Kenneth Lay Case Study of Leadership and Management
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Business |
| ✅ Wordcount: 2997 words | ✅ Published: 13 Sep 2017 |
CASE STUDY – KENNETH LAY, ENRON
1. Personal ethical perspectives
- Character is a very essential part in any decision-making process. (Johnson, 2012) Looking at Ken’s background he started from a scratch as he grew up as a poor preacher’s son and went on to create Enron. This very well shows his positive attitude and positive psychology. He discovered his vocation and went on to follow his ambitions taking him from the bottom to the top of the world with his clear directions & interests towards his goal. But again, in Ken’s case its quite evitable that he was not able to confront the shadow side of his personality as he was continuously projecting his shadow side on the other employees during the crises and whenever there was any pressure situation. He forced the employees to rig the accounting records and those not following his orders were fired as an excuse of not being creative. So, this led to destructive behaviours of the employees. Ken’s virtues weren’t defined as he always turned to lying about Enron’s financial forecast in under pressure situations. He identified his personal values but took an unethical path to achieve it as he was a big-time gambler who took high risks just to raise Enron’s stock price which portrays his bad habits thus justifying for the actions done for his personal benefit especially lying about buying stock himself to his own company’s employees. (Li, 2010)
- Spirituality assumes a critical part in basic leadership handling as it demonstrates the individual moral development and ethical improvements of our companies or associations. (Johnson, 2012) In Ken’s case, the three aspects of his spirituality that affected his decision-making were:
- Desire – He was not ready to accept that his company is going down. He wanted to be the most successful executive in the US as this was his main desire. He expanded the company operations all over the world overlooking the company’s abilities to manage it. His limitless desire turned him to unethical and immoral ways of laundering money. Internally, he created the chief finance officer scheme to make himself rich at the expense of the employees. He created an off-web balance sheet with the help of Skillings so that they both can make money secretly and illegally. (Enron Case study, 2015)
- Honesty – He was not at all honest during his run as one of the most successful executives in the US. He continued lying to the public as well his own employees that Enron’s future looks perfectly bright and financial forecast is profitable for the investors. Ken with Skillings and Fastow secretly transferred property in their names which was illegal. He fired the employees that were honest and questioned him about rigging the financial and accounting figures of the company and gave a false explanation that they were not creative and imaginative as he would like them to be. His dishonesty led to a corporate culture that was showing false financial statements to the investors and Enron’s ability to meet its borrowing capacity. (Li, 2010)
- Fear – He loved his company a lot as he started from the scratch and made Enron such a successful company in the US. So, his fear of losing all the reputation and hard earned profits led him to take the position of company’s CEO. He feared that if Enron’s actual financial statements come out in public and its inability to meet its borrowings then its share price would go down pretty quickly leading to huge loss to the company which was already suffering a massive loss plus his own illegal secret money laundering would be affected as well. He thought that stepping in the shoes of CEO of the company, he might be able to steer up the profits for the company and save it from being bankrupt and that was the reason behind his false claims of Enron’s healthy financial forecasts as well as current financial statements to the public after Skillings resigned and he took hold of the position. His fear of loss of his self-built company led him to even disclose half information which he did about buying back Enron’s share himself worth $4 million and not throwing light on the selling of his shares of $24 million in the past months. Fear costed Ken his entire company going bankrupt and so many law suits against him and his fellow partners who were illegally laundering money with him through off web balance sheets and transfer of properties. (O. C. Ferrell, 2010)
- The three aspects of transformation in action that were evident in Ken’s case are
- Embracing the hypocritical self – Kenneth Lay was continuously embracing his hypocritical self and its pretty evident from the instance when he fired the employees saying that they were not as creative and imaginative as his organisation wants them to be but the story was something else. Ken wanted the employees who would agree to manipulate the accounting figures in return for monetary awards. But those employees tried to be ethically and morally right which did not work out well for them. Ken said that his duty is owned of good faith and full disclosures which in itself shows his highly hypocritical behaviour as they were running a secret transfer of properties within the organization without any knowledge about it to its employees or the public. Ken even laid in Enron’s code of conduct that they deal with the customers with all the integrity and honesty. Ken never left a chance to embrace his hypocritical self. He was committing fraud the entire time and in public he always showed a sense of truthfulness and integrity towards his investors.
