Global Logistics & Supply Chain Management of H&M
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: International Business |
| ✅ Wordcount: 1406 words | ✅ Published: 23 Sep 2019 |

1.0 Executive Summary
This report focuses on a multi – national retail company, Hennes and Mauritz AB (H&M), and their quest for high – quality production aimed at achieving sustainability and environmental objectives. A short background of the company, what they do and their market position, their products and services to give us a better understanding of the following analysis. This analysis will include the supply chain structure, key challenges and trends within the supply chain, competitive strategies used to differentiate the supply chain of H&M, value – added supply chain activities and analysis-based recommendations to maintain and strengthen their market position.
2.0 Introduction
Hennes and Mauritz AB (H&M) is a Swedish brand founded in 1947 by Erling Persson (Forbes, 2018) in Vasteras, Sweden, with the idea of offering affordable ‘ mode and quality at the best price’ (Slack, Chambers and Johnston, 2010). Its product portfolio includes accessories, footwear and cosmetics for women, men, teenagers and children. Germany is its largest market, followed by Sweden, the USA and the United Kingdom. In 1964, H&M opened its first international store in Norway outside Sweden and has since expanded to over 4,739 stores in 69 different countries on five continents with more than 171,000 employees (H&M Group, 2017). The H&M group also owns COS (style collection), ARKEI, Fabric Scandinavian, which includes the Weekdays chain, and Monki as well as Cheap Monday (About.hm.com, 2018). This ensures that the stores have a wide range of styles for all ages.

Fig.1 H&M Global Location. Source: (About.hm.com, 2018)
H&M has no factories, but its products are outsourced to around 800 independent suppliers, mainly in Asia and Europe, with 16 manufacturing offices. Suppliers have their own subcontractors and a total of 2700 manufacturers (H&M, 2018). Today, H&M ranks as the world’s second largest clothing retailer based on annual sales, with a turnover of SEK (232 billion) including VAT, it has a significant online presence with online shopping in 33 counties (H&M.com.2017). H&M’s top competitors are Zara, the US GAP, Japanese Uniqlo, Benetton and UK Topshop (H&M, 2018).

