Analysis of Market-driven Companies
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Business |
| ✅ Wordcount: 3397 words | ✅ Published: 23 Sep 2019 |
International Marketing
Assignment
Table of Contents
Introduction to the concept of market-driving and market-driven companies
Topic: “A market-driving firm claims to educate its customers towards better incentives and value-propositions.”
Introduction to the concept of market-driving and market-driven companies
The classification of companies makes them operate in the market in different ways. This study will be discussing the market driving companies and market-driven companies and how they operate in the market and their strategies. Market driving companies are the companies that tend to innovate and make their customers surprise by adding uniqueness in the new products and services. These companies tend to rule the market. On the other hand, market-driven companies focus on the requirements and the needs of the customers. These companies follow market trends and competition. For instance, Apple is a market driving company that tends to surprise their customers by innovating new ideas and adding values to their products, whereas Microsoft is a market-driven company and hence follows the existing rules of doing business.
Discussion
The market-driven companies operate fully in a different way than that of market driving companies. Market driving companies are innovative, and they continuously amaze their customers by adding values to their products. IKEA uses unique and simple ways in designing their products, and that attracts their customers whereas market-driven companies are reactive in nature and have clear goals and objectives of doing their business. Microsoft follows the usual trends of doing their business (Aragall and Montana, 2016).
Market driving companies are continuously changing their ways to business and aim at increasing efficiency (Cateora and Ghauri, 2000). IKEA being the market driving company entering into international markets and are changing accordingly. Market-driven companies are incremental in nature, and they focus on adding features to their existing products. Microsoft adds features to its existing products because they are regarded as a brand and they believe that adding features will satisfy their customers. Market driving companies use creative ways to solve the problems of the customers; IKEA uses customer-specific ways to solve the issues that the customers are facing. Market-driven companies are basically the companies with a huge brand name, and they generally remain insubstantial in responding to customer’s queries, and they remain unresolved.
Market driving companies like IKEA are very competitive in nature whereas market-driven companies like Microsoft are not that much competition in nature due to their late reactivity. Market driving companies are conclusive in nature as they quantify the risks measured by them in doing the business whereas the market-driven companies are not sure in researching and measuring the risk. IKEA conducts research before developing any products (Bereznoi, 2015). Market driving companies like Apple are very much clear with their business models to satisfy its customers whereas market-driven companies like Microsoft are unclear and perplexed in implementing new business models in order to reposition themselves in the market. Market driving companies are dynamic in nature and are ready to adopt the change like IKEA is very dynamic in adapting change management, but market-driven companies are rigid and static in nature and can serve in existing markets only (Chang, 2016).
Market-driven companies believe in performing rigorous market research in order to understand the existing and new customer’s requirements. These companies undertake many validation cycles with the documented requirements and elaborative specifications of characteristics and advantages in writing. A rigorous and exhaustive process is then undertaken in order to develop and test until new and differentiated products and services are recognized. Sometimes rigid and transparent market segments can also work. P & G for their products sometimes follows this segment (Dhillon and Gupta, 2015). Market driving companies tend to focus on the future as they are unaffected by the existing ways of doing business and the industrial norms regarding the development of new products and services. These companies tend to focus on innovation related to customer’s needs and requirements. The main objective of threes businesses is to create value networks through technology and business model creativity. Apple’s iPod is a great example where the company has built a value network in the business market (Dolata, 2017).
IKEA is a market driving company, and Sweden based multinational company operating its business globally. The business strategies adopted by IKEA are different from country to country, but still, they follow a basic strategy for every country. Value proposition by IKEA is commendable. They produce good quality and stylish furniture for the middle-class population so that everyone can afford to buy the furniture. The valued network for the business of IKEA is great to sustain in the market. It includes products, store locations, price, promotion, and logistics. The products are fashionable and are good for furnishing the apartments and most importantly the furniture reflects the sizes of the apartments. The store locations are in the suburbs that are next to the cities and are easily accessible by cars and public transport. The prices of the furniture are very economical so that it can be afforded by everyone. Promotional activities that are followed by IKEA are catalogues, advertising in print media, social media and website advertisements. Products are made in highly skilled and developing countries like China, Malaysia and then shipped to other countries.