(Li, 2010)
- Disturbing the system – Kenneth Lay’s greed led to the disturbance of the entire system. No matter it was the entire stock market i.e. Wall Street or his organizations working, nothing stopped Ken and his partners in crime to commit to the illegal means of money laundering. The entire stock market was shook after Ken declared Enron bankrupt worth $586 billion. It even took down world’s largest accounting firms Arthur Anderson. All this led to a total disturbance to the financial system not only Enron but also the entire stock market resulting in an immense loss to the investors. (Li, 2010)
- Surrendering to the emergent process – After all the havoc caused by Ken’s illegal activities within Enron to make wealth for his personal purposes he decided to surrender and declare Enron bankrupt after it all went out of hand. He disclosed all the information to the public as he could not make it any further with his lies and illegal activities. He even said in the interview that he did not want Enron to end this way and neither did he want Enron to go down that’s why he stepped up as CEO after Skillings resignation in an attempt to steer up the firm from the losses. (O. C. Ferrell, 2010)
2. Ethical decision making and action
Step 1 – Gather the facts: Ken never gathered the facts or even tried to see how his actions for personal benefit will affect the company and others. He kept on expanding his operations without even calculating Enron’s ability to manage those operations without the sufficient resources. (Li, 2010)
Step 2 – Define the ethical issues: Ken did not define any ethical issues or ethical values for Enron. He just defined the general ethical code of conduct regarding respect, integrity, communication, and excellence. Unfortunately, Enron did not even comply with these basic codes of conducts and those who tried to, were fired by Ken Lay. (Enron Case study, 2015)
Step 3 – Identify the affected parties – In the Enron’s case, Ken and his partners in crime Skillings & Fastow did not bother to identify the affected parties and kept on doing their illegal activities. They did not check whether the shareholders are at a loss or what is the percentage of the loss that’s being incurred in order to steer the firm to a stability. And in his last interview he even said that he did not have any idea about Enron’s inability to meet its expansion plans. (Li, 2010)
Step 4 – Identify the consequences – The entire case study is an example that no one in the company who was laundering money tried to identify the consequences of their actions which resulted in Enron’s bankruptcy. (Enron Case study, 2015)
Step 5 – Identifying the obligations – In this case study, Ken was very well aware of his obligations and he moulded them to his own advantage. He exploited the loop holes in them and used them for his own benefit. (O. C. Ferrell, 2010)
Step 6 – Consider your character and dilemma – Ken had a pretty strong character that was one of the reason he was running such a big company. His character was put into test when Skillings resigned but Ken was very confident and stepped up as the CEO for the company knowing about its massive losses. (O. C. Ferrell, 2010)
Step 7 – Think Creatively – Ken was a creative person and his success from being a poor preacher’s son to a successful business man is evidence of it. But what was unfortunate that he used is creativity for his own benefit later on and chose the wrong path to achieve more success. (Li, 2010)
Step 8 – Check your gut – Ken always denied of being the reason for Enron’s failure and there is no such evidence where its evitable that Ken used his gut except the last interview he gave. He said he was pretty confident that he could steer up the firm but he failed eventually. (O. C. Ferrell, 2010)
Moral Sensitivity – The essential ability required in settling on great good choices is affectability to the moral issues required in a considerable lot of our regular exercises. Frequently we may act in an ethically sketchy way since we were harsh to the moral way of the circumstance. Obviously, once in a while we may make the best decision just by sense, without considering at all what we are doing. For any number of insignificant choices, this is completely suitable. (Johnson, 2012)
Moral judgement – Moral judgment is the procedure by which one characterizes decision making to what isn’t right, great, awful, crazy, completely unusual, strange, semi contemplated, moral versus exploitative versus nonpartisan or bordering deviations to the past as expressed that warrant classifications voluntarily relying upon the way of the question. (Johnson, 2012)
Moral motivation and character – At the point when scholars discuss moral motivation while decision making, this is the fundamental wonder that they look to get it. Moral inspiration is an occurrence of a broader wonder-what we may call regulating motivation. Moral character refers to the personal moral qualities of a person that would trigger him towards making a decision which would be morally correct. (Johnson, 2012)
What happened in Ken’s case was not at all morally correct and there is no evidence of his any moral sensitivity, judgement, motivation or character as he violated all of these and even fired people if their practice of morality came between his personal objectives. (Li, 2010)
3. Ethical interpersonal communication
Mindfulness – A mental state accomplished by concentrating one’s mindfulness on the present minute, while serenely recognizing and tolerating one’s emotions, contemplations, and substantial sensations, utilized as a helpful strategy. A mindful personal is always on his toes and more alert, aware & receptive of the situations. (Johnson, 2012)
