Offline to Online Transactions in Travels and Canteen Segments
| ✓ Paper Type: Free Assignment | ✓ Study Level: University / Undergraduate |
| ✓ Wordcount: 6339 words | ✓ Published: 08 Jun 2021 |
Executive Summary
The report includes work done during the internship at ftcash head office located in Mumbai from 17th April, 2017 to 10th June, 2017. My objective of my project was to develop a market of O2O (offline to online) transactions in Travels and Canteen segments in Mumbai. The objective encompasses preparing a sales pitch, do an effective marketing of the product to the target segment, acquire the potential merchant and train the merchant in regard to usage of the product. I had to visit the existing travel merchants and ask them to increase the volume of the transaction on our platform as a part of key account management (KAM). At the fag-end of the internship period, I was part of a promotional campaign at a canteen in Narshee Monjee Institute of Management Studies (NMIMS). I even got a chance to interact with all the three co-founders of the organisation in the latter half of the internship and got numerous insights on many subjects which will help me in my future endeavours.
Overview of the Industry
The Payment Industry in India
The Payments Industry in India has largely been driven by cash. Presently, cash transactions accounts for 78% of all transactions in the country. This status quo is set to change rapidly in the near future. The ongoing digital and technology revolution in India coupled with several progressive regulatory changes has revolutionised digital payments in India. The Government’s Digital India vision and entry of large corporates such as Reliance in the telecom sector is aiding an unprecedented growth in the Internet penetration in India. The number of internet users in India is set to double in the next 5 years from about 300 million today to 600 million in 2020. About half of the 600 million internet users are expected to transact using digital payment methods. Digitisation of payments presents a large opportunity in the Indian context. It is estimated that the total payments via digital payment instruments will be in the range of US$ 500 billion by 2020, which is 10x the current levels in India
The Government and other regulators have been a driving force for establishing a robust digital payments system in India:
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI): UPI is an open architecture set up to stitch together all payment services into one common platform. The open source platform encourages participation from every payment service provider, viz. banks, Fin-Techs, payment banks, e-wallets, etc.
- Payment Bank Licences: The Reserve Bank of India has issued 11 payment bank licences in the past one year, aiming to achieve a deeper penetration in rural markets
- KYC Norms for small transactions: There is no requirement for customers to undergo a KYC process for transactions upto INR 10,000 (USD 150) per month on payment wallets. This key guideline has resulted in a large adoption of e-wallets. Paytm (a leader in e-wallets in India) is the fourth largest Fin-Tech unicorn globally with a valuation of about USD 5 billion as of the latest funding 01round.
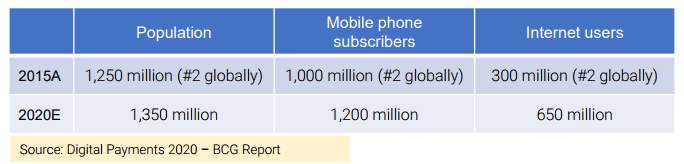
India represents one of the largest market opportunities for digital payments. With a population of 1.25 billion, India accounts for roughly 18% of the global population. The two key drivers of digital payments – mobile phones and internet users are already well established in India. To date, India has about 1.0 billion mobile phone subscribers and 300 million internet users, ranking 2nd on both metrics globally.
Key Development: Demonetisation
India’s Prime Minister, Narendra Modi, announced on 8th November 2016 that existing INR 500 (about USD 7.5) and INR 1,000 (about USD 15) banknotes would no longer be legal tender, with airports, railway stations, and hospitals only accepting them for a brief period of time.
This move will be a game changer for the payments industry in India:
- Limited availability of cash will drive people to digital alternatives. The government is restricting the number of notes a consumer can exchange to INR 4,500 (about USD 67). There are also restrictions on ATM withdrawals, and huge queues have already formed outside of post offices and banks. This means people may not be able to retrieve the new cash they need before official businesses stop accepting the old bills, which could force them to turn to other methods of payments they have not previously considered, including mobile wallets and P2P solutions.
- The unbanked may now have no other options except digital payments. Many segments in India are unbanked, especially drivers, small grocery store (kirana) owners, small retail shop owners, and travel agent businesses. With a suddenly diminished availability of cash, these segments will be compelled to find alternatives — and many will likely turn to mobile wallets as they are typically easier to acquire than bank accounts with debit cards.
- More digital transactions will generate more customer data. This will allow online lending platforms, alternative lenders, and other Fin-Tech’s to make better assessments of potential borrowers’ creditworthiness. As a consequence, availability of credit from these Fin-Tech’s may increase.
- A boost to the Fin-Tech sector could help another government policy succeed. The Indian government has been promoting digital finance for some time. Earlier this year, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) launched United Payments Interface (UPI), a tool that allows users to access multiple bank accounts and merchant payments within a single mobile app. The government is keen on a transition to a cashless economy because it could be cheaper to run, help reduce the underbanked population, and reduce financial crime as electronic payments are easier to track. Growth of the Fin-Tech industry, and increased use of Fin-Tech products, will only further drive the move toward a cashless economy.