Microsoft being a market-driven company adopt comprehensive and concentrated growth strategies for their business. Microsoft uses Market Penetration strategy as its major strategy that focuses on operating the business in the existing market. The secondary strategy for Microsoft is a product development strategy that ensures growth through developing and selling new products like Microsoft develops new software products which are a base for generating revenues. Market development is the last and supporting strategy used by Microsoft that focuses on entering into new markets. Diversification is also regarded as a supporting growth strategy which ensures the growth and development of the company by entering into a new business like Microsoft entering into Smartphone and hardware market by acquiring Nokia (Frow et al., 2015.).
The main concept of doing the business is understanding and identifying the value of the company that is value proposition and the communicating them with the customers in order to make them understand their importance (Cateora and Ghauri, 2000). The value proposition can be defined as the way how valuable items like products and services of a company are designed in order to fulfil customer’s needs and requirements. IKEA is a market driving company, and the value proposition of the company is delivering the value by producing the items at low cost and proving the customers the experience of a better home and a better life every day worldwide by producing the home decors and furniture at affordable price. Cost leadership: The cost of the products and services are the important factors that are considered for designing value proposition because customers will always prefer the new and innovative products at a lower price (Cateora and Ghauri, 2000.). IKEA ensures value to its customers by making final delivery of its products at thirty to fifty per cent less than the competitors in the market. The customers can pick up items of their choice, and the deliveries of the items are done against some fee. Cost is the most important factor for the company, and that is why the price of the product is set at first, and then materials are chosen and designed and manufactured. Expensive woods are used in furniture to make them look classy and only used in the first layer of the furniture (Halal, 2015).
Experience in shopping: This strategy ensures that if the customers are satisfied in the shopping experience, they will prefer to visit the store again and again. The shopping experience of the customers in IKEA is commendable because it sells furniture in a room like set up so that the customers do not need any decorator for fixing up things. IKEA also serves young customers who are not that much well off and work for daily livelihood, and they generally come to the store at the unusual time, so IKEA on weekends open their store till late night and also provide service delivery for delivery charges (Hennessy and Najjar, 2017). Designs: The very first thing that will attract the customers will be the design of the new products and how far they are unusual from the regular products. IKEA designs its furniture according to Swedish designs and keeps it simple and functional. Design of the furniture is the last step of the value proposition strategy.
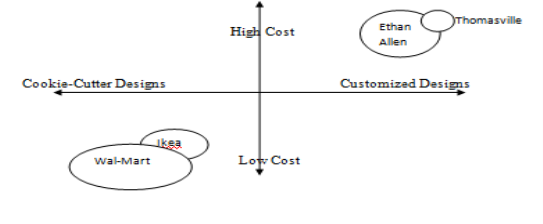
Fig: Positioning map of IKEA
(Source: Kjellberg et al., 2015)
The customers of IKEA are fully aware of the incentives and the value proposition provided by the company as this Swedish company is serving its customers since 1943 and Forbes ranked this company’s brand as 46th most valuable brand worldwide (Kjellberg et al., 2015).
PESTLE Analysis of IKEA
IKEA is a Swedish multinational company that designs and sells furniture, kitchen appliances, and home accessories.
The political factors are there in every country that affects the business, and it includes supply chain management to sales. The stability in the political issues ensures the economic stability which in turn guarantees better sales and profits. The political system in the US is very stable over a long period of time and as a result of that IKEA can do well in the US (Fozer et al., 2017). Economic factors play a very crucial role in the business environment. The economy of the country determines how much profits and revenue the business will earn. IKEA is operating its business in the US where there has been an economic recession, and the economic growth has been slowed down for the last two years. The amount of disposable income available to each individual in the US is high, and thus, there is a considerable segment in the society who can afford to buy the products sold by IKEA.
Other economic factors like inflation rates, interest rates wage rates and minimum wage legislation of US also affects IKEA in doing business because they are market driving company and economic factors are important for the expansion of such business.
Before stepping into the international market, it is very important to know about their sociological and cultural factors. The US market is very flexible, and they are at the highest stage of consumerism. IKEA being a market driving company can do well in the US because their culture is very open and they are ready to accept the new products and can give a trial on new products (Sadgrove, 2016). Being a market-driving company, IKEA needs to understand the cultural and societal norms of a particular region, before advertising for their products through the media, so that their commercials are accepted by the customers and they can market their products effectively.
