Management and Leadership Roles in Organisation Operation
| ✓ Paper Type: Free Assignment | ✓ Study Level: University / Undergraduate |
| ✓ Wordcount: 8802 words | ✓ Published: 06 Jun 2019 |
This assignment will look at the vital role that managers and leaders play in the operation of an organisation and how this componence work together to utilise various resources through strategic and models to see that the organisation benefit in achieving their objectives and goals that have set. This assignment will hopefully evaluate the different types of management and leadership skills that are in practice within an organisation and the individual strengths and weaknesses that arise with each method. There will also be a look at the managerial and operational needs that vary from organisation to organisation, all depending on the circumstances of the organisation and the variety of the management and leadership skills.
LO1 & LO2 Differentiate between the role of a leader and the function of a manager
Apply the role of a leader and the function ofmanagers in given contexts
P1. Define and compare the different roles and characteristics of a leader and a manager.
Manager: Managers are the people who drive the goals and objectives of the company by the pre-determined plans that have been assigned to them. To accomplish these task, managers have to develop and establish approaches to the organisation’s strategies and to ensure that the planning of the workforce performs in a way that meets the objectives of the organisation. The positive aspect of managers is that they can be distributed at various levels within the business which allows them to be able to manage the tasks across different departments. Managers will also have the responsibility of dealing with the appraisal of their team, the process of assessments will be based on the performances of an individual and how they perform their duty.
Leaders: Leaders are those who get the work completed from those employed by the business. Just as managers, leaders are an essential factor in the role of motivating the workforce through the use of their communication and leadership skills. They are skilled in making their team achieve their objectives and goals, the most favourable outcome of a leader is that they can influence and motivate an employee for them to perform at their level.
The various functions of management and leadership are shown below:
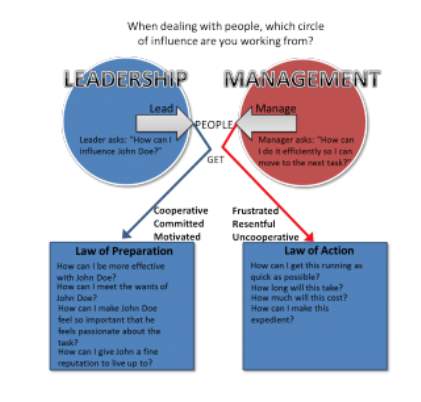
The above image shows the difference in the mindset of how a leader and manager operates.
Image 1: http://www.varsityfs.com/leader-or-manager-what-are-you/
Management: can be described as the area where managing all aspect of a department/team is needed in the best possible manner, this is a skill that is lacking to be able to get the work completed. One of the differences between management and leadership is that:
- Management is for the organised and formal individual, Leadership is directed at both formal and informal groups
Leadership: A characteristic of inspiring people, who will be able to meet their objectives. Leadership is not precisely the same as management because direction is one of many elements of control.
Differences between managers and leaders
Often the roles of managers and leaders can be seen as an interchangeable factor, but there is a clear difference between these functions. Managers accomplish their task by setting out the objectives of the organisation while leaders are tasked with communicating the vision of the organisation which will inspire the workforce. The below table gives an example of the difference between the skills set of managers and leaders:
| Managers | Leaders |
| The task of setting the objectives of the organisation. | Bring around the objectives/goals being developed by the manager. |
| Policies have to be communicated to the leaders. | Communicating and influencing employees to work as per the given policies. |
| Direct their department. | Direct their team. |
| Creating a progression plan that will be used by the organisation. | Are given the task of implementing the goals set out by the organisation. |
| Primary focus on the goals and objectives of the organisation. | To focus on the workforce. |
| Able to contribute more to the planning of the organisation. | To inspiring the work environment. |
| In charge of directing the work to the team. | To motivating the employees to work. |
From the table above, it can be seen that there is an absolute difference between leaders and managers, even with this difference these individuals play an essential part in the success of the organisation. A fully informed leader and manager can see to it and provide the support that the business needs to ensure for the long run of their business and ensure that they stay ahead of their competitors.
The role of a leader can be seen as a decisive role as they ensure to look into the hidden talent of their team so that they can provide guidance to ensure that their goal is achieved not only for the business but the individual. As for managers, they can come across negatively as they can criticise their team, to a certain level, to be the best in the field but this action can sometimes be seen as demoralising the individual.
P2: Examine examples of how the role of a leader and function of a manager apply in different situational contexts.
- A behavioural theory of leadership: The leadership theory highlights the leader’s behaviour and how they can use their skills in the best way known. The behavioural method is the most critical tool for measuring the potentiality of the leadership for a specific situation
- The behavioural approach in this situation looks to highlight the behaviour of the employee in the organisation. This theory sees to provide a result of effectiveness in the organisation so that it allows for a certain level of results and increases the productivity of the business.
- The classical theory of management: Classical theory promotes the particular task that decisions are distributed among team members/departments. The traditional approach also looks at the compelling role management plays in identifying the organisation’s perspectives.
- Managers would apply this theory by carefully explaining the task so that they can enhance the productivity and increases the efficiency of the organisation. To use this theory manager will sift through the task before-hand so that the skills of their team can be matched with the most suitable option.
- Contingency theory of management: The use of contingency theory within management is based on the efficiency that will drive the behaviour and the solution of a department towards a result. The primary function of contingency management is based on the practical techniques used for the growth of the organisation in an efficient manner.
- This theory can be applied based on the circumstances and resources available. Even with new situations, positive and negative factors will arise, management must ensure the correct decisions are made for this situation.