Fig .2. Source: (www.slideshare.net, 2018)
OTHER BRANDS

Fig.3 Source: (H&M Brands) https://about.hm.com/en/about-us.htm
3.0 H&M SWOT ANALYSIS
In this research, a SWOT analysis is used to identify the strengths, weaknesses and opportunities open to the business and the threats to H&M business competition, planning and forecasting.
|
STRENGTHS
|
WEAKNESSES
|
|
OPPORTUNITIES
|
THREATS
|
Fig 4. SWOT Analysis Source: Loretta Ofoma.
3.1 H&M Business Methodology and Analysis using Porter’s five forces
It is a tool for identifying and analysing the five competitive forces that shape each industry and help to determine the weakness and strength of the industry. (Porter, 1989)
- Competition in the industry
- Potential of new entrant
- Power of suppliers
- Power of customers
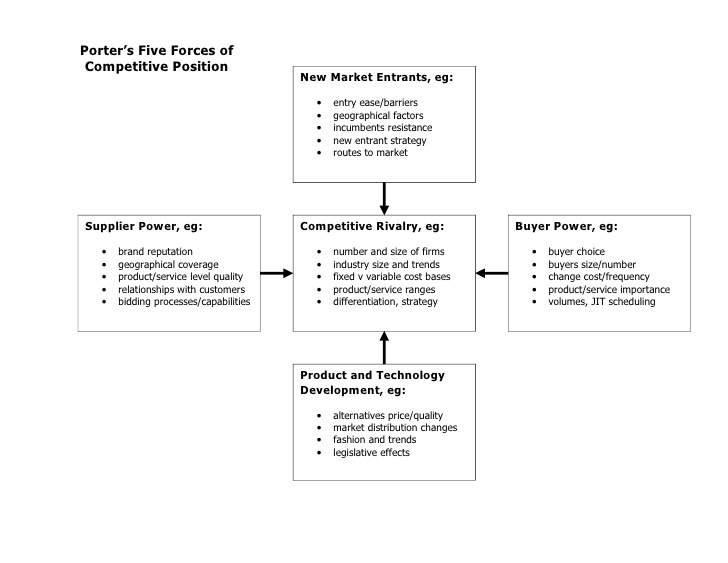
Fig.5 Source: https://www.slideshare.net/bearing21/porters-five-forces-template
The five forces of the Porter can be applied to H&M, giving a clear view of how they offer quality at the best price by analysing their competitors, buyers, suppliers and how they can operate economically, environmentally and sustainably.
4.0 H&M SUPPLY CHAIN STRUCTURE
The supply chain is the management of all activities, data, knowledge and financial resources associated with the flow and transformation of goods and services provided by raw material suppliers, component suppliers and other suppliers, in order to meet the expectations of end users of products. (Lysons and Farrington, 2006). (Mangan et al., 2014) defines the supply chain as ‘the network of organizations involved in the various processes and activities producing value in the form of products and services in the hands of a definitive purchaser through upstream and downstream linkages’.
According to Martin Christopher (1998), logistics and supply chain management are the two segments that “the two goals of cost reduction and service improvement can be achieved.” Logistics is not a component of the supply chain but a resource that enables a supply chain to be implemented.
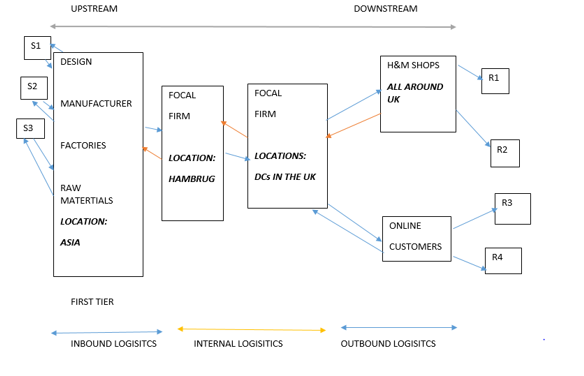
Fig.6. H&M Supply Chain Structure. Source: Loretta Ofoma
H&M controls each stage of its supply chain as an importer, wholesaler and retailer. The continuous development of IT offers excellent support for the logistics of H&M. Transportation is under contract with third parties while H&M handles stock management manually. The bulk of the flow of goods is routed and transmitted through its terminal in Hamburg, Germany and then distributed to various distribution centres in various countries. When goods arrive at these locations, they are inspected and then allocated either in the store or in a centralized storage room called a ‘ call off warehouse. ‘(About.hm.com, 2018).
4.1CHALLENGES AND ISSUES FACING H&M
Major shift in the industry:
Increasing digitisation has influenced this. H&M sees many opportunities arising from this shift, as the group has the capacity and resources to seize them, but there are also risks for those who during this transitional period are not fast and agile enough. As more and more shopping take place online, mainly via mobile phones, the shift poses challenges to physical retail stores across the industry.
Fashion:
In the fashion industry operation is a risk in itself. Mode has a limited shelf life and there is always a risk that some of the collections are not commercial enough, i.e. Customers will not be well received. Purchases of fashion are often emotional and can be adversely affected by unforeseen geopolitical and macroeconomic events.
Weather:
Products of the H&M Group are sold based on normal weather patterns. Divergences from normal weather affect sales. This is especially true in the transition from two seasons, such as from summer to autumn or from autumn to winter. If autumn is warmer than usual, it can have a negative impact on the sales of weather – related clothes, such as outerwear and chunky knitwear sales, which already account for a significant proportion of total sales in several markets.
5.0 RECOMMENDATION:
It can be prescribed that H&M ought to redistribute a portion of its supply chain functions to independent agencies, by re- appropriating procurements would not imply that they had lost its control of sourcing and purchasing process, rather it will enable them to give careful consideration on its core competencies which will make it a market leader by making change in its quality and standards.
- H&M needs to strategies how they outsource all production activities, which makes it hard for them to control products quality and dependability of supply.
- They need extra inspection time on final goods, to help increased lead times
- They should invest in multiple suppliers as they only upstream in their designs.
- They should pursue downstream vertical integration
6.0 CONCLUSION:
H&M is an apparel company, against all odds and challenges faced in the clothing industry, they still emerged as one of the top clothing industries. This was achieved through the adaptation of trends and challenges faced through competitive rivals, they were able to go with the trend of been sustainable especially in the way they outsource their materials from start to finish, engaging in been environmentally friendly and the fist company to list their suppliers on their websites.
References
- About.hm.com. (2018). H&M group | Markets. [online] Available at: https://about.hm.com/en/about-us/markets-and-expansion.html [Accessed 19 Nov. 2018].
- Christopher, M. (1998). Logistics and supply chain management. 4th ed. prentice hall.
- Forbes. (2018). Stefan Persson. [online] Available at: https://www.forbes.com/profile/stefan-persson/ [Accessed 18 Nov. 2018].
- Lysons, K. and Farrington, B. (2006). Purchasing and supply chain management (6a. ed.). Harlow: Pearson Education.
- Mangan, J., Lalwani, C., Butcher, T. and Javadpour, R. (2014). Global logistics and supply chain management. 2nd ed. Chichester: Wiley, p.10.
- Porter, M. (1989). How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy. Readings in Strategic Management, pp.133-143.
- Slack, N., Chambers, S. and Johnston, R. (2010). Operations management. Harlow: Pearson Education.
- www.slideshare.net. (2018). SlideShare.net. [online] Available at: http://www.slideshare.net [Accessed 18 Nov. 2018].
- YouTube. (2018). H&M. [online] Available at: https://www.youtube.com/user/hennesandmauritz [Accessed 14 Nov. 2018].
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


