Microeconomic Analysis of Coca-Cola
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Business |
| ✅ Wordcount: 1889 words | ✅ Published: 23 Sep 2019 |
Microeconomics 201 Coca-Cola Analysis Milestone 3
Costs of Production
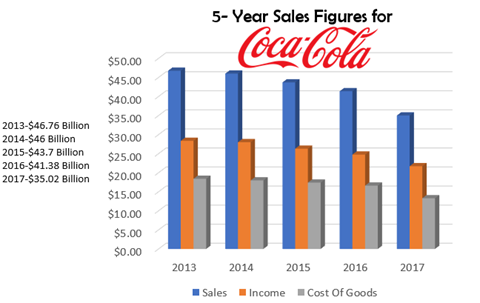
(“Coca-Cola 10K Report,” n.d.)
In analyzing the cost of production for Coca-Cola there is a noticeable decrease from the year of 2013-2017. The chart above along with the table included below provides a more discrete breakdown of the noticeable decreases.
|
Coca-Cola Annual Revenue As reported by Market Watch |
|
|
2017 |
$13.3 billion |
|
2016 |
$16.62 billion |
|
2015 |
$17 billion |
|
2014 |
$17.99 billion |
|
2013 |
$18.4 billion |
|
(“Coca-Cola 10K Report,” n.d.) |
|
With the information provided it is determined that Coca-Cola suffered a 19.97% loss in their cost of goods production. Furthermore, a decline was evident in their gross sales in this timeframe, however, sales only plummeted 15.38% that’s a 4.59% difference in the sales and COG combined. Considering the difference from COGS along with Coca-Cola sales it’s would seem likely to conclude that Coca-Cola sales wasn’t affected much by the decline. One reason Coca-Cola noticed a decrease in their figures from 2013-2017 is because consumers are shifting to more healthier brands i.e., they were beginning to choose less of the surgery and carbonated beverage all together. Although, there hadn’t been much growth for the company the losses Coca-Cola encountered could have been more astronomical if the business was not able to meet consumer’s needs. As mentioned earlier alongside the long-standing revered Coca-Cola classic Coke has released Powerade, Hi-C, Sparkling water, Dasani water as well as many other products under its umbrella to accommodate consumers who are moving away from Coca-Cola classic for more healthier choices as well as alternates (“Coca-Cola Brands,” n.d.). In addition, along with meeting a need of its consumers it seems Coke strived to reduce the amount of its losses from 2013 up to this present point. It is reported from Coca-Cola’s 4th quarter financial statement from 2017 that the business received a 6% organic revenue growth through the sales of its Water (Dasani) and sports drinks. Additionally, its tea and coffee sales were reportedly up a 2% from its previous quarters (“Coca-Cola Analysis,” n.d.). This data indicates Coca-Cola consumers are indeed looking for healthier alternatives from the soda products and that Coca-Cola is on the right track by offering these products to bounce back from its 5-year losses.
A firm can face a multiplicity of expenses in producing a good or providing a service. These costs can range from (but not limited to) a fixed cost, operating costs, sunk costs, variable costs, marginal costs, short run costs and long run costs (“Economic Cost,” n.d.). Operating cost is affected through time rather it be positively or negatively. For example, since The Coca-Cola company and its bottling plants operates large fleet of trucks along with other motor vehicles to distribute and deliver its product to the consume an increase in the cost of fuel, disruption of its supply or shortage of the resource would increase Coca-Cola’s operating cost while adversely impacting the firm’s profitability. As time continues to progress and a firm’s operation increase so will the operational cost.
Furthermore, water is a main ingredient in the creation of Coca-Cola’s products; this is because water is one of the raw materials used in the production of Coca-Cola (“Coca-Cola 10k Report,” n.d., p. 8). Although Coca-Cola has never experienced any water deficiencies if we created a scenario to where Coca-Cola begin operating in Mexico, Pakistan and certain parts of Africa where clean water isn’t located the variable cost over time would become negatively affected because of the limited amount of clean water. Additionally, there would continue to be a decrease in the variable cost if there was a shortage in the raw material that created aluminum, glass and plastic as this is Coca-Cola main bottling preference (“Coca-Cola 10k Report,” n.d., p. 8). However, considering Coca-Cola hasn’t experienced any notable difficulties in receiving this material from the multiple suppliers they use to buy their raw material the variable cost would continue to positively affect the firm and its profitability.