- Action-centred leadership: This is the base for any leadership and management within an organisation, this factor ensures for the adopting of techniques that will be used to direct the result that will see growth for the organisation. Managers will roll out the actions that are needed to produce results and leaders will develop the team’s productivity.
- This approach resulted from the increased level of enhancement that was needed for the productivity that would ensure results for the organisation. For this theory to succeed, the team/individual needs to be managed accordingly to achieve these goals.
- Transactional leadership: Transactional leadership is the managerial direction that will enhance the fulfilment of an employee through rewards or penalty to ensure an increase in their performances. Transactional leadership is emphasised in all organisations as an essential factor that will mean the compliance that is needed for administration.
- When applying this theory, managers will recognise the best individuals based on two factors, their past and recent performances.
- Leadership traits theory: In this theory, managers will focus on the oriented approach that will improve the morale of employees so that there is a level of motivation towards their task. This theory can be an uncertain route to take, as one factor could be to focus on retaining the image of the organisation but on the other hand, it can result in the loss of productivity if the focus is mainly centred on one factor.
- When an organisation decides to consider the training and development of their employees, this factor can solely be the responsibility of managers and leaders. Managers will recognise the area for training, whereas leaders will identify the long-term training that is needed to improve the personal and professional areas that will benefit the employee.
- Management by objectives theory: This is the form of a management model that will outline the objectives of the process of management. This factor emphasises on ensuring the contribution of employees to achieve the goals and objectives which will produce results for the organisation.
- This theory is used to increase and enhancing the performance of the organisation and to ensure the effectiveness to produce results. There will be a definite objective for both management and the employee which will be emphasised by the organisation. It will be the technique of recording and monitoring the activities of the organisation that will enable management to analyse the growth of the business.
- Transformational leadership: This is the form of guidance where little is known about this approach, leaders will look to inspire their team to the highest standard that will guarantee a sense of motivation for employees. The outcome will result in employees feeling that they have an impact on the decisions that are made within the organisation.
- Managers will apply this theory by way of asking their team to recognise the training and the development that is needed. Managers will then see to agree and discuss the training and development using planning with their team and will seek to approve before starting.
P3. Apply different theories and models of approach, including situational leadership, systems leadership and contingency.
Situational Leadership: In the late 1970’s, Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard developed the situational leadership model, the development of this model came from the idea of managers and organisation being able to adapt to different styles of leadership according to different situations that would arise within a business. For any global company, conditions will occur within the organisation that would differ from time to time and are mostly out of the control of management. It’s seen as an essential factor that the style of leadership can adapt to these situations, so that is it able to provide the required solution for the organisation.
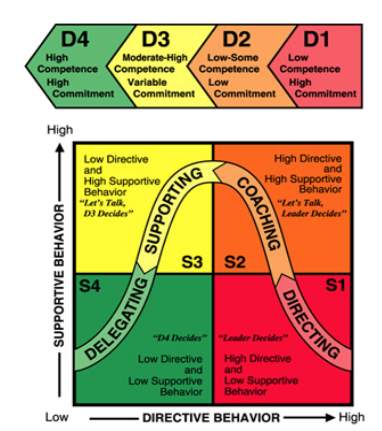 There are two factors which mainly drive the situational leadership model, the directive and supportive behaviour of leadership. The benefit of this model is to ensure that the organisation can adapt to various situations within the business and to provide that the decisions making of managers and leaders will assist in the growth of the company.
There are two factors which mainly drive the situational leadership model, the directive and supportive behaviour of leadership. The benefit of this model is to ensure that the organisation can adapt to various situations within the business and to provide that the decisions making of managers and leaders will assist in the growth of the company.
The Hersey and Blanchard model show the direct effect of the use of the situational leadership at different stages within an organisation.
Image 2: https://hubpages.com/business/What-is-the-Situational-Leadership-Theory
The sense of the above model is to be able to develop the communication skills that are required at all levels of management so that it guarantees the growth of the industry. This model provides leaders with the skills to navigate through the increase in the diverse work environment and the evolving market globally. When adapting to the circumstance that arises within the organisation, this model will ensure that leaders will be able to address the pressing trials that persistent in the organisation.
Systems leadership: The systems leadership outlines the guidance across the organisation and the geopolitical boundaries. The idea for this style is to ensure that leaders across the board not only look at their perspective or the company but to look at the boarder geopolitical development that would change to system and structured process of the business.
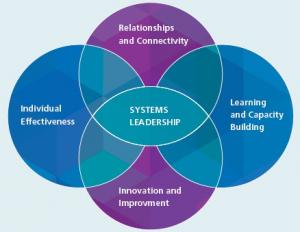
The above model shows cases the four drives towards system leadership.
Image 3: http://www.leadershipeastmidlands.nhs.uk/our-programmes-0
When applying this model, the organisation should seek towards appointing a leader who sees the long-term vision of the organisation because all leaders aim to ensure that their strategies and procedures can gain new heights and growth for the organisation.
Contingency Approach: Fiedler’s contingency leadership was created in the mid-1960s by a scientist who was studying the characteristics and personality of leaders. The theory is based on the factor that there isn’t just one kind of leadership model that is suitable for any organisation. It is a driven idea that the best possible course of action will all depend on the internal and external factors that affect the business and how a leader will appoint their decisions within this situation.
