Economic Impact of the Indonesian Mineral Law
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Economics |
| ✅ Wordcount: 1880 words | ✅ Published: 16 Mar 2018 |
Abstract
Raw mineral ores is one of excellence natural product in Indonesia. For many years, the mineral mining company in Indonesia can export raw mineral ores directly over the world. A new mining law mandates the mining company to process the ores domestically then export its product. The government purpose is to increase value added of the mineral ores and creates domestic industry activity. The problem arises since there are only few smelters which ready to process the mineral ores. In short run, this new law has a negative impact to mineral export activity and GDP growth become slower.
1 Introduction
Indonesia is one of rich countries with abundant mineral resource. Bauxite, copper, gold, nickel and tin are Indonesia’s excellence mineral resource export product. This mineral ores are spread over in Indonesia region, mostly in Kalimantan Island, Papua Island, Sumatra Island and Sulawesi Island.
The latest report of U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) mentions the estimation of bauxite reserves in Indonesia is 1,000,000 metric ton, ranked Indonesia in 6th of biggest bauxite reserves in the world. Meanwhile the reserve of Indonesia’s copper is 28,000 metric ton, the 8th largest in the world. Gold reserve is 3,000 metric ton, placed in 5th largest reserves in the world. Other Indonesia resources, nickel and tin are estimated 3,900,000 and 800,000 metric ton reserved beneath the earth. Indonesia’s nickel is 6th largest deposit and tin reserve ranked this country at 2nd position in the world (USGS, 2014).
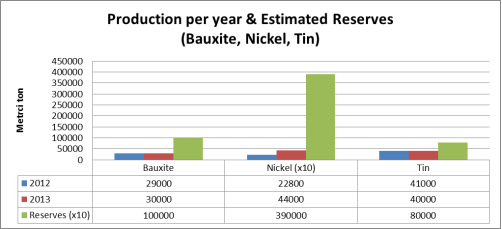
Figure 1.Production per year & its reserves (bauxite, nickel, tin) (source: USGS, 2014)

Figure 2.Production per year & its reserves (copper, gold) (source: USGS, 2014)
These generous resources are being used by Indonesian government to add national income by export the mineral ores to foreign country. Since 1967, Indonesian government attracts foreign company to invest in mining sector. To regulate the Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in mining sector, the government had been issued several mining law which has revised over the time. Since then, the mining sector is become favorite among foreign investor (Bhasin & Venkataramany, 2007).
These mining activities contribute to Indonesia’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Together with oil & gas and quarrying, mining sector accounted with 7% in real GDP at 2012 (at constant prices). Even though this sector does not contribute more in contrary with another natural resource e.g.: agriculture, livestock, forestry and fishery with 12% contribution in GDP, mineral sector still contribute USD 61.3 billion in Indonesia’s total GDP of USD 875.72 billion

Figure 3. Indonesia GDP 2012 at constant prices (source: Central Bureau of Statistics)
2 Indonesia New Mining Law
After spending almost four years discussion in the House of Representatives, on 16th December of 2008 the parliament members agreed a new mining law, replacing old mining law which had been applied almost 40 years. This new mining law officially signed by the president on January 2009 and the law is known as Law No.4/2009 Concerning Mineral and Coal Mining (Syahrir, Bongaerts, & Drebenstedt, 2013).
The government’s purpose to implement this new mining law is not only regulates the contract term for foreign investor company and obligate them to have a mining license, but also better environment and increasing added value of mineral resources (Syahrir et al., 2013).
In order to protect the environment area which affected by mining operation, the new mining law also regulate the mining company to keep the environment and ensure them to fulfill the minimum requirement of environmental standard operational based on their level of license. Beside the environment purpose, the new law also regulates the company to undertake domestic processing. The Law no.4/ 2009, Chapter XIII, article 102 and 103 stated:
Article 102
The holders of Mining Business License (IUP) and Special Mining Business License (IUPK) shall increase the added value of mineral and/or coal resources in carrying out mining, processing and purification activities as well as in making use mineral and coal.
Article 103
- The holders of Mining Business License (IUP) and Special Mining Business License (IUPK) for operational production shall process and purify output of the domestic mining.
- The holders of IUP and IUPK as referred to in paragraph (1) can process and purify the mining output from others holders of IUP and IUPK.