Cash verses Non-Cash Transactions
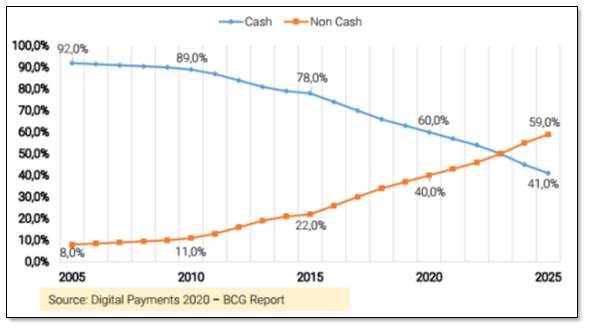
Traditionally India has been a cash economy. Currency in circulation in India accounts for 18% of the GDP versus 3.5% to 8.0% in matured markets such as the UK and USA. In 2015 cash accounted for 78% of total transactions in India, against 20%-25% in developed economies of UK, Germany and France. But, the percentage of cash for transactions has seen a rapid decline in the past few years in India. In 2010, the percentage of cash in all payments was 89% compared with 78% in 2015. This rapid decline is a result of an increased adoption of non-cash instruments such as cards and digital payments such as mobile wallets, electronic transfers, etc. Stored value instruments like mobile wallets (Paytm, Mobikwik, Citrus, etc.) and prepaid and gift cards have made payments though internet devices convenient and easy.
Digitisation of payments is a large opportunity: It is estimated that total payments on digital platforms to be in the range of USD 500 billion by 2020, up from current estimates of USD 40- 50 billion. The key driver for this rise will be an increase in the user base. The number of users in the digital payments instruments segment is estimated to be about 50-60 million, expected to rise to 300 million by 2020. Digital payment users will comprise 50% of all internet users by 2020. Scale is critical to make a payments business model viable. Building world-class payments business requires significant investment in technology, infrastructure and partnerships. Participating players must look to build a sizable scale over the next few years. This will drive a consolidation in the payments industry with smaller businesses being acquired by larger multinationals which will look to gain critical size for outperformance.
Industry Participants
Bank-led: Banks have been integrating their banking apps with integrated bill payment solutions; most of these apps do not require a bank account to be opened with the bank – allowing for a much wider reach in the market.
Telco-led: Large telecom operators such as Airtel, Idea, Vodafone and Idea have launched mobile payment solutions with the aim to capture a large part of their already existing clientele.
Wallets: Backed by VC & PE Funding, Wallets such as Paytm, Mobikwik, Freecharge, PayUmoney, etc. have spent heavily on customer acquisitions driven by discounts. Discounts have visibly reduced as companies are now looking at profitable growth. The marketing initiatives have gradually moved towards providing a wider and more seamless experience. Wallets have found a large acceptance in unbanked/under banked areas in India. Innovative solutions such as cash pickup services and tie-ups with banks for cash loading at bank’s retail branches. Wallet users are already triple the number of credit card users in India.
Payment Banks: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issued 11 entities approvals to set up payment banks. The scope of services of a payment bank includes demand deposits of up to INR 100,000 (USD 1500) per customer, issuance of debt/ATM cards, acting as a business correspondent to another bank, distribution of mutual funds, etc. The primary aim of a payment bank is to drive financial inclusion and provide essential financial services to the unbanked population of India.
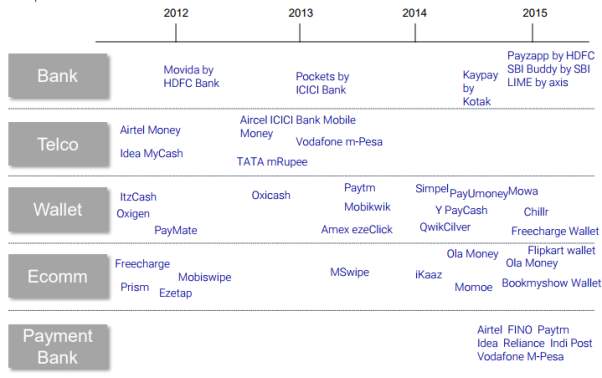
Source: Payment Industry India 2016, IMAP
Indian Consumers Insights towards Digital Payments: BCG-Google Report
Digital payments in India are not limited to being an urban and affluent phenomenon. Trends show that future adoption and growth of such services will be driven by the next set of low income users. Currently, users of digital payments lie across a wide spectrum of income, consumption profiles, attitudes, pain points and motivations. While some of these needs have been addressed with current propositions, the rest present a huge opportunity to include masses into the envelope of digital payments users.
In order to better comprehend preferences, behaviour and pain points of these varied user segments towards digital payments, BCG in association with Google, undertook a survey conducted by Nielsen aimed at understanding what it will take to build a successful payments play in India. The survey spanned 9 cities (metros and non-metros) and covered approximately 2,500 consumers and 920 merchants, who were aware of digital payments. Insights from this research, combined with industry interviews and knowledge from our existing client work have helped outline a set of initiatives that payments players should undertake in order to successfully unlock the potential of the Indian digital payments space.