In the given case study of Kenneth Lay, Enron, its quite evident that Kenneth Lay was a complete with mindfulness. He was aware of all the loop holes in the company, all the situations, prices of Enron’s stock and the result that will be portrayed to the public after the figures will be rigged. His rise to the top is itself an example of how mindful he was. He did a PhD in economics and held the presidency for the dry fraternity at University of Missouri. He used his mindfulness in the wrong direction but he was very aware of the different ways to increase the stock price of the firm. He was able to manipulate the staff to rig the figures because of his mindful acts. He knew the employees would resist doing so as it was not morally right and totally illegal to do so but he did accomplish. Because he was well-aware of their responses in advance and different situations he will face in order to fulfil his personal needs. He took all the benefits of his mindfulness by earning loads of money but at the end of the day he used his quality for a wrong and illegal cause which costed him eventually. He was a very clever person as he was aware that he would be needing political ties for the kind of work he and his teammates were doing. So, he contributed in the presidential campaign of George W. Bush. This was the act of pure mindfulness as he knew he would require help from him in the later stage so he played a major role in the president’s campaign. He read the situation before anyone else did to his own benefit. One more instance of Kenneth Lay’s mindfulness is his plans to expand his business and accepting new ideas as well and welcoming them. He engaged Enron into building a water company and bought a major one in the UK plus cracking a deal in Argentina. They went into the broadband industry as well even though no one in the entire company had experience related to it but his openness to new projects and welcoming them showed how mindful he was. (Li, 2010)
Conflict Management – Conflict management alludes to methods and thoughts intended to diminish the negative impacts of contention and upgrade the positive results for all gatherings included. The procedures and thoughts utilized rely on upon the sort of contention that needs overseeing – specialists separate between full of feeling (social) and substantive (execution, process or assignment in particular) clash, and in addition interorganisational strife (between at least two organizations) and intraorganisational (struggle inside associations). Conflict resolution can be a point of peace promotion however not all refereeing procedures or styles have struggle determination as a definitive focus as it may not be possible. (Conflict Management, 2017)
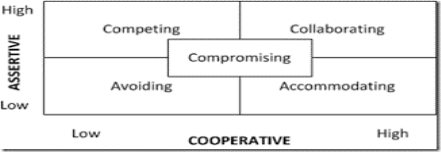
http://sourcesofinsight.com/conflict-management-styles-at-a-glance/
So, in the given case there were a lot of conflicts that arose in the Enron’s management but Kenneth Lay was pretty successful in overcoming them as he knew what the other person wanted or he already did favours to the people he knew could be useful or cause any harm to him. He was a good conflict manager as per the case study. Let’s take a look at an example, he knew the employees will be having a conflict of interest so he already had plans for them which were either to accommodate or avoid them, meaning either to offer them money to manipulate the figures or sack them if they don’t agree to it. Second example is of the top-level management; he was well-aware with the fact that Fastow and Skillings would not tolerate his illegal activities and it won’t be possible without them so he collaborated with them in his plan. Thus, all of them teamed up for money laundering. The third example can be seen of the political ties. He knew that to carry out such dealing within the organization he would definitely require a powerful support so he collaborated with the president as well in order to carry out his illegal activities smoothly. Even if someone from his company would file a suit against him he would be able to sort that out because of his strong political ties. So, all in all, Kenneth Lay was an effective conflict manager but when the situation went out of hand he was hopeless as the people who supported him were either arrested or had resigned before-hand. But till the end Ken kept on solving conflicts even when Skillings resigned he did not think twice and stepped as the CEO. (Li, 2010)
4. Exercising ethical influence
Kenneth Lay was a very powerful personality with a strong character and firm political ties. He was a major contributor in the presidential campaign of George W. Bush. Due to his strong political ties, he had no fear of being caught so he used to ask his staff to rig the accounting figures & financial forecast statements. Those who did it without any further questions were alright but those who raised any questions or did not agree with him on doing so were fired as an excuse for non-creative and not imaginary enough to work at Enron. Ken fired the entire accounting firm of Enron called Deloitte Haskins Sells for the same reason given above as they did not agree to manipulate the figures. He was successful in convincing the staff to change the figures because he offered them money to do so and those who did not do it were prey to quick sacking of employees. All this created a sense of insecurity in relation to the job which resulted in Kenneth Lay’s motive being successful. So, everyone started doing it and thus it led to the creation of Enron’s immoral corporate culture where if any of the staff is not playing with the figures would be thrown out of the company without any fear of the consequences. This was all because of Kenneth Lay’s strong reputation and ties all over the country including the president of the United States at that time. (Li, 2010)
References
Conflict Management. (2017). Retrieved from HR ZONE: http://www.hrzone.com/hr-glossary/what-is-conflict-management
Enron Case study. (2015). Retrieved from Applied Corporate Governance: http://www.applied-corporate-governance.com/enron-case-study.html
Johnson, C. E. (2012). A Practical Approach. In C. E. Johnson, Organizational Ethics (Second ed.). SAGE Publications Inc.
Li, Y. (2010). The Case Analysis of the Scandal of Enron . International Journal of Business and Management , 1-5 .
O. C. Ferrell, L. F. (2010). The Last Interview with Ken Lay. Journal of Business Ethics, 1-11.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