- Further provisions on the need to increase the added value as referred to in Article 102 as well as on the processing and purification as referred to in paragraph (2) are to be provided for in government regulation.
Furthermore, the Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resource (MoEMR) also issued a regulation no.34/2009 in order to control production and export of mining product. This is reflected from article 5 MoEMR no.34/2009 which stated:
The Mining Company as cited in Article 3 paragraph (1) shall be allowed to export the mineral or coal as long as it is capable of fulfilling a Minimal Percentage of Mineral Sale or Minimal Percentage of Coal Sale.
This policy issued as government want to ensure the supply for increasing domestic demand. With this Ministry Regulation, the company may export their production, but is encouraged to fulfill domestic demand which calculated by Domestic Market Obligation (DMO) (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2012).
Despite this new mining law was signed on five years ago in 2009; the effect will be enforced on 12 January 2014. Therefore, after 12 January 2014 the mining company cannot export mineral unprocessed. This situation is totally different when in the old mining rules regime[1], the mining company still allowed to shipping the mineral ores directly to their buyer; industrial countries, such as: China, Japan, EU countries and United States.
At that time the mineral ores are exported and then processed by the buyer in order to add the value of ores product. Later, Indonesia’s industry sector will import the metal product to supply their production (Syahrir et al., 2013). For example: Indonesia shipyard industries have to import steel from China where the China’s steel plant produced steel from Indonesia’s iron ores.
Based on this situation, the idea of adding value to mineral resource in Indonesia came to surface. And later the President of Indonesia Republic signed it as the new mining law. This law and regulation will close the mining company’s curtain to export the mineral resources directly to the buyer unless the mineral is processed domestically.
3 The Lack Preparation of Mineral Refinery Sector
After the new law has been signed on December 2009, the mineral resources have to be processed or extracted in domestic smelter or extractor. In the other hand there are only three available mining refinery in Indonesia by 2012: PT Aneka Tambang, PT Indonesia Asahan Aluminium and PT Smelting (Hogan Lovells, 2012). After another regulation MoEMR reg. no.7/2012 come into force to mandate the mining companies to increasing the value through mineral processing, some mining company are intended to invest smelter in Indonesia which are: PT Vale Indonesia, PT Freeport Indonesia, PT Newmont Nusa Tenggara, PT Weda Bay Nickel, PT Jogja Magasa Iron and PT Agincourt Resources.
Those mining companies should build mining refinery in order to comply the law even though they are facing uncertainty condition to build a smelter caused by unrealistic deadlines and unclear concept of Contract of Work (CoW) (McBeth, 2014).
Indonesia’s inconsistence policy and high risk investment made the companies considering build a smelter are decreasing (Jensen & Burton, 2014). This unprepared mineral refinery industry to anticipate the new mining law is being unhealthy to Indonesian mining sector as their ore cannot be shipped.
Fortunately, the government already received several refinery plant proposals coming from domestic investor and foreign investor. However only three are expected to start the project this year with takes at least 5 years to complete (Jensen & Burton, 2014).
4 The Effect of Mineral Law
As mentioned above, there is some increasing amount of mineral ores in mining companies’ stock pile as it cannot be shipped over the world. After the new mining law has been applied, the export activity especially in mining sector is decrease which can be shown by following figure:

Figure 4.Export of Mineral Ores (source: Ministry of Trade)
The figures describing the export of mineral ores; especially: tin, copper, nickel and aluminum. After the new law has been signed, the mining companies start to boost the production in order to add extra revenue before they could not export the ores unprocessed.
When the MoEMR no.7/2012 released to mandate them to increasing mineral value added, they start to slow down the production as they cannot export directly to their buyer.