Key Insights
- Users of digital payment instruments prefer these to other non-cash modes
- Convenience is as important as offers in driving digital adoption
- Prepaid mobile recharge and bill payments remain the most popular use-cases
- Point of sale to form the largest use-case for digital payments in future
- High frequency use cases driving usage of digital payments
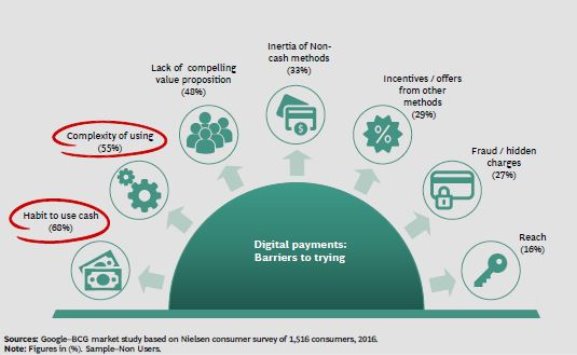
- Habit to use cash, complexity and perceived lack of value proposition key barriers to adoption
- Security, identity theft and fraud are not big barriers in India
- 3 out of 4 merchants believe digital will grow big, accelerating future sales
- No clear benefits over other methods, proclivity towards cash and complexity are key barriers for merchant trials
- Building a transaction ecosystem for merchants is critical
See APPENDIX – for Reason for Using Digital Payments
See APPENDIX – for key Barriers for Adoption
Building a transactional ecosystem for merchants is critical
Cash is deeply embedded in the ecosystem that small merchants operate in. Customers rarely ask to pay digitally and the upstream supply chain also demands payments in cash. To ensure universal acceptance is built, digital payments players need to ensure a gradual transition into customers and merchant transaction ecosystems.

- Linear adoption: Increase awareness and presence and offer better support.
The digital payments instrument must generate merchant demand by driving trials and adoption, as well as through a simple and convenient merchant acquisition process. Both the on-boarding and the fee structure need to be kept highly simple, especially for the unorganised retailer. Further, payment service providers must ensure requisite support is provided in the form of call centre / agent support, toll free numbers, and transparent processes (for example in case of disputes, refunds etc.). This will provide the required confidence to merchants to come on to the digital payments platform.
- Incremental adoption: Address need gaps and pain points.
In order to drive merchant adoption of digital payments, it is imperative for payment service providers to improve the products offered—with easier processes, reporting, reconciliation etc. Digital payments should be faster—for example, touch based. Merchants are worried about long queues if that transaction takes time to complete. This has to be given disproportionate importance to drive large scale offtake. Further, digital payments players will need to develop more use-cases where digital clearly beats cash, to ensure momentum of changed user habits to carry through in situations where benefits of digital payments are not that differentiated.
- Disruptive potential: Establishing the transaction ecosystem.
The acceptance of money in digital payments for merchants is directly linked to their ability to pay their distributors and vendors through the same instrument. Establishing this transaction ecosystem helping merchants manage their inbound and outbound transactions will be critical to drive universal acceptance.
The future of Digital payments in India
While the exact form and shape of disruption will only be unveiled over time, the crystal ball
indicates seven trends set to transform the payments landscape over the next five years:
- Technology will make digital payments simpler
- Merchant acceptance network to grow 10X by 2020
- Payments will drive consumption—and not the other way around
- Consolidation will drive ubiquity
- Modified UPI will be a game changer
- Digital identity will accelerate customer acquisition
- Cash to non-cash ratio will invert over the next ten years
In summary, digital payments in India is in a unique position—given the nature of the product, ubiquity of acceptance is a must, and hence mass appeal which can harness the power of network effect and push the product universally is a pre-condition to success. At the same time, there is intense heterogeneity of the user, use cases, motivations, attitudes and barriers towards digital payments. The right product thus has to cater to both these seemingly conflicting needs—have mass appeal, and yet be able to cater to all these varying needs in a customised manner.
Profile of the Organisation
Organisation History
ftcash is a fast growing financial technology venture which aims to empower micro-merchants and entrepreneurs with the power of cashless payments and loans only using a bank account and feature phone. ftcash aggregates all payment methods including credit/debit cards, net banking and mobile wallets to create an open platform for merchants to start accepting electronic payments in less than 5 minutes. In addition, ftcash creates unique and proprietary transactional data which can be leveraged to provide institutional finance to these merchants. 15+ NBFCs to provide working capital loans to its merchant partners. With an interest rate of 18-30% per annum and a ticket size between Rs 25,000 to Rs 5 lakh, the company aims to meet the regular credit requirement for small retailers who otherwise depend on unorganized sources of finance such as moneylenders to meet the demands of their business. At present, catering to over 20,000 merchants on its platform leveraging its differentiated offerings, ftcash has already lent around INR 2 crore to 150 merchants in a pilot and has seen a strong repayment trends.
Started in mid-2015, after a successful launch in Mumbai, ftcash has expanded countrywide by acquiring over 3,500+ merchants across various segments such as kirana stores, milkman, newspaper agents, travel agents, coaching institutes etc. The team comprises of senior executives from Deutsche Bank, KPMG, Capital One, World Bank among others with a pedigree from Wharton Business School, Harvard University, IITs, SRCC etc.
ftcash is backed by PayPal, as it was adjudged the winner at Start Tank Challenge. It was awarded winner at the UK Trade and Investment – Great Tech Rocketship Initiative, IIM Ahmedabad CIIE-IIFL Fellowship, Village Capital Program, KPMG Hot 100 Startups, iSPIRT InTech50 among other accolades. ftcash was selected for World’s first Impact Investment Show – The Real Deal on NDTV and Young Turks on CNBC.
ftcash is funded by IvyCap Ventures and several marquee international angel investors.
