Microeconomics of Apple Inc.
| ✓ Paper Type: Free Assignment | ✓ Study Level: University / Undergraduate |
| ✓ Wordcount: 1982 words | ✓ Published: 12 Aug 2019 |
Part of: Microeconomics
Apple is one of the biggest technology companies out there, and the microeconomics of the company will be discussed in this report. Apple is widely known for a variety of products including the iPhone, iPad, and Macintosh software and computers. Apple was founded in April of 1976 in Cupertino, California. The company’s founders are Steve Jobs, Ronald Wayne, and Steve Wozniak. Apple’s “secret” for success is their skill in creating exactly what consumers want and how they want it. Through their differentiated business strategy, Apple has penetrated and dominated every market it’s entered. Over the past few years Apple has begun to slip in the smartphone market, slowly losing more and more market share and eventually giving up the lead to their biggest competitor, Samsung. The purpose of this paper is to analyse the smartphone market and the supply and demand conditions, price elasticity, cost of production and the different actions Apple can take to maximize the profit of the iPhone.
For more information about Apple and how they operate as a business, take a look at our Apple PESTEL, SWOT, and Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis.
History of the Company
Steve Wozniak, the company’s cofounder, initially built the Macintosh computers by hand. Wozniak wanted to sell his hand-built computers for a low cost, but Steve Jobs wanted a higher price. It further developed the Macintosh and later the apple computer over time. However, in 2007 apple brought out the first iPhone. (Ritchie 2016) It was definitely not the first of its kind in the smartphone market, but it had very advanced technology that Apple came out with. After the original iPhone was produced, apple began adapting the phone with better technology and further producing iPhone 3g and 3gs. (Ritchie 2016) With this production, price decreased. This is because when considering the elasticity of the iPhone and the market at the time the price of the phone decreased to make it more desirable. As Apple further developed the iPhone, the price and quality increased. iPhone is one of the top leaders, next to Samsung, in the phone community.
Supply and Demand Conditions
Apple has always been in high demand when it came to the iPhone. They consistently had issues with keeping up with supply and demand though. December 26, 2015, Apple posted its largest quarterly earnings. (The Data Team 2016) Their earnings were $18.4 billion which exceeded to what the company was anticipating and probably the largest quarterly earnings for any company ever. (The Data Team 2016) Additionally, in 2012 the iPhone 5 exceeded the company’s goals so much to where the people who preordered the phone were put a waiting list. However, these last couple of years is a different story. In fact, the company is expected to cut its production by 30% this year. As you can see in the graph below, iPhone sales skyrocketed in late 2012 to early 2013 and continued to grow. However, the company had a really hard time with forecasting it’s supply and demand. Apple took steps to improve its supply and demand problems for the iPhone 6 but 2 months after it launched more than 42% of its product was still unavailable. (Federico-O’Murchu, 2014)
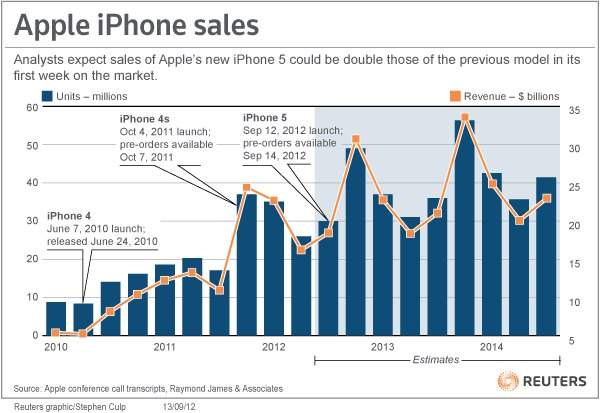
The graphs below represent the supply and demand problems that Apple has faced over the years. To have a better understanding of the supply and demand issues at Apple and what steps can be taken to improve the process, we have to understand how they got there. Because the iPhone is in high demand, Apple’s inability to meet consumer demand has not affected its revenue. We know this because, as stated above Apple hit an all-time high in deposit in December of 2015. So the question is, is apple’s inability to meet demands affecting the business at all? The answer is no. In fact, by limiting the availability of the product could indeed control the rate at which the product sales and could raise anticipation for it next iPhone generation. By supplying only, a set amount sales growth can be maintained continually.