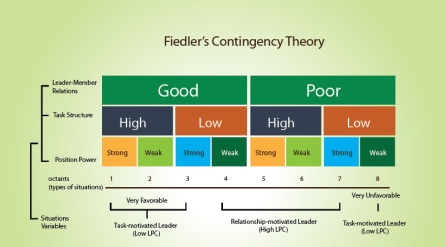
The above models show how the Fiedler’s contingency is used to decide the style of leadership that will influence the behaviour of a manager.
Image 4: https://www.tools4management.com/article/a-detailed-study-of-fiedlers-contingency-theory/
Before applying this model, the business has to examine the challenges which have arisen within the company so that they can ensure that the most suitable leadership style is picked so that it is useful in this situation. The outcome of this overall solution will be that the business will be able to benefit from the increase in employees productivity, the development of their work culture and a sense of motivation for their employees.
Chaos Theory: The chaos theory comes into action at particular points of time within the market, this model is mainly connected to the market when it is undergoing development, i.e. a slowdown in the global economy or a change in the demand from customers. It is managements point of view, to ensure that the organisation is capable of adapting to these changes so that they can avoid a loss to the business.
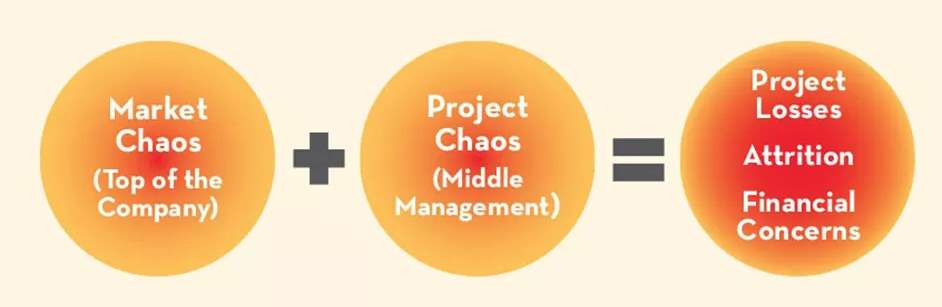
The chaos model showcases how the different marketing environment results in the chaos theory.
The two advantages that an organisation can benefit from when applying this theory is that management will see a more efficient and effective development of the adaptability skills of their employees. The outcome of this path is that there will be convenient ease in the way that employees react to the specific condition
Management by objectives: Management by objective is the model which aims to develop the performance and productivity of the business by defining what the goals are for the organisation, to ensure that these objectives are agreed upon and that these objectives are achievable by both parties.
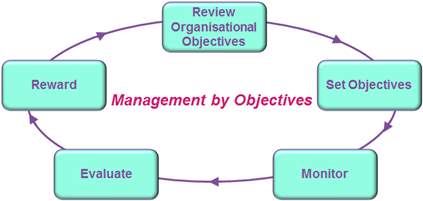
The Five stages that bring the management of goals into action for a business.
Image 6: https://www.pocketbook.co.uk/blog/2011/08/02/management-by-objectives/
By applying this model, management will be able to ensure that the tasks and objectives that are set will have a more methodical process to them. Employees will be fully assured of their roles and responsibilities while accomplishing this objective. This path could be seen as a positive approach to undertake for any organisation, as this will benefit the employee in being able to stay focus throughout the process which will guarantee growth for the organisation.
M1. Analyse and differentiate between the role of a leader and function of a manager by effectively applying a range of theories and concepts.
The various theories of leadership and management are discussed below:
Leadership theories:
1. The transformational leadership theory is described as the principle which guides the skills of leaders to causes specific changes to individuals, the work environment and even the local community which the business operates. Leaders will look at this factor to create a valuable and positive change in the workforce, the ultimate objective of the company is to be able to develop their employees into leaders. The transformational theory procedure for leaders is best suited for an organisation who aim to succeed at each point of their planning decisions to ensure that there is no shortage of leadership qualities and abilities in the organisation in the future.
2. Contingency theory of leadership is based on the approach to a particular situation at a specific time within the organisation. The method that is applied will be according to the condition that the business is experiencing at any given specific time. The contingency for leaders can be used at various times to circumstances such as to increase productivity from the workforce, to improve employees co-ordination when working in different groups, to ensure that employees take more responsibility for their work approach and to facilitate employee retention in the organisation.
3. The trait theory is based on the characteristics and qualities of a leader who leads efficiently, but this theory can sometimes fail to establish the trait that should be common for most managers. This theory can be best suited for organisations where there is enormous customer demand for their products/services, and therefore the need to control productivity within the workforce must be strictly looked at.
4. The action centred leadership theory focuses on the relations between managers and leaders and how they can control the three factors that control this model – team, task and individuals. The aim of this theory is too guarantee the success of leaders and managers to be able to achieve the organisation’s goal and objective, to build solid principles, improve the quality of the working environment and to develop teams and productivity. This model is best suitable to businesses where there is a sense of efficiency and support between groups, the results from this model will be that leaders will see all departmental teams develop and coordination between each level to further productivity.
Management theories:
1. Classical Management theory is based on the idea that employees only have physical and economic needs of an organisation. It has been noted that most organisations do not take into account what could be considered the social needs of the worker and ensuring the satisfaction of their job. Instead, they direct their notions on the emphasis on specialising in labour skills, seeing to centralising leadership, maximising organisationally profits and the making of decisions. This theory is mainly connected to organisation’s where their only emphasis is in regards to productivity and not the needs of the worker.