Top Management Details
ftcash is the brain-child of Sanjeev Chandok, Deepak Kothari and Vaibhav Lodha.

Sanjeev Chandak
He has 20+ years of experience in Financial Services and Technology. He has served as ex-CFO of Deutsche Bank and as Director of Capital One. He did his MBA from Wharton and graduation from IIT Kharagpur.

Deepak Kothari
He has 9+ years of experience in strategy consulting. He has worked in KPMG, Deloitte, and Grant Thornton. He is a chartered accountant and an alumnus of SRCC Delhi and The Doon School.
Vaibhav Lodha
He was Director – Global Development at XPRIZE, leading World’s first global prize that targets the problem of access to water. He had previously been associated with The World Bank, LGT Venture & Lodha Group. Vaibhav is an alumnus of Harvard University and NIT Trichy. He is awarded ‘Power 30 under 30’ by Apex Society, USA and ‘Global Shaper’ by World Economic forum.

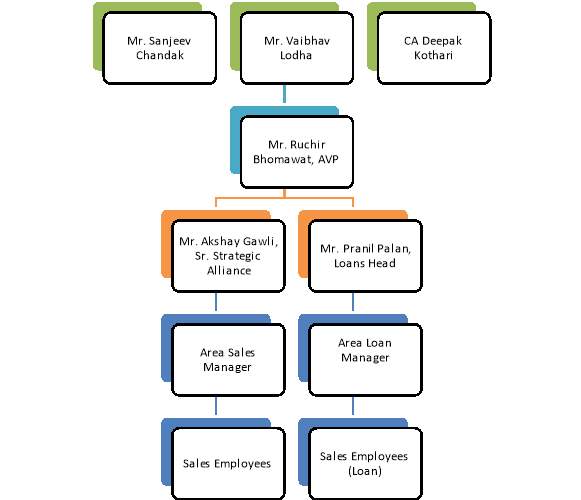
Hierarchy in the Organization
Vision and Mission of the Organisation
Vision: To enable offline transactions quickly by aggregating all payment modes including credit cards, debit cards and mobile wallets under one channel.
Mission: To facilitate swift and seamless financial transactions for Indian merchants over a digital medium, and to allow them convenient access to other financial products such as loans.
Size of the Organization
The Organisation consists of a workforce of 90 employees. Out of the 90, 60 work have field duty and the remaining 30 work in office. The are 8 employees each working in the operations and Marketing team and the support team each while 1 each for the HR and graphic design position. There are a total of 5 finance employees and 10 in the application development team. Also there are 4 data entry associates and 7 work in the loan team.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
- Provides a stage for cashless exchange which is fate of India
- It makes exchange less complex since the clients don’t need trivial trade out hand
- It offers advantage over wallets as cash is specifically moved into the record of the trade
- It gives the clients differed paying alternative
- Physical nearness of the client is not required since remote instalment is conceivable through connections
- Micro-merchants can acquire advances with no record as a consumer
Weakness:
- TDR rates are seen to be high by dealers
- Lack of promoting of the item by the organization
- No follow-up if there should arise an occurrence of advance
- Model of ftcash does not fit with organizations having high footfalls
- The plan of action does not fit with plans of action of a few ventures
- Though endeavours have been made to change over the Indian economy from money to cashless, numerous Indians are impervious to make their day by day exchanges cashless
- Many businesses would prefer not to announce white cash
- Many traders felt that the instalment procedure was excessively lumbering
- Most of shippers as of now have exchange instalment alternatives, for example, POS machines and wallets like Paytm and do not want to incorporate more choices
- Some organization as of now have tie up with banks
- Low versatile penetration. The achievement of JIO is yet to be tried and the market in India is as yet developing and has not yet achieved development arrange
- Data issues: Indians are not extremely sure about entering subtle elements, for example, Visa numbers and passwords as they depend more on the brand, as large brand names dependably guarantee information security. So these security issues are one of the greatest shortcomings an organization can confront in Fintech industry.
- Unavailability of wide money related structure
Opportunities:
- Our Prime clergyman of India has begun different plans and one of his was ‘Computerized India’ – its roundabout thought process was to push India into a cashless economy, the current demonetisation likewise demonstrated the same. Consequently, this could be viewed as an open door for fin-tech new companies to enter the market and accumulate greatest client base.
- Lots of financial specialist subsidizing
- Innovation in innovation
- Changing attitude of the general population
- Inculcation of biometrics in innovation
- Partnerships with banks or different players
Threats:
- Many players are going into the market with giving comparable administrations and this could prompt absence of development and fin-tech’s may achieve a decrease arrange soon
- Security/security break is viewed as one of greatest risk in cell phone industry
7S framework of ftcash
- STRATEGY: The company’s strategy is to enable cashless transactions and allow the merchants and customers to use mobile payment options, including wallets, cards and net banking under one platform. Small merchants have traditionally been outside the financial system with over 80 % using cash and hence limiting their ability to get loans from banks. Ftcash enables electronic payment acceptance using their existing bank account and a basic mobile phone. This is amongst the first few investments of IvyCap ventures trust fund-2 and forms part of our early-stage strategy.
