the intent to creating a dominant manufacturing infrastructure (PM India, 2019).
The star shining in this movement is the mobile phone industry, where Chairman Mahindroo of India’s Cellular and Electronics Association, explained that manufacturing units increased from 2 to 268 in 2019: a 95% increase (ET, 2019). With large investments and expansion of factories in India, Samsung India initiated the Make for the World’ movement aiming to export smartphones made in India overseas, classifying it as a brand factually made in India (Samsung, 2019). These numbers portray the increase of FDI to India as a counter-effect to the trade war between China-US.
As mentioned earlier, China was forecasted to be the largest economy in the next 15 years, but their growth may be stagnated due to these major corporations shifting basis to countries such as Vietnam and India.
In recent news, POTUS and Xi have signed a phase one trade deal, which entails China purchasing agricultural goods worth just under $50bn and POTUS approving the US to cut tariffs on Chinese goods, with claims to cancel next round tariffs as well. This lead to major jumps on US stock indexes, with record high major average, including increases in the DOW, Nasdaq Composite and S&P 500 (CNBC, 2019). These numbers add light to the effects the China US trade war has on international business, globalization and world trade. The implications and effects of the ongoing trade war between these two countries have been negative for the two, but positive for other countries such as India capitalizing on this.
If the next phases of the trade deal are positive, many of the forecasted effects will stagnate, but some consequences such as 50 countries shifting manufacturing focus out of China is a negative impact that will take years to make up for. Companies require stability instead of volatility, and with governments supporting manufactures such as the ‘Make in India’ movement with attractive benefits; companies will not easily shift back to China for their manufacturing needs.
Bibliography
- https://www.bbc.com/news/business-45899310
- https://www.cnbc.com/2019/08/05/us-china-trade-tensions-could-be-the-end-of-the-world-as-we-know-it.html
- https://www.bloomberg.com/graphics/2019-us-china-trade-war-economic-fallout/
- https://blogs.imf.org/2019/05/23/the-impact-of-us-china-trade-tensions/
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/268750/global-gross-domestic-product-gdp/
- https://www.nytimes.com/2019/06/26/world/asia/united-states-china-conflict.html
- https://www.cnbc.com/2019/12/12/stocks-are-set-to-add-to-thursdays-rally-as-us-and-china-near-signing-of-trade-deal.html
- https://www.cnbc.com/2019/12/13/china-says-it-has-agreed-to-us-trade-deal-text-indicates-next-step-is-signing.html
- https://news.samsung.com/in/make-for-india-to-make-for-the-world-a-timeline-of-samsungs-noida-factory
- https://www.pmindia.gov.in/en/major_initiatives/make-in-india/
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/tech/hardware/samsung-to-make-more-in-india-invest-rs-2500
- https://www.wsj.com/articles/india-sees-opportunity-in-trade-fight-luring-big-companies-from-china-11571572741
- https://www.scmp.com/economy/china-economy/article/3038993/china-wont-give-its-state-led-economic-model-top-trade
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/tech/hardware/how-mobile-manufacturing-made-the-most-of-make-in-india/articleshow/70628237.cms?from=mdrcr/articleshow/69151972.cms?from=mdr#:~:targetText=Kolkata%3A%20Electronics%20behemoth%20Samsung%20has,ramped%20up%20further%2C%20they%20added.
- https://www.reuters.com/article/us-samsung-elec-smartphones-china/samsung-to-shut-mobile-phone-plant-in-chinas-tianjin-idUSKBN1OB0YP
- https://m.economictimes.com/tech/hardware/samsung-to-make-more-in-india-invest-rs-2500-cr/articleshow/69151972.cms
- https://www.wsj.com/articles/samsung-plans-760-million-investment-in-india-1496831068?mod=article_inline
- https://asia.nikkei.com/Economy/Trade-war/China-scrambles-to-stem-manufacturing-exodus-as-50-companies-leave
- https://www.reuters.com/article/us-samsung-elec-smartphones-china/samsung-to-shut-mobile-phone-plant-in-chinas-tianjin-idUSKBN1OB0YP
- https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2019-08-28/u-s-china-trade-war-timeline-what-s-happened-since-may-2019
- https://www.china-briefing.com/news/the-us-china-trade-war-a-timeline/
- https://www.reuters.com/article/us-usa-trade-china-timeline/timeline-key-dates-in-the-us-china-trade-war-idUSKBN1WP23B
- https://www.scmp.com/comment/insight-opinion/united-states/article/2160342/why-donald-trumps-trade-war-aimed-foreign
- https://www.reuters.com/article/us-usa-trade-china-timeline/timeline-key-dates-in-the-us-china-trade-war-idUSKBN1WP23B
- https://www.bbc.com/news/business-49122849
- https://www.bbc.com/news/business-44529600
- https://www.bbc.com/news/business-45899310
- https://www.bbc.com/news/business-48196495
- https://www.wsj.com/articles/manufacturers-move-supply-chains-out-of-china-11563096601
- https://www.wsj.com/articles/samsung-plans-760-million-investment-in-india-1496831068?mod=article_inline
- https://www.wsj.com/articles/for-manufacturers-in-china-breaking-up-is-hard-to-do-11566397989?mod=article_inline
- https://www.wsj.com/articles/india-sees-opportunity-in-trade-fight-luring-big-companies-from-china-11571572741
- https://www.theguardian.com/business/2019/nov/07/china-hopes-end-us-trade-war-both-agree-ease-tariffs-imf
- https://www.wired.com/story/us-china-trade-war-spills-over/
- https://www.cnbc.com/2019/07/18/more-than-50-companies-reportedly-pull-production-out-of-china-due-to-trade-war.html
- https://www.scmp.com/economy/china-economy/article/3014564/samsungs-last-china-smartphone-factory-closing-raising
- https://www.ft.com/content/4d8285a2-eff0-11e9-ad1e-4367d8281195
- https://www.reuters.com/article/us-samsung-elec-china/samsung-ends-mobile-phone-production-in-china-idUSKBN1WH0LR
- https://www.cnbc.com/2019/07/18/more-than-50-companies-reportedly-pull-production-out-of-china-due-to-trade-war.html
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