2. The behavioural theories of management are seen as the behavioural of leaders and how they approach a challenge if they choose not to use the situational approach. These types of managers are task-oriented and find themselves not being a relationship with mind, but this mindset can differ depending on the leader who management is working with. The behavioural theory of management can also be connected to human relations, as this addresses and focuses on the better understanding of human behaviour within the organisation. These theories can be seen as being better suited for organisation’s where management focuses on achieving the goals and objectives of the company by ensuring that they empower and motivate their employees.
3. The contingency theory of management looks at the leadership style which is applied to within the business; this theory is only applied when management look to increase the business productivity above all and meet the goals set by the organisation. The task of management when using this theory wants to improve the working environment of the organisation by developing a good relationship with the employee so that it motivates the employees towards accomplishing the goals of the organisation.
4. The chaos theory of management describes the chaos or interruption which arises from a change in the public demand or a slowdown in the economy. This model is connected to control when their employees are adequately skilled in handling when a critical situation arises.
5. The objectives of management states to improve the operation of the business by defining their goals, these objectives are approved upon by management and employees of the organisation. Start-up business finds that they use this model as management see that it’s ideal to include their employees in the decision process of the market.
6. The transactional theory of leadership is similarly known as managerial leadership; it sees to focus on the supervision, organisation and performance of the business. This model promotes management to use the reward and appraisal system for employees within their department. This theory is suitable for companies where the management team purposes to improve the efficiency of the organisation and to also develop a sense of right relations with their employees.
M2. Assess the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches to situations within the work environment.
All the theories mentioned above have their strengths and weaknesses these are explained below:
Situational Leadership Model
| Strengths: | Weaknesses: |
| •no one style of leadership provides the best possible selection of multiple leadership styles instead of developing the same processes.
•Working environment will remain relaxed and efficient as it helps build the team. •Boosting the team’s motivation, this will involve employees being involved in the decision making of the organisation. •Enhances the awareness of employees so that they can monitor the working conditions to ensure that they are aware of the leadership style being used. •The flexibility of leadership decision process can sometimes result in the reversal of roles between employees. |
•The lack of experience within employees can lead to a lack of understanding surrounding the demographic of the business.
•Can lead to a possibility of confusing employees as the situations can affect the various organisation factors. •The short-term strategies of the organisations are emphasising because it focuses on only the current scenario of the business. |
Systems Leadership Model
| Strengths: | Weaknesses: |
| •It provides a glossary of terms regards to research from different fields.
•The presentation and understanding of the realities and phenomenon of the business. •Clarifies the complexity of the environment and provides a framework for building the businesses ideas. |
•The process is lengthy and complicated as it ensures to engage several different parameter levels.
•Lesser adapted approach by leaders, as seen as an element of risk so widely not accepted. |
Task-oriented approach
| Strengths: | Weaknesses |
| •The goals and objectives of the business have specified the leader.
•Task definition – employees are fully aware of their task and responsibilities. |
•Focuses on the usual mode of working, can lack creativity.
•The leak of motivation for employees. •There can be lack of innovation in training and development. |
Relationship-oriented Approach
| Strengths: | Weaknesses: |
| •Reward scheme motivates employees.
•Increases employees job satisfaction. •An improvement made to the working atmosphere. •The employee better understands the working environment of the company. |
•The performance level is lowed due to a lack of pressure to accomplish tasks.
•Dissatisfaction from customers because of a lack of services. •Decreased organisation profitability due to the incomplete work due to lack of deadlines or pressure. |
Chaos Theory
| Strengths: | Weaknesses |
| •Ideas are freely exchanged amongst customers and the organisation.
•Being an adaptable organisation will allow fora comfortably change within departments. •Numerous options are available to the organisation – a variety of ideas •Organisation flexibility can be adjusted due to the situation of the business. |
•Loss of time due to processes being adapted.
•Departments being neglected. •Decrease in productivity due to employees taking advantage of available free time. •Overview of changes is not made available within a specified period. •Establishing the objectives of management can vary from time to time. |
Management by objectives
| Strengths: | Weaknesses |
| •To changes the objectives from time to time.
•Different objectives ensure improvement are made within management. •Goals and objectives are achieved by setting targets. •Requires monitoring to provide that process run correctly. •Greater participation of employees to complete all objectives set by the business. •Communication is encouraged, this leads to employees confidence. |
•Can be time-consuming, even tricky when to change from one goal to another
•Processes can be poorly misjudged. •Unable to measure objectives due to the changing needs of the organisation. |
LO3 & LO4 – Demonstrate an appreciation of the role leaders and managers play in the operations function of an organisation
Demonstrate an understanding of the relationship between leadership and management in a contemporary business environment
P1. Explain the key approaches to operations management and the role that leaders and managers play.
Total Quality Management:Total Quality Management is the process in which tasks and activities are overseen in the desired way to ensure that they are sustained at a level which will satisfie the organisation. The need for TQM is to be able to focus on the improvement, the performance and the quality of all the functions that run within each department and to ensure that there is a balance with each process.
The primary seven principles of the Total Quality Management or TQM are as follows:
1. People Involvement
2. Strong Leadership
3. Continual improvement
4. Decision making
5. Customer Focus
6. Supplier relation
7. Management
| The roles leaders play in this approach | The roles managers play in this approach |
| The productive process of the entire workforce through the involvement and to utilise the different business functions.
Leaders aim to remain committed and involved in their departments so that they can provide a plan to support the organisational. Developing the processes by the performance and measurement of each functioning stage. |
To ensure that the organisation focuses on both the internal and external customers.