- STRUCTURE: The structure of the company is a kind of HORIZONTAL FRAMEWORK. Since it is a start-up, there is no departmentalisation. Since the company is operating on a small scale and trying to increase the operations, there can be no separate departments product wise.
A total of 90 employees were working for ftcash out of which 60 were having field duties and the remaining 30 were working in the office. There were 8 officials working in the marketing and the operations side while 1 HR and graphic designer was also working. 8 members were there in the support team and 7 were working in the loan team.
- SYSTEM: At the functional level, technical measures to be set in place along with frequent feedback and reports given at the subordinate level to provide knowledge of results, along with rewards and incentives to tie in performance to alignment to objectives.
- SHARED VALUE: They have an informal work environment inside the organization. Also, they are extremely client friendly.
- STYLE: Style of working is extremely traditional. Client identification and product promotion is done by contacting and visiting the potential clients and demonstrating them the business model of the company.
- STAFF: They put efforts in training and development of their sales force and teaching them negotiation skills and tactics because it’s the most important element of their business model.
- SKILLS: Ftcash has achieved its present level of excellence through investing in its human resource, whose skill and knowledge constitute the basis of every initiative–be it technology or communication. Developing skills and capabilities of employees to improve man power utilization is the key thrust area of Human Resource Management (HRM) at Ftcash. Not only employees, but it gives utmost priority to its customers and therefore hand hold the customer from the point of application till the time of final disbursals.
Competitive Position in Industry (Porter’s Framework Analysis)
- Threat of new entrants
- Threat of substitutes
- Bargaining power of suppliers
- Bargaining power of clients
- Rivalry among existing competitors
Future plans
The company is planning to disburse INR 150 cr loans by March 2018. Founded in June 2015, ftcash plans to get profitable by December 2019 and increase its merchant base to 150,000 by this year end. Speaking on the announcement, Deepak Kothari, ftcash, said, “Till now, small merchants have been facing challenges in acquiring unsecured loans at low-interest rates. We are rolling this loan service out for all the 20,000 merchants on our platform after successfully completing the pilot. With the loan amount ranging from INR 25,000 to INR 5 lakhs, merchants can get higher loan amounts based on either repayment of smaller ticket loans or basis their increasing usage of the payments platform. The objective is to tap the under-banked and unbanked segments. ftcash has set a target to acquire 1 million merchants in the next two years.”
Project Work
Objective of my Project Work
To develop a market of O2O (offline to online) transactions in Travels and Canteen segments in Mumbai
Methodology
Ftcash has a rich sales team on-field and they target clients based on known-contacts, area-wise, segment-wise, and randomly. I was given the freedom to approach the potential clients through any these methods. I chose to approach clients segment-wise because:
- It is a focussed approach
- It increases the competitiveness of the firm from a holistic view
- It helps to create an effective segment marketing strategy for better promotion
- It encourages customer retention through life-cycle of a customer
- It increases profitability of the firm
Upon discussing with my mentor, he put me into the travels and canteen categories. My major job responsibility was divided into following parts:
- Product Pitching
- Marketing
- Merchant Sign-up and Training
- Key Account Management (KAM)
- Promotional Campaign at NMIMS Canteen
Product Pitching
The motive of a product sales pitch is to persuade the client to use our product and close the sale of the same. For delivering an effective sales pitch, I needed to have a thorough knowledge about the company’s product and its offerings. For this, I had to gain some preliminary knowledge about the industry, how a fin-tech company works, its financial product and how it can provide a value addition to the client. Moreover, I needed to know about the client to whom I am pitching to, their business model and the problem which the financial product can solve upon implementation. This helps in customizing the product pitch as per the client need. Also, I had to keep abreast with the various competitor’s strategies and advantages of ftcash as an online payment aggregator over its competitors. For this I had to research the business models of various competitors such as wallets like Paytm, POS machines and m-swipe to gain a basic understanding of their working and try to position ftcash as a superior product over its competitor’s.
I had approached the clients through cold calling and walk-ins. The main objective of cold-calling was to set-up a first time face-to-face meeting with the head of the accounts person or the head of the organisation. This was so as because I am proposed to sell a financial product which is better perceived by these people. My sale pitch had to be crisp as I had merely 15 seconds of interaction over phone. Moreover, it had to be engaging so that they become interested towards the product and increases the chance of meeting fix-up. I made sure that I had taken the contact details of the person to whom I spoke over phone. It helped during physical meetings. The number of walk-ins had been less as compared to the number of cold calls. The walk-in method was not successful as compared to cold-calling because the tours & travel category personnel did not entertain any sales person other than to prior meeting set-up.
Marketing
After setting up a meeting with a client, I had to meet as per his convenience and market the product. My interaction which each merchant was unique as I tried to fit the ftcash business model with the merchant’s business model. As my primary segment was tours & travels category, the payment system was one the bottlenecks in their business.