Coca-Cola revenue is recognized when a persuasive evidence of arrangement exists (“Coca-Cola 10k Report,” n.d., p. 79). This means that the delivery of the Coke products must have occurred for revenue to be recognized. This occurs once the title of their product is transferred to the bottling partners, other customers (such as restaurants, diners, hotel breakfast bars, etc.) or resellers. However, if the price of which the product can be sold can’t be determined for whatever reason the seller the seller can’t conclude what to record as the revenue. In this case the vendor’s fees are fixed or determinable and collectability is probable.
Overall Market
In conjunction with Coca-Cola Pepsi Co along with other brands are top competitors of The Coca-Cola company. Despite the numerous competitors in the market with Coca-Cola through brand loyalty, crafty marketing strategies and innovation Coca Cola is a soft drink industry that has earned its dominance in the soft drink market.
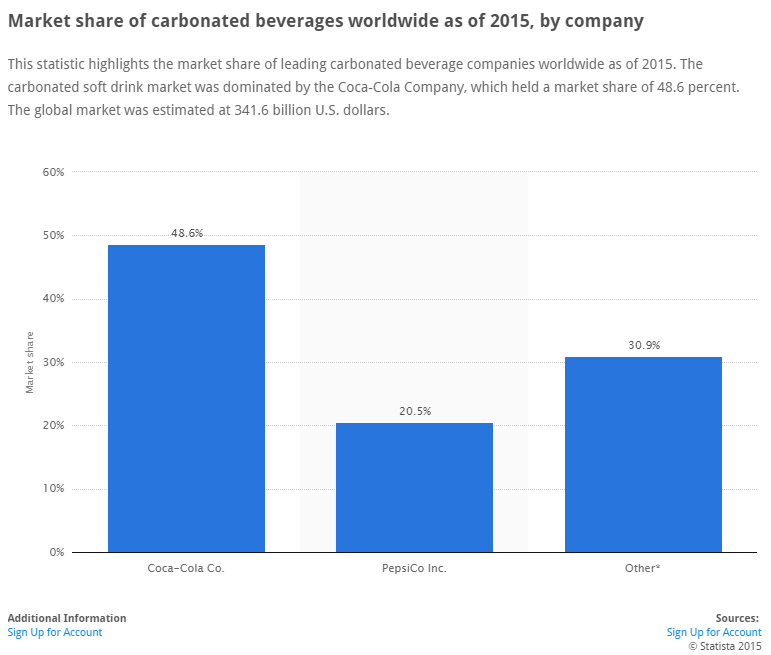
(“Coca Cola Market Share Data,” n.d.)
With the statistical data provided in the chart for Coca-Cola, Pepsi and other brand figures from 2015 it is noticeable that Coca-Cola has a strong impact in the soft drink industry and has proven that through its sustained competitive advantage by brand recognition and its global distribution network. Additionally, further analysis proves that the soft drink industry can expect to see a 1.9% growth annually in their soft drink sales (“Soft Drinks Statistical Data,” n.d.). This data would extend to PepsiCo. along with other top contenders as well causing analysis to believe that there would be limited room for growth in their market share as the years progress.
The structure of market uses many competitive strategies to maintain its dominant place in an industry or in Coca-Cola’s case in the soft-drink industry. Coca-Cola is a limited competition being shared by a small number of producers or sellers making the market structure for Coke oligopoly. Considering Coca-Cola and Pepsi are the two leading brands in the soft drink industry this positions them to have more autonomy then other brands themselves giving them more control over the market they share. Furthermore, new competition would not likely have much of a negative effect on Coca-Cola considering Coke along with Pepsi is a leading competitor in the market. This would cause the barriers of entry for new competitors to be significantly high. A low threat of new entrants causes an industry to be more attractive-causing a high barrier to entry (“Threats & Barriers to Entry,” n.d.). In this case Coca-Cola and Pepsi would be able to enjoy the increased profit potentials if a new competitor were to enter the soft drink market because the technology, building lease, fleet of trucks, production of product, raw materials, advertisements and other costs require high investments.