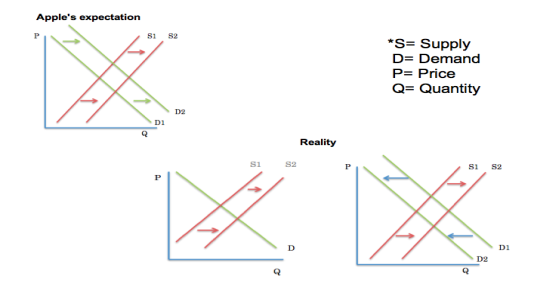
Price Elasticity of Demand
When analyzing the price elasticity of demand for the iPhone it is important to determine if the iPhone is an elastic or inelastic product. Considering that there are not very many substitutes to the iPhone, the demand tends to be inelastic. It is also important to determine if the iPhone is a luxury or a necessity. It would seem like smartphones are a luxury rather than a necessity, but as society becomes more technologically advanced smartphones are becoming more of a necessity rather than a luxury. After analyzing the smartphone industry the Apple iPhone is inelastic product and consumers will not be overly price sensitive because of their need for a smartphone and the oligopolistic smartphone market that offers limited substitutes. When assessing how the price elasticity of demand impacts Apple’s pricing decisions it seems that Apple stays focused on maximizing profit over the short-run. Since the iPhone is in oligopolistic competition, Apple makes a short-run output and price decisions. Considering the iPhone is an inelastic product Apple can raise the price of new products without seeing a drop in demand. Apple can also prepare and make pricing decisions when other firms are getting ready to release a new product to the market. Apple can predict the effect of an increase in the price of the firm’s new product on the quantity of iPhones demanded by holding other factors constant and determining the cross-price elasticity of demand.
Costs of Production
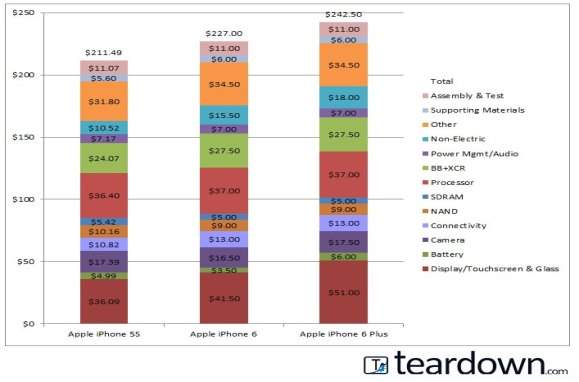
There are normally four main categories of costs for a phone. The first category is the bill of materials, also known as BOM. The Bill of Materials represents the cost of the components that go directly into the device. The second category is transportation and warehousing. This is simply the cost to transport and store the product before the sale in any store. The third is manufacturing costs which does include labor. Finally, the last category is the warranty expense which is paid back to customers for any returned product that can no longer be sold due to issues. Since the original iPhone release in 2009, the COGS have been rising since. For the iPhone 4, the COGS were $112, following $132 the next year for the iPhone 4s, and shot up to $167 for the iPhone 5 the next. The figure below shows the COGS for the iPhone 5s, iPhone 6, and the iPhone 6 Plus. Figure 4. Manufacturing costs for the iPhone 5s, iPhone 6 and iPhone 6 Plus. Retrieved from Business Insider: http://www.businessinsider.com/analysis-iphone-6-plus-costs-prices-and-profits-2014-9 While we can also analyze the manufacturing costs, it is very important to analyze the operating costs, including the administrative costs and R&D (research and development). Apple spent roughly around $1.18 Billion on the research and development, and that includes IOS and most of the software that comes with it.