The issues in payment collection
- Customer not present at the address or prefers remote payments
- Customers not having adequate cash to make payment
- Unscrupulous delivery agents and counterfeit
- High operational costs
- Cash management and related issues
The incapability of the businesses to solve the problems
- Expensive POS hardware
- Tedious interface with Banks
- Cash related Fraud & Error
- No Remote Payments
How ftcash payment works
ftcash enables merchants in India with a feature phone or a smartphone to receive online payments securely, conveniently and cost-effectively. ftcash platform is built upon existing financial infrastructure of bank accounts of the merchants to create a real-time payment solution. It delivers a product ideally suited for SMEs, offline micro-merchants, remote businesses who all are currently underserved by traditional payment mechanisms.
The products for the Merchants
- ftcash merchant App
It is a mobile-based dashboard in which merchant can check the transactions on a real time basis. The application is available in Google Play store only. For other IOS and Windows users, they use their respective unique merchant link to open the dashboard in any browser. The merchant application has four parts: (Photo in Annexure – )
- Balance – Here, the merchant can see the credit of the amount paid by his customer. It will zero amount once the amount gets credit to the merchant’s bank account.
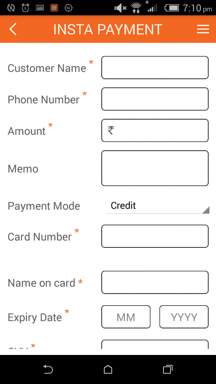
- INSTA payment – The merchant can use it for proximity payments from their customers.
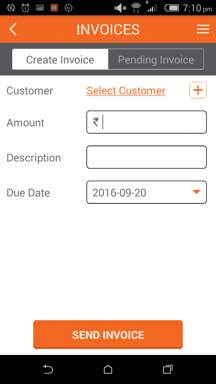
- Invoice – This is one of the unique features of the product. The merchant can create invoice which can be mailed and messaged to the customer including the due date of payment. Also, they can track the pending payments.
- Transaction History – Here, the merchants can track the overall transaction history.
Apart from mobile application, merchants can use the dashboard through their desktops by entering the login credentials in the following link: https://www.ftcash.com/app/mdashboard/mLogin
- QR code
The merchants are provided with QR code which upon scanning will open up their payment page. It is provided in the form of standees for proximity payments. It is also mailed so that they can attach it in their bill for remote payments. The customer can scan the code through any QR code scanner or use the following link: www.ft.cash. The link will open to a camera scan mode. The payee can pay to the client without downloading the ftcash mobile application. That is its USP.
- Merchant Unique Payment Link and Payment Gateway
As soon as the merchant gets signed up, an exclusive link of the merchant is created apart from the normal app for payments which the merchant can send to their customer and vendors through SMS, Whatsapp etc. and accept payments remotely. The Travel Agent Federation of India (TAFI) is one of the esteemed client of the company in the travel category. So, the unique payment of theirs is www.ftcash.com/tafi. See APPENDIX – for TAFI payment page. For payment gateway, the tech team at ftcash sends a system package which can be integrated in the merchant’s website by their counterpart.
Advantages for Travel Merchants
- No Cost: There is no installation fee or monthly rental.
- Swift Sign-up: The merchant is signed-up in less than 5 minutes. It is the fastest in India.
- Non-Exclusive option: The ftcash payment system can easily be integrated to the merchant’s existing system of fee collection, not replacing but providing better convenience for those desire the same.
- No bounced Cheques and faster collection cycles: All the payments made on ftcash are verified on real time basis; hence any problem with customer account is immediately highlighted.
- Real-time MIS: Dashboard shows real-time update on transaction details.
- Multiple Payment options: The platform offers multiple mode of payments that a merchant can accept payment from their customers. The payee can pay through credit card, debit card, net-banking, UPI and wallets. For international payments, the platform offers PayPal.
Advantages for Customers
- Ease of payment: Payment in a single click using 40+ banks, credit card, debit card, UPI, wallets.
- 24×7 Customer Support: Customer support is available to all on transactions carried out on ftcash
- Safe and Secure: PCI-DSS secure platform and RBI mandated safeguards ensures complete safety of consumer money


 Flow of Transaction
Flow of Transaction

Customer’s Account
Payment Methods
Payment Confirmation
(to Customer & Merchant)

 Flow of Money
Flow of Money




Merchant
Bank Account
Money gets transferred
to ftcash nodal account
in T+1 day
Money transferred to
Merchant Bank Account
in T+1 day
Customer
Commercials for the Travel Merchants
- Debit Card: 0.75% + S.T. (upto ₹2000 of transaction)
1% + S.T. (beyond ₹2000 of transaction)
- Credit Card: 1.8% + S.T. (upto ₹1,00,000 of transaction)
1% + S.T. (beyond ₹1,00,000 of transaction)
- Net-Banking (46 banks): ₹25 + S.T. (irrespective to volume of amount)
- Wallet: 1.8% + S.T.
- UPI: 1% + S.T.
- AMEX: 3% + S.T.