Recommendation
Coca-Cola can see an increase through innovation, strengthening its relationship with their consumers, smart optimization through low demand periods and acquiring its competitors. Innovation is widely recognized for how it introduces new ideas, creative thoughts and new imaginations in form of device or method (“Innovation,” n.d.). Innovation is also viewed as the application of better solutions that meet new requirements, unarticulated, or current market needs (“Innovation,” n.d.). To help manage its future production Coca-Cola could use an innovative strategy to help improve sales and customer relations; this could be proven true by improving or replacing the business processes to increase organizational efficiency and productivity. Additionally, this can help the organization extend its existing line of product quality. After implementing an innovative solution for sales and customer rapport the consumers will eventually notice the value Coke is adding and the value will extend to the customers and their gratitude will transcend into the sales. Innovation can also lead Coca-Cola to remain one of the top contenders in the market place; this is because it will allow Coca-Cola to have an upper hand by being able to anticipate the move of its market before the takes place. Through this Coca-Cola would be able to swiftly adapt to market shifts and remain ahead of opportunities so they aren’t forced to react to unforeseen shifts.
Given its strong dominance in the oligopoly market Coca-Cola can increase its performance by back-to-the basics marketing strategy, consumers loyalty programs and increasing its brand to an unsegmented group of consumers. Going back to the basics sometimes allows individuals to take a second look to receive a clearer understanding of information that was overlooked or not recognized originally. When saying going back-to-the basics it is implied that Coca-Cola should consider utilizing some of the tactics that Asa Candler used when he initially purchased Coke. Originally when Asa Candler purchased Coca-Cola, he used a variety of marketing strategies to build consumers awareness of the brand by giving free Coke coupons, Coke glasses, Coke T-shirts and more. Over time his effortless marketing strategy led Coke to become dominant in the soft drink market; considering the world is shifting to more healthier choices Coke should try to use some of these original tactics to meet the need of consumers who have become health concise. Additionally, as the economy continues to grow Coca-Cola will need to strongly penetrate the market to appeal to consumers tastes preferences; this can be done by offering more products that is unsegmented to reach a more diverse consumer demographic this would likely help increase Coca-Cola’s profit margin.
For Coca-Cola to sustain its success and its dominance in the oligopoly structure the organization needs to optimize when needed and acquire its competitors. Optimization is simply making the best or most effective use of a situation or a resource. Considering Coca-Cola utilizes a multiplicity of resources to produce, manufacture and distribute its product when there is a noticeable shift left of the demand curve the business through optimization should force the supply curve left. This help would seem effective for Coca-Cola given the income data provided on the 10k annual report. Optimizing resources when demand lowers will help cut cost when business is down and prevent a surplus in the supply curve; this could also be done through the help of innovation. Additionally, Coca-Cola needs to acquire its competitors this act has been used by businesses worldwide to help increase its profit margins. An acquisition is when one company obtains a majority stake in a firm without changing the name or legal structure (Renaud, “Merging Companies & Why?” n.d.). This could be a good way for Coca-Cola to promote its new acquisition while receiving an ROI in return.
References
- Coca Cola Market Share Data. (n.d.). Retrieved February 09, 2019, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/387318/market-share-of-leading-carbonated-beverage-companies-worldwide/
- Economic Cost. (n.d.). Retrieved February 09, 2019, from https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/glossary/
- Innovation. (n.d.). Retrieved February 09, 2019, from http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/innovation.html
- Renaud, R. (2019, January 24). Merging Companies & Why? Retrieved February 09, 2019, from https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/why-do-companies-merge-or-acquire-other-companies/
- Soft Drinks Statistical Data. (n.d.). Retrieved February 09, 2019, from https://www.statista.com/outlook/20020000/104/soft-drinks/north-america
- Threats & Barriers to Entry. (2018, December 04). Retrieved February 09, 2019, from https://strategiccfo.com/threat-of-new-entrants-one-of-porters-five-forces/
- Coca-Cola Analysis. (2018, February 16). Retrieved February 10, 2019, from https://www.coca-colacompany.com/press-center/press-releases/the-coca-cola-company-reports-strong-operating-results-for-fourth-quarter-2017
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