The technological factor is one of the external factors that exercise immense impact on the functioning of IKEA. It has an up to date website from which the customers from the US can view its items online. Being a market-driving company, it is important for IKEA to regularly update its customers about their products so that they can also know what innovation the company is doing. IKEA is a global brand, and it has to follow many laws and legislation in the US in order to operate its business over there. The laws and legislation in the US are a bit strict, so IKEA had faced problems in entering into US markets. Sustaining business globally has been an important area where the companies are focusing on. The market driving companies always innovate the things in their own way and do not follow the usual ways of doing the business. IKEA has been very sensitive to environmental issues. In the US market, IKEA has entered as a market driving company, and it makes the optimal use of raw material and energy and also tries to reach green targets which have an overall positive impact on the environment.
SWOT Analysis of IKEA
The significant strengths of the company include the packaging of IKEA, which makes it easier for transport, the classy and minimal design is very much acceptable and popular in US culture, the brand recognition of IKEA in the US, which is very strong as well as the strong business model for the US market. Apart from that, offering low-cost furniture and household items with innovation at every step and a committed and strong relationship with the customers as well as suppliers of the US are also significant benefits enjoyed by the company (Abdel et al., 2018).
The significant weaknesses of the organization include factors like IKEA is a foreign company selling its items in the US so there has been a difficulty in understanding their needs as well as the innovation of items does not always work. Customers of US are interested in ready to use furniture, so unassembled furniture does not attract the customers, lesser post-purchase services in the US by IKEA, home delivery options are not available frequently for the customers of US, and a lesser number of stores in the US are few more factors which act as weakness for IKEA (Sarsby, 2016).
The significant opportunities for the organization includes the price-sensitive target market of US, increased popularity in the US market and the chances of expansion in US markets, while the threats for the organization includes factors like in the US there are low-end furniture retailers so IKEA might face competition from them and other companies in the US adapting IKEA’s business model. The people of the US are less willing to change their furniture frequently, which is another barrier to sales by IKEA (Vinay et al., 2017).
Market driving companies adapt many strategies in order to succeed in the undertaken ventures. Strategic innovation: The organizations adopt strategic innovation in order to reinvent and redesign the strategy of the business that will ensure the growth and success in the business. We often associate innovation with technology up gradation, but strategic innovation can be a value proposition also. IKEA adopted this by providing the advantage of clean Scandinavian design and immediate delivery of furniture and cultivating various ways to make innovation in their services (Pisano, 2015). Leap in customer value: Market driving companies need to adopt the leap in customer value strategy in order to sustain in the competitive market because they are not following the usual ways of business. So the leap in customer value can be achieved by producing customer friendly products, simplicity in the usage and design, convenient products and services, reduction in risk, and environment friendliness. In order to deliver a leap in customer value, IKEA had to reconfigure continuously its business model (Vahlne and Jonsson 2017).
Unique business system: The unique business system of IKEA is designing simple and economical furniture, the parts used in the furniture are interchangeable, new and modular, the reach to the customers are very easy, and the service provided by IKEA is consumer friendly and home delivery is also available (Whelan and Fink 2016). The standardization for the items produced by market driving companies is not very prevalent in the market because the market is driving companies are risk-taking companies as they first innovate things and then market those things, so it is not possible for them to gather the standardization certificates for their products. So the market driving companies can adapt strategies in order to succeed in their proposed ventures, but they cannot provide prior standardization of their products.
The success rates of market-driven and market driving companies with reasons can be explained with the help of the example of two companies namely Microsoft being a market-driven company and Apple being a market driving company. User interface: Whenever it comes to technology the first thing that comes into mind is to use the technology with ease. Microsoft has been customized with a start key in order to access all the files and folders, and Apple has a folder named finder folder which ensures to locate everything with ease and comfort. The user interface of Microsoft is easy to use compared to Apple. Cost: In order to start a new business or starting a computer lab in a school needs IT equipment, but the budget is not high. Microsoft wins the situation because it provides IT equipment at a lower cost compared to Apple. Apple, on the other hand, is expensive in the market. Microsoft computers provide great workflow whereas Mac computers do not provide the art and design required for smooth workflow management.