Guaranteeing that suppliers are treated as business partners was that they could provide a better service to the business. To focus on the improvement of the organisation and the processes of production. |
Just-in-time inventory: The just in time inventory process is outlined in the policy to increase the effectiveness of how an organisation can decreasing their waste by accepting goods which will only be needed for in production. Ensuring that this process is in place, allows management to be able to support the business in lowering their storage space and only to see goods that are needed at a specific time. This process is also guaranteed by reducing the investments in the business because by accepting products when it is not required will only increase cost for the company.
| The role of the managers in Just in Time approach | The role that leaders play in this approach |
| To order goods at the right time and date from a known supplier.
Ensuring that the right quantity is ordered. Maintaining good relations with suppliers when ordering. To ensure that suppliers supply the correct amount of goods. |
Ensure that all goods will be utilised throughout the production process.
To ensure that all employees are informed of their roles and responsibilities before completing a project. To perform checks on all equipment used in the process of production. |
Continuous improvement or Kaizen:The constant improvement of the business function is defined as the approach within the workplace where improves are made on the overall role of the business. This process aim is to remove wastes from the organisation’s system so that improvements can be made to the business processes. Understanding the Kaizen method practitioners can incorporate this process into their overall sigma efforts.
The method of Kaizen is based on the five categories, sort, set shine to standardise and sustain by applying the Kaizen process in operations management the business will be able to the development and break down the different barriers within departments.
| The role of managers in Kaizen approach | The role that leaders play in Kaizen approach |
| The need to identify the scope of different tasks within the business.
Ensuring that employees are aware of what the Kaizen group are working on. Measuring the success of using the Kaizen method in the organisation. |
Recognising that specific tasks need to be assigned to particular individuals.
To confirm that the team benefits from the process. To assist the assistants with any challenges and to ensure that work is delegated if need be. |
Six Sigma:The six sigma approach is outlined as the method which looks at the different functions that will enable the organisation to remove the defects in products and service processes across the business. Upon the application of the six sigma approach, the organisation will eventually be able to achieve the maximum customer satisfaction by isolating defects in the market which will be able to ensure that they are a sensible growth within the company to achieve its goals and objectives.
| Role of leaders in six sigma approach | Role of managers in six sigma approach |
| Invest in the six sigma through training and resources.
To communicate the importance of the six sigma. Outlining the six sigma projects. Recognising and supporting employee’s contribution to the six sigma. |
Showing how management can save cost through the six sigma by goal setting and review.
To providing support and reviews to employees, these outcomes will be eventually directed to management. To monitor the implementation of the six sigma approach in the organisation. |
Lean production:The lean manufacturing process is described as the systematic and straightforward method which sees to the removal of wastes within a manufacturing system. Applying the lean process throughout production can assistance the operational management in refining the quality of not only products but the morale of the workforce as this method involves the entire business to contribute to a better process for clients.
| Role of the leaders in lean production | Role of managers lean production |
| To enable workers to understand what their responsibility is in regards to the lean production better.
Able to provide directions to employees to increase production. Taking the lead in monitoring the procedures of eliminating of wastes. |
To analyse the effectiveness of products and services.
Ensuring that no useful materials are eliminated. To report the progression process to executive managers or even board members. |
Queuing theory:The queuing method is defined as the mathematical analysis of waiting for lines by constructing the queue lengths and the waiting lines periodically. The application of this theory to operations management will help guide the organisation in resolving challenges based on scientific consideration. This will guarantee that the business will be able better understand the requirement of clients and ensure that they meet their needs.
| Role of leaders in Queuing theory | Role of managers in Queuing theory |
| Being able to identify delays in the queuing system.
Recognising the cause of the delays. Resolving the processes involved in these delays.
|
Supervising the entire process, from the start of the queuing system.
To guide employees to reduce the queuing delays.
|
P2. Explain the importance and value of operations management in achieving business objectives.
The importance and value of the Operation Management are as follows:
Controlling and distribution systems: This function is an essential factor in ensuring that operations management are accountable for the monitoring of the production process within the business. To see that they provide that the appropriate distribution of merchandises is completed to achieve the goals and objectives of the company. When this function is fulfiled, the organisation will see that their intentions to be able to utilise resources properly will be achieved.
Transformation of materials into finished goods and services: This function acts as the opportunity for operations management to be able to analyse the demand that customers will have on their products and services. The business will be able to utilise their service and product to produce the final product in the most intelligent manner possible. The outcome of the business objective is to see that departments/manufactures produce high-quality service/products that are acceptable to potential customers.
Capacity Management: For manufacturing services, the capacity of management in operations management identifies the capability of the development of the production process. This factor acts as a guideline to ensure that no additional goods are produced when other assets are delivered there can be an increase in the difficulty of the production process. Without guaranteeing the quality of the product the production process will be hampered, this will earn a bad reputation for the company and will also be reflected through their customers which is against the objectives of the organisation.
The design process: The process of designing a product is a fundamental function for operations management, as by specifying the production process the organisation will be able to meet the demands of the customers and to guarantee a profit for which will in return achieve the business objective. This function fulfils the business objective by being able to design a product or provide a service according to the requirements of the customers.
Scheduling management: Scheduling management is an essential function for operations management as this ensures for the correct scheduling and circulation of the tasks to the employee whose skill sets matches those that are needed to complete the project. The resources that are used and the time available can sometimes be insufficient for certain organisations who are working on short deadlines; it is very vital that before starting a task that the process of scheduling is in place as this creates the framework for jobs to be completed on time. It is the principal for all businesses to be able to accomplish their purposes as it helps in achieving their processes within the shortest potential time limit as possible and also helps the company to be able to gain a competitive advantage over their competitors.