- PayPal: 3.9% + $0.3 USD (from 0 to $10,000 USD)
3.7% + $0.3 USD (from $10,000.01 to $100,000 USD)
3.4% + $0.3 USD (above $10,000 USD)
Currency conversion fee at the rate of 1.5%
Settlement Period: Money gets credited into their bank account in T+1 day except for payments through AMEX cards. For AMEX cards, it is T+3 day. Al these days excludes Sundays and bank holidays.
Merchant Sign-Up and Training
The interested merchant is signed up into the ftcash system through an agent application. The agent application is a mobile based application available for Android and IOS platform. It is available with everyone in the sales team. The sign up process is very fast as it takes merely 15 minutes.
The flow of ftcash Agent App
Page-1
- Agent Total number of monthly Signup Detail
- Create a New Merchant Option
Page-2(Visit Details)
- Merchant Name
- Shop Name
- Location
- Category (Eg. Travel, Education etc.)
- Size of shop
- Overall Business
- Digital payment Used
- Has merchant agreed to sign-up or not?
Page-3 (Merchant Details)
- Store Name (Gets Pre-filled)
- Address
- City
- Pin Code
- Merchant’s Mobile Number
- Alternate Mobile Number
- Merchant’s Email ID
- Create Password
- Store Phone Number
Page-4
- TDR Rates
- TDR Applicability
Page-5 (Bank Details)
- Account Name
- Bank Name
- Account Number
- Confirm Account Number
- IFSC Code
- Aadhar Card Number (Optional)
Page-6
- Unique URL Choosing Option
Page-7 (Soft-copy of documents to be Upload)
- Ftcash Merchant Receipt (See Appendix – for sample merchant receipt)
- One Bank Detail Photo (Cheque/Passbook)
- One Business Proof photo (Gusmata/Pan Card etc.)
- One ID card photo (Aadhar Card/ Driving license etc.)
- Shop’s Photo
After the document verification and soft-copy upload in the agent app, the merchant gets a one-time password (OTP) in their registered mobile. That OTP is put on the agent app and Voila! the agent gets signed up.
The merchant gets an automated welcome SMS and Email. To make sure the merchant’s account is activated, a payment of ₹1 is done to the merchant and check whether merchant receives the notification. Push-Pull stickers of ‘ftcash accepted here’ is pasted onto the doors on the permission of the merchant. See Appendix – for the sample sticker. Also, the customer care number (0983496939) is shared with the merchant for any issues. If the merchant is not transacting with our system after 1 week his signup, then follow up is done to hand hold him in using the system.
After all these activities, merchant is trained about how to use the product in regard to how to send the payment link and QR code in their bill and receive payments. They are also trained how to use the merchant app and send SMS invoice.
Key Account Management (KAM) of Travel Agents
Key account management (KAM) defines full relationship between your business and the customers you are selling to. It describes the individual approach of sales people to their customers in order to create long everlasting business relationship. It plays a strategic role in the growth of the supplier.
Ftcash is in B2B sales and we are dealing with many travel agents. So, it is good to record pertinent facts about decision makers within the account that they are dealing with. It is all about accessing this information in order to engage in an effective and systematic way and grow key accounts into profitable long-term relationships. For this, I had to meet up the clients and request them to transact more on our system. At the same time, ask what we as an organization could do to increase the transactions. The approach was to differentiate the key accounts from the standard accounts and develop a relationship of partner. One very key reason for doing so is that the better your client succeed, the more our product or service is going to succeed at that company.
Promotional Campaign at NMIMS Canteen
I along with 3 interns of IMNU was part of a promotional campaign at F3 canteen, Narshee Monjee Institute of Management Studies for 3 days from 5th June to 7th June, 2017. I was the point of contact there since I had signed it up.
The motive of the campaign was to make aware about the company among the students and the offer the company was running. The promotional offer: 25% off straight from the bill amount. Maximum discount was ₹25. It is limited to single user per day. There was no minimum bill amount. The USP of the offer was, firstly, there was no cashback and secondly, the offer was for infinite period of time. We had to make sure that the students download the ftcash app and use it to make payment.
On the first day, we didn’t have any success because there was a glitch with the freecharge wallet in our app. Some of the students got irritated because of this. Moreover, our promotional posters had many errors which was also pointed out by a faculty there. Our mentor decided not to proceed with the campaign further lest it can fireback and tarnish the brand name. Taking the reactions and feedback, we went to the office to re-design the marketing campaign. I had to sit with the graphic designer to re-design the promotional poster. We also discussed with the Assistant VP about the campaigning approach. Next day we went back with new posters and glitch free app and response was good. We went student to student stating the tie-up with the canteen and offer on their food bill. We also asked the students to do word-of-mouth about the offer. On the third day, the response of the students was much better. They were asking from upfront about the offer and were doing excessive word-of-mouth. It was an overwhelming experience for me. We were appreciated for the effort.
My Value addition at ftcash, Mumbai
- Number of Merchant Sign-ups – 7
- Travels – 5
- Canteens – 2
- List of Travel Merchants Acquired
- Stop-n-Shop
- Air Arena
- Dayal Tours and Travel
- Columbus Travels
- Thakurjis Destinations
- List of Canteens Acquired
- Taylor Hall Mess – NITIE
- F3 Canteen – NMIMS
- Number of Merchants in Pipeline – 10
- Lawson travel and tours
- Amigoo Travel Services
- RightChoice Tours n Travel LLP
- Leading Edge – Travel Management Pvt. Ltd.