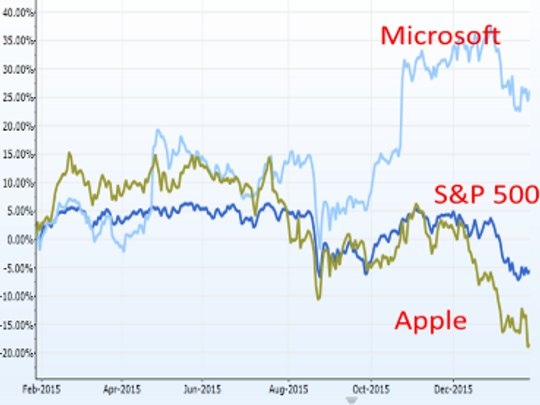
Security: Security is a major issue when it comes to computers and IT. Microsoft has gained a competitive advantage against Apple in this case because the antivirus and other security options of Microsoft are more popular than Apple (Wilburn et al., 2015). So from the above discussion it can be concluded that the success rate of market-driven companies are more than that of the market driving companies because the market-driven companies operated in the existing market which already have a customer base of its own and they are loyal and used to customers of the products and services offered by the company. A graph attached in the appendix shows that Microsoft is a market-driven company is doing well than that of a market driving company Apple.
Conclusion
The difference between market-driven companies and market driving companies and their ways of operating business, their strategies towards business are studies thoroughly in this study. in a nutshell it can be concluded that the market-driven companies are following traditional ways of doing their business and they are ruling the market but the market driving companies are also giving tough competition to them, and they are future giant companies because they are innovative and are concentrating more to amaze and surprise their customers by new products and services. This study had focused on the companies like Microsoft, Apple, and IKEA and how they are sustaining in this market and the strategies adopted by them.
Reference list:
- Abdel-Basset, M., Mohamed, M. and Smarandache, F., 2018. An extension of neutrosophic AHP–SWOT analysis for strategic planning and decision-making. Symmetry, 10(4), p.116.
- Aragall, F. and Montana, J., 2016. Universal design: The HUMBLES method for user-Centred business. Routledge.
- Bereznoi, A., 2015. Business model innovation in corporate competitive strategy. Problems of Economic Transition, 57(8), pp.14-33.
- Cateora, P.R. and Ghauri, P.N., 2000. International marketing: European edition. England: McGraw-Hill.Chang, J.F., 2016. Business process management systems: strategy and implementation. Auerbach Publications.
- Dhillon, I. and Gupta, S., 2015. Organizational Restructuring and Collaborative Creativity: The Case of Microsoft and Sony. IUP Journal of Business Strategy, 12(1).
- Dolata, U., 2017. Apple, Amazon, Google, Facebook, Microsoft: Market concentration-competition-innovation strategies (No. 2017-01). Stuttgarter Beiträge zur Organisations-und Innovationsforschung, SOI Discussion Paper.
- Fozer, D., Sziraky, F.Z., Racz, L., Nagy, T., Tarjani, A.J., Toth, A.J., Haaz, E., Benko, T. and Mizsey, P., 2017. Life cycle, PESTLE and multi-criteria decision analysis of CCS process alternatives. Journal of cleaner production, 147, pp.75-85.
- Frow, P., Nenonen, S., Payne, A. and Storbacka, K., 2015. Managing co‐creation design: A strategic approach to innovation. British Journal of Management, 26(3), pp.463-483.
- Halal, W.E., 2015. Business strategy for the technology revolution: competing at the edge of creative destruction. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 6(1), pp.31-47.
- Hennessy, J. and Najjar, A., 2017. Apple Computer, Inc.: Think Different, Think Online Music. Kellogg School of Management Cases, pp.1-24.
- Kjellberg, H., Azimont, F. and Reid, E., 2015. Market innovation processes: Balancing stability and change. Industrial Marketing Management, 44, pp.4-12.
- Pisano, G.P., 2015. You need an innovation strategy. Harvard Business Review, 93(6), pp.44-54.
- Ross, J.W., Beath, C.M. and Sebastian, I.M., 2017. How to develop a great digital strategy. MIT Sloan Management Review, 58(2), p.7.
- Sadgrove, K., 2016. The complete guide to business risk management. Routledge.
- Sarsby, A., 2016. SWOT analysis. Lulu. com.
- Vahlne, J.E. and Jonsson, A., 2017. Ambidexterity as a dynamic capability in the globalization of the multinational business enterprise (MBE): Case studies of AB Volvo and IKEA. International Business Review, 26(1), pp.57-70.
- Vinay, A., Srivastava, I., Vij, S. and Rawat, S.R., 2017. IKEA: The Furniture Guru-An Exploratory Study.
- Whelan, T. and Fink, C., 2016. The comprehensive business case for sustainability. Harvard Business Review, 21, p.2012.
- Wilburn Green, K., Toms, L.C. and Clark, J., 2015. Impact of market orientation on environmental sustainability strategy. Management Research Review, 38(2), pp.217-238.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