Inventory and logistics management: This factor can be seen through the manufacturing services, the inventory and logistics process is a very crucial factor for any business as without proper logistics support the completed goods cannot be transferred to the market on time. Being unable to perform such duties will lead to the decrease in the demand for the goods and services to customers. The organisation must at all times focus on their inventory management and how they will be able to store the remaining of their products which will be utilised at some point further down the line.
P3. Assess the factors within the business environment that impact upon operational management and decision-making by leaders and managers.
1. CSR: The Corporate Social responsibility is the function which ensures the sustainability and development of the economic, social and environment of an organisation. The CSR policy affects all decisions that are made within a business because it is the guidelines from the CSR policy which will ensure that an organisation makes the right decision in regards to the ethical nature of their business. Leaders and managers have an enormous task to guarantee that the organisations are complying with CSR:
– Adopting short-term goals that will be beneficial in the long run for the business.
– Adjusting and compromising to be able to practice CSR.
– Ensuring that the CSR policy is committed towards the development of the local community.
– Using natural resources in production.
– The production process is coordinated at all time so that additional products are not produced.
– The business does not contribute to the increase in pollution level.
– To guarantee the decreasing in the pollution levels within the surrounding areas that the company operates in.
2. Culture: The culture of a place/country can affect the way that an organisation can and will operate in. The business environment looks to identify and connect with the culture where it works from; the idea is to be able to design a product that will be acceptable to that community. Culture plays a vital role in operations management because during these processes the culture of the workforce is engaged more with the strategies of the business and it allows the organisation to be able to increase the effectiveness of the workforce of a particular culture.
– Whatever decisions are made by the company their will always keep the culture of the community in mind.
– People will quickly accept or welcome a product/service by perceiving it as a part of their culture.
3. Values: For an organisation to function within its chosen market, they have to look at the benefits of their customers and analyse these values so that they can provide a product/service that will be welcoming and acceptable to their customer. In operations management, values are regarded as an essential consideration when finalising production and the working standards of the organisation.
– Through decision making, the benefits of a customer play a crucial factor in the business.
– Business location helps the organisation with their decision making and how these are implemented.
– Managers and leaders will focus on developing a suitable working culture.
– To provide a platform for the employee to showcase their skills and talents.
4. Ethics: To follow the CSR policy, the organisation has to ensure that they are working as an ethical business and that any decisions that are made do not affect the stockholders and the environment of the company. The task for managers and leaders is to ensure that the company complies with the mission and vision of that country which they operate from.
– To promote the welfare of the stockholders, to encourage sustainable development.
– Ensuring that ethical policies are followed through in all the hierarchical level of the organisation.
– To support the underlying code of conduct for and when doing business.
– Should not promote their product in a false manner.
5. Sustainability: Sustainability in the operations management guarantees that any resources purchased/used by the business are utilised efficiently without mismanaging the funds of the company. This process is an essential factor for any company as every organisation wishes to promote themselves as an accountable organisation to the general customers.
– To see that the objectives and the strategies of the company are sustainable to nature.
– Not using resources that are harmful to the cultural and social ethics of the society.
6. Stockholders: Individuals or bodies who have invested in the business and who have been able to purchase a certain percentage of the company. Stockholders can be mainly customers or employees of the organisation, suppliers or creditors, the government of the country and the community. Stockholders play an essential role in the operations management of an organisation, as managers and leaders look to operate the business to ensure that they meet the demands of their customer who on the one hand could be their most significant stockholder. It is, therefore, the decision of management to safeguard the company by complying with the activities of the stockholders and their expectations.
– Stockholders are individuals or entities that hold stock in an organisation.
– The business is fulfilling the needs and demands of their stockholders.
– Consumers stockholders: expects quality products.
– Employers stockholders: proper working environment.
– Suppliers stockholders: expect adequate order and payment.
– Government stockholders: hopes sufficient taxation policy and other legislation followed.
7. Developing, encouraging and sustaining intrapreneurship: Intrapreneurship plays an essential factor in the local/global growth of any business, there are many processes of intrapreneurship, but the primary function of this factor is to allow a company to identify and create their approach to the market. It is that approach that allows an organisation to be able to gain the popularity of their customer and to ensure the growth of the company. It is vital that leaders and managers understand the policies that are set out by intrapreneurship, as these guidelines will ensure that they can implement systems within the business and that they can develop new methods towards market or even be able to change the organisational structure. By adopting this model, managers and leaders will see the increase in productivity for the company through each department.
The role of a manager is to encourage, develop and to sustain intrapreneurship:
– Ensuring that employees are served with their basic physiological needs to function in their position.
– To find ways to motivate employees continually.
– Rewarding staff for completing their tasks.
The role of a leader in encourage, develop and to sustain intrapreneurship:
- To arrange training and development for the employee.
- Employees are mindful of their individual goals and responsibilities.
- To encouraging employees regarding the continuous learning process from different resources.
8. Supporting, developing and sustaining entrepreneurship: Leaders and managers play an essential role in the theory of entrepreneurship, as this function sees a business make oriented risk decisions for the welfare and growth of the company. The role and responsibilities of managers are to develop and encourage sustainability in which the business environment can identify the skills of an entrepreneurial through an employee and help them to follow their entrepreneurial vision.
The role and responsibilities of a leader:
– To identify the drivers of entrepreneurship in the workforce.