- Apex Travels and Tours Pvt. Ltd.
- Mango Holidays
- Sky Wings
- Star Holidays
- Harvey India
- Trade Wings
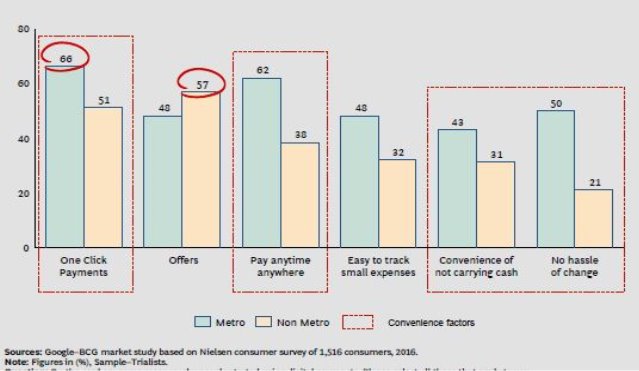 APPENDIX – : Reason for Using Digital Payments
APPENDIX – : Reason for Using Digital Payments
APPENDIX – : Key Barriers for Adoption
APPENDIX –

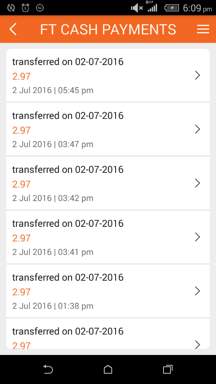
Balance helps you see amount to be transferred to your account.
INSTA payment facilitates customer payments via merchant app. Fill in the details with 3 clicks.
Download ftcash merchant app from play store. Login using email/Phone no and password.
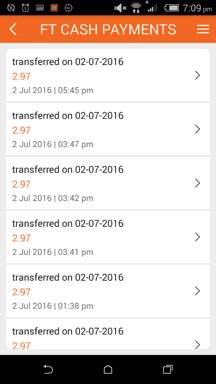
View all previous transactions on the transactions tab.
Add customer details and click send invoice to raise an invoice directly to customer
Mail or call us in case of any issues from the support tab.
APPENDIX –
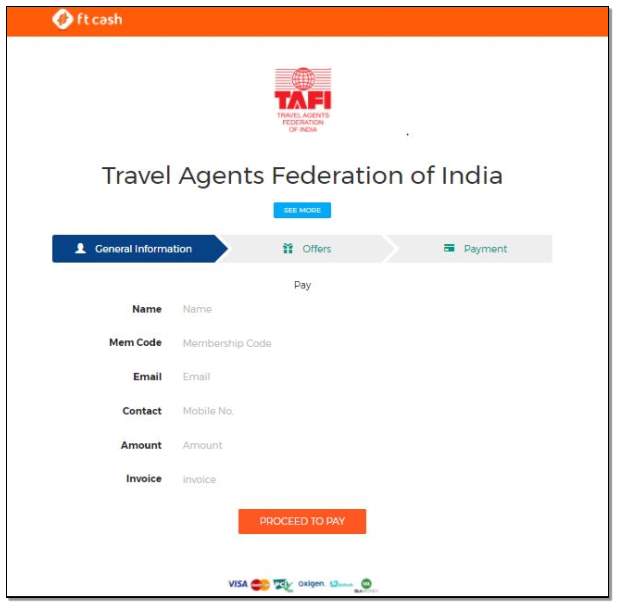
APPENDIX –
| Mobile Wallets (Paytm, Freecharge, etc.) | Swipe Machine (mSwipe, HDFC) | Payments Bank (Eg. Airtel Money) | ftcash | |
| Monet Transfer | Wallets | Bank Account | New Account with KYC | Bank Account |
| Acceptance and Interoperability | Wallet to Wallet | CC/DC/Wallets | CC/DC | CC/DC/PayPal/UPI/Net Banking |
| In-person vs Remote Payments | Both | In-person | In-person | Both |
| Transaction Limit (INR) | 20-100k (after KYC) | No Limit | up to 100k | No Limit |
| Scalability | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Focus | Customers | Merchants | Merchants | Merchants |
| Others | Closed Loop System | Expensive Hardware | Lending not Permitted | Open Architecture |
APPENDIX –
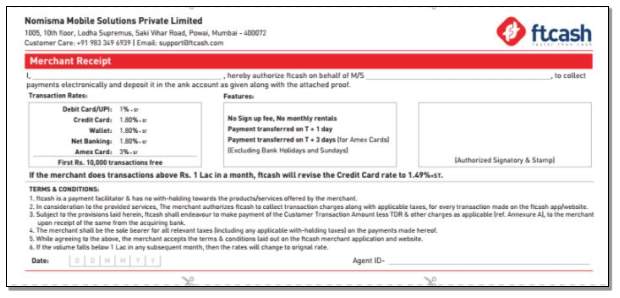
APPENDIX –

Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this assignment and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