|
SECTOR |
2013 |
2014 |
||||
|
Qtr I |
Qtr II |
Qtr III |
Qtr IV |
Qtr I |
Qtr II |
|
|
Agriculture, Livestock,Forestry And Fishery |
23.33 |
2.53 |
6.42 |
-22.84 |
22.54 |
2.79 |
|
Mining And Quarrying |
0.58 |
-0.62 |
2.19 |
1.72 |
-3.56 |
-0.57 |
|
Manufacturing Industry |
-2.16 |
2.78 |
2.92 |
1.72 |
-2.31 |
2.63 |
|
Electricity, Gas And Water Supply |
-1.24 |
1.04 |
0.7 |
6.1 |
-2.89 |
4.24 |
|
Construction |
-5.08 |
4.11 |
3.35 |
4.45 |
-5.04 |
3.76 |
|
Trade, Hotel And Restaurant |
-2.81 |
4.44 |
1.76 |
1.44 |
-2.81 |
4.15 |
|
Transport And Communication |
1.2 |
3.12 |
3.27 |
2.36 |
1.1 |
2.72 |
|
Finance, Real Estate And Business Service |
2.79 |
1.3 |
2.04 |
0.5 |
2.18 |
1.36 |
|
Services |
-0.09 |
0.76 |
2.9 |
1.62 |
0.33 |
0.73 |
|
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) |
1.44 |
2.57 |
3.07 |
-1.42 |
0.95 |
2.49 |
|
Non-Oil & Gas GDP |
1.51 |
2.72 |
3.2 |
-1.51 |
1.11 |
2.64 |
Table 1.GDP growth quarterly at constant price (source: Central Bureau of Statistics)
This condition also affecting Indonesia’s GDP growth as the mineral trade also contribute to Indonesia GDP as shown in previous table. From nine sectors of GDP contributor, only mining and quarry sector which decrease consecutively in 1st quarter and 2nd quarter of 2014. Throughout the first quarter of this year, the value-added mining and quarrying decreased about 0.38% when compared with last year in the same quarter. If calculated based on constant 2000 prices, the value added produced by the sector in the first quarter of 2014 was only Rp 48.2 trillion. The figure is lower than the first quarter of 2013 amounted to Rp 48.4 trillion and fourth quarter 2013 amounted to Rp 50 trillion (Central Bureau of Statistics, 2014).
However, in the trade, export of coal only US $ 5.63 billion, down 13.29% compared to the first quarter of 2013 amounted to US $ 6.49 billion. In fact, coal became the biggest contributor to non-oil exports. So that the growth of exports to the first quarter of 2014 GDP is minus 0.78% (Central Bureau of Statistics, 2014)
5 Conclusion
In the short run, the result of new mining law is negative to mining trade activity and to national income growth. In the long run after the smelter built, the mining sector will increase again and the domestic industry also growth since the mineral ores should be processed domestically. As the result, in the long term this law will lead greater national income growth.
Literature References:
Bhasin, B., & Venkataramany, S. (2007). Mining Law and Policy: Replacing the “ Contract of Work ” System in Indonesia Mining Law and Policy: Replacing the “ Contract of Work ” System in Indonesia, 1–16.
Central Bureau of Statistics. (2014). Pertumbuhan Ekonomi Indonesia Triwulan II-2014, (63).
Gandataruna, K., & Haymon, K. (2011). A Dream Denied? Mining Legislation and The Constitution in Indonesia. Bulletin of Indonesian Economic Studies, 47(2), 221–231. doi:10.1080/00074918.2011.585951
Hogan Lovells. (2012). Investment in Indonesia ’ s Mineral Refining and Processing Sector: Value-added Regulations and Industrial Policy, (July).
Jensen, F., & Burton, M. (2014). As smelters weigh cost, Indonesia’s ore export ban may backfire. Retrieved December 11, 2014, from http://www.reuters.com/article/2014/01/27/indonesia-minerals-smelters-idUSL3N0KY20P20140127
McBeth, J. (2014). How to kill an industry in Indonesia. Retrieved December 11, 2014, from http://www.atimes.com/atimes/Southeast_Asia/SEA-01-100214.html
PricewaterhouseCoopers. (2012). Mining in Indonesia Investment and Taxation Guide, 4th Editio(April).
Syahrir, R., Bongaerts, J. C., & Drebenstedt, C. (2013). The Future of Indonesian Mining Activities after the Implementation of Law Number 4 of 2009 Concerning Mineral and Coal Mining ( The New Mining Law ). IMRE Journal, 7(4).
USGS. (2014). Mineral Commodity Summaries 2014.
[1] The mining predecessor law no.11/1967 used over than 40 years in Indonesia mining industry. At that time, the mining company which most of them is foreign investor act as contractor under government and tied with Contract of Work (CoW) agreement (Gandataruna & Haymon, 2011)
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