– Ensuring that they are utilising their creativity and innovation skills for the growth of the organisation.
– To encourage the individual to develop their vision.
The role and responsibilities of a manager:
– To ensure that the department is not all involved in the tasks set by the organisation.
– Allowing the employee the chance to pursue their entrepreneurial opportunities.
– Utilizing the risk-taking capability of the employee to be able to conduct various operational tasks.
M3 Evaluate how leaders and managers can improve efficiencies of operational management to successfully meet business objectives.
Employees productively: Leaders empower their team in producing the highest quality of work by offering flexibility to an employee’s working environment. This method has always been shown to allow employees to provide the best possible job, through the freedom and more exceptional ability in a creative environment. This method helps operational management, as workers are given the flexibility to work within their preferred hours and preferred locations. This path can, in turn, help to maintain the quality of the product and improve the increase in the productivity of the employee. But leaders and managers should ensure that they empower and provide employees with the option of working remotely, this fulfils the objectives of the organisation in regards to developing work productivity so that the business can meet the demands of the customers.
Labour redundancies: At specific points in time, all organisation have to look at the restructuring of the business to ensure that there is a sense of efficiency running throughout the industry. Leaders and managers have to look at how the hierarchical positions work at every single level of the company throughout the progression of any essential task. Applying this process will see that senior management will engage with the points and ideas of lower management regards to the organisation’s decision making, this path will be ideal in ensuring that there is an essential improvement on the efficiency of operational management within the business.
From operational management, this method helps in clearing the elements that occur during the production process and which can affect the productivity of the working environment. One of the primary roles for leaders and managers is to be able to identify these factors and to guarantee that the communication procedures are present in the business, such matters will help the industry to maintain the efficiency and productivity that is needed for operations management. This path will enable the company to fulfil the objective of looking after the welfare of their workforce.
Improving Collaboration: A technique that managers ensure to follow to enhance the efficiency of operations management, it helps to increase interactions between each department while allowing for better bonding and understanding among employees. As a result, there will be a healthier environment experienced by the employees who will be able to work freely and assist each other. For operational management, this path is beneficial as it is showing the development of communication within the production process as the rate of production will increase because of the improved understanding and partnership of the employees. This will fulfil the organisations objective regarding promoting co-ordination and co-operation within the company.
Incentive programs: This is a technique that managers will follow to be able to increase operational efficiency within the work environment and to motivate employees who will work more efficiently for the organisation. For executive management being able to drive department is an assurance that these individuals will succeed to reach the goals and objectives set by the business because ensuring the path of motivation will see the improvement of the organisation’s productivity. Fulfilling this objective will understand that no matter what size an organisation can be, managers strive to motivate their employees so that they can encourage them to work harder towards these rewards.
Customer Service: Customer service is an essential function of any business, managers at all times need to ensure that they know the customer needs and the customer’s expectations for a product/service. Being able to communicate these factors plays an essential role in the organisation because from a business point of view you have to understand the buyer needs and wants. Thus operations management need to see that proper communication between the customer and business is always clear so that there is an increase in the efficiency of their product and service. This fulfils the organisation’s objective of developing a good sense of the relationship between the customers and itself; this path will also help the operational management to understand the demands of customers better and to ensure that they produce goods according to these demands.
Logistics Management: The logistics and inventory management supervises the flow and the activities of goods which will enhance the customer’s needs and wants. This function also plans and implements the control on how efficient products are distributed from the warehouse to the user. Through logistics management, managers and leaders will work on achieving the inventory plan by transforming the systems which enrich the activities of the control system for the organisation. It will also ensure that they govern an effective logistic channel which controls the distribution of their merchandise.
Scheduling: The scheduling of work is seen as the act where a task is assigned to an individual/team to complete the goal set by the business. The schedule involves the following processes: arranging, controlling and enhancing the activities that are included in the manufacturing process. Managers will see the use of programming as providing efficiency and leaders will see this process as increasing efficiency within the business. In scheduling, the foremost duty for managers and leaders is to ensure that they achieve the organisations objective by optimising the process of orders through the operating system which will accomplish the given results required by the organisation.
Constant planning and development: This process requires the organisation always to ensure that they are achieving the effect necessary to improve the level of business which is needed to produce a profit for that business. It is the task of managers and leaders to ensure that they accomplish the optimal level of satisfaction and enhance the skill set to motivate their team so that they can increase the efficiency level of the business. To ensure that the planning and development process is always achieved, managers and leaders should ensure that they follow the guidelines that are set by the organisation. These guidelines will see that they can increase the control and distribution policy that is in place. This process will guarantee to provide the desired results expected by the organisation and to allow for the necessary updates that are essential to developing and planning for maintaining the efficiency of the business.
M4. Analyse how these different factors affect the business environment and wider community.
The organisation is primarily influenced by the policies set by Corporate Social Responsibility;
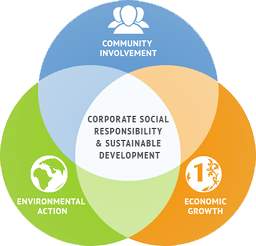
Image 7: https://www.treyburnhr.com/corporate-social-responsibility-business-approach/
These are adopted by the organisation to ensure the improvement of the brand image of the business and to promote the organisations socially responsibility. Below are methods that are influenced by the CSR policy:
The below gives examples of how the CSR’s systems impact the environment and community areas:
Culture: The organisation will help in maintaining the lifestyle of the surrounding area which they operate in, to ensure that they do not negatively interfere with the community and that they will look at working together to preserve this culture. Maintaining this connection, will promote the organisation’s socially responsible and ensure that they work toward to improve the society. By conserving the culture the organisation will be able to focus on proposing products which are suitable for culture of a particular community, this process will assist in maintaining the organisation environment and protect the rights of the broader community.
Value: The organisation will look at preserving various costs that are related to the community that they are operating in. This will ensure that the business is maintaining the benefits of the population, this act will see that the company will be able to gain a better understanding of the surrounding area and be able to promote their products to their potential customers even if their beliefs are not similar to each other. This theory helps that organisation create a sense of responsibility within their working and even their business environment. Showing such a guide to the community will allow the organisation to be able to fulfil their obligation towards the society.
Ethics: The organisation ensures that the business follows the ethics followed by the company are at balance with the general business ethics which is to promote a sense of transparency within the business environment and their product/service. For any business to ensure customer loyalty, there has to be a sense of not misguiding their customers any shape or form. This sense of responsibility will result in customers showing a sense of loyalty to the business. For any business there has to be a sense of beliefs, these have been set out by the organisation stakeholders that have to be followed by management, one fundamental idea is to ensure that the organisation can show a sense of responsibility to their customers at all times. With this act in place, employees will begin to see and understand that they must comply with the welfare of stakeholders outside of the idea of achieving personal growth and development. Whatever path that taken, the business must compile with the purpose of improving the branding of the business so that it can increase the reputation of the market which is ethical.
Sustainability: Ensuring that the products that are produced are developed using sustainable material and in a sustainable manner. The aim that all businesses should reach is to ensure that they can maintain a sense of environmental sustainability by avoiding polluting the surrounding areas or putting pressure on natural resources. The results that business should aim at is to practise the use of sustainability so that it reflects on the impact that is will have on the community in the short and long term. Aiming to sustain the environment that a business operates in, will allow the organisation to ensure that the society will benefit the most from the reduction in the consumption of resources. The results should be the decrease in the pollution level, the broader community and business environment aiming directly to preserve and conserve the natural resources and to seek more at promoting the use of renewable resources.
Conclusion
This report evaluates the performance of operations management and how this function plays an activating role in the organisations, from the start of the production process to the distribution of their goods/services. Leaders and managers must ensure that they follow principles, reach has been set out by the organisation, to provide that they are encouraging their department/employees to approach their task efficiently which will result in the growth and development of the business.
This report also summarises the factors that organisations have to follow the Corporate Social Responsibility policies to ensure that they protect the ethics set out by preserving the culture and protecting the environment that they operate sustainably. For the business to practice as an ethical business, they have to consider the facts that at all times within a company that there will be a certain amount of impact reach occurs throughout the function of management and operations. And to be able to present an ethical industry to the broader community, management has to ensure that there is an understanding and grasp the aspect that will grab the attention of potential customers.
Reference:
- Nigel Slack Stuart Chamber, and Robert Johnston (2010) Operations Management. (6th Edition)
- David Loader (2002) Relationship and Resource management in operations. (1st Edition)
- Paul Falcone (2016) 75 Ways for Managers to Hire, Develop, and Keep Great Employees
- Benjamin Sweeney and ClydeBank Business (2017) Lean Six Sigma QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner’s Guide to Lean Six Sigma (2nd Edition)
- D.R. Kiran (2016) Total Quality Management: Key Concepts and Case Studies
- Steve Watkins and Nick Orchiston (2015) ISO 9001:2015 – A Pocket Guide
- Matthias Holweg, Jane Davies, Arnoud De Meyer, Roger Schmenner (2018) Process Theory: The Principles of Operations Management (1st Edition)
- Harold Kerzner, Harold R. Kerzner (2017) Project Management: A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling (12th Edition)
- David B. Grant, Chee Yew Wong, Alexander (2017) Sustainable Logistics and Supply Chain Management (2nd Edition)
- Alex Hill and Terry Hill (2018) Essential Operations Management (2nd Edition)
Website
- 5/02/2018: https://www.topmba.com/mba-programs/what-operations-management
- 5/02/2018: http://www.informit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=2167438
- 8/02/2018: https://www.slideshare.net/MEQUEST/functions-of-production-operation-management
- 13/02/2018: https://www.mheducation.co.uk/he/chapters/9780077133016.pdf
- 14/02/2018: https://www.paypervids.com/factors-influence-business-environment/
- 16/02/2018: https://iedunote.com/organizational-environment-elements
- 20/02/2018: https://www.slideshare.net/aasthasahi/internal-and-external-business-environment
- 14/03/2018: https://www.tools4management.com/article/a-detailed-study-of-fiedlers-contingency-theory/
- 14/03/2018: https://managementhelp.org/blogs/leadership/2010/04/21/leadership-theories/
Images:
- Image 1: http://www.varsityfs.com/leader-or-manager-what-are-you/
- Image 2: https://hubpages.com/business/What-is-the-Situational-Leadership-Theory
- Image 3: http://www.leadershipeastmidlands.nhs.uk/our-programmes-0
- Image 4: https://www.tools4management.com/article/a-detailed-study-of-fiedlers-contingency-theory/
- Image 5: http://enewsletters.constructionexec.com/riskmanagement/2013/08/deconstructing-chaos-applying-chaos-theory-to-todays-construction-industry/
- Image 6: https://www.pocketbook.co.uk/blog/2011/08/02/management-by-objectives/
- Image 7: https://www.treyburnhr.com/corporate-social-responsibility-business-approach/
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this assignment and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