Since Apple built its’ entire operating system ‘in-house’ and iPhones cost half of all sales being made, we can assume that Apple puts in half of their research and development into iPhones alone. Just based on that information, we can assume Apple made around $589 million to 31 million iPhones sold within three months. After calculations, per device being sold it comes out to roughly $18.85 per iPhone. (Sherman, 2013) Another cost Apple has to deal with are the “selling, general, and administrative”, which can include anything from paying electric bills of factories, offices, and stores to salaries. Shipping and storage costs for the iPhone alone come out to $2.65 Billion. When you cut that amount in half, you get roughly $1.32 billion for iPhones to account for, only leaving $42.33 to tack onto the cost of each iPhone (Sherman, 2013). Most increases to the COGS are caused by the variable cost. The fixed costs have stayed consistent over the years and Apple continues and will continue to focus on the R&D. The main factor to the increasing COGS and the variable costs are the changes Apple continues to make to the design of the iPhone. From the manufacturing aspect, the biggest variances in cost are in the larger touchscreens and the improvements to the battery. While the changes may add to the COGS Apple has made clever pricing decisions to maximize profit. Apple released the iPhone 6 and the iPhone 6 Plus, which is slightly bigger than the iPhone 6. Since the screen is larger on the iPhone 6s, it’ll add an extra $15.50 to the production cost. Apple still charges an additional $100 though. The larger screen on iPhone 6 Plus costs $9.50 more, bringing the total screen cost to $51, and the larger battery is $2.50 more, bringing that cost to $6 (Edwards, 2014).
Overall Market
The smartphone industry is an extremely competitive one. Most phone companies are always looking to get the “best” and the “latest” phones out there. Some of the phones that have been recently announced that are similar to the iPhone today are the LG K30, Google Pixel 2, Samsung Galaxy and so many more options that are actually cheaper compared to the iPhone. The biggest competitor for Apple with the iPhone is the Samsung Galaxy. It has been competing against the iPhone for years now! One reason Apple continues to be a technology giant is the high barriers of entry for other businesses to even begin to compete. The greatest barrier of entry is the versatility and compatibility of their products. For example, you can receive text messages and phone calls from your iPhone on your MacBook or iPad. Every Apple user has an iTunes account which can be synced to all of your Apple products.
Another barrier is the overall success and money, Apple has billions of dollars to spend, it can use predatory pricing to keep other competitors from succeeding in the marketplace. The most significant barrier of entry for Apple is their operating system. Apple is the only company that has their own exclusive operating system, companies like Samsung run on the Google operating system, which is the Android operating system. The smartphone market is oligopoly. The companies that dominated oligopoly and monopolistic competition are usually maintain the position in the market because it’s too costly or difficult to any potential rivals to enter the company which mean there are entry barriers. Apple Inc. is oligopoly in the smartphone’s operating systems’ firm. There are 3 mainly operating systems which is very competitive in the market are iOS, owned by Apple Inc., Android, which is owned by Google, Windows phone, owned by Microsoft.
Recommendation
The one thing I would personally suggest to Apple is a couple of things. The first one would be for them to not change their products so much! It seems like almost every 6 months to one year they are coming out with a new phone, and yes, it’s great and all, but the people who spend $500+ on the latest phone now regret buying that one because it is not the newest phone out there. Apple needs to focus on the cost-benefit principle and opportunity costs. An important question to keep in mind is; what is the opportunity cost of constantly investing large amounts of resources in the development of the iPhone from year to year? I think Apple should invest more resources in a new smartphone product in addition to the iPhone, and to maybe make it more affordable for more people. When considering the cost-benefit principle Apple would earn more money by investing more money in the development in a new smartphone product, the benefit would outweigh the cost.
References
- Edwards, J. (2014, September 24). Apple’s Manufacturing Costs Reveal The Profits It Will Make On iPhone 6. Retrieved from Business Insider: http://www.businessinsider.com/analysis-iphone-6-plus-costs-prices-and-profits-2014-9
- Federico-O’Murchu, L. (2014, December 2014). Why can’t Apple meet demand for the iPhone 6? Retrieved from CNBC: http://www.cnbc.com/2014/12/05/why-cant-apple-meet-demand-for-the-iphone-6.html
- Sherman, J. (2013, July 26). SPENDY BUT INDISPENSABLE: BREAKING DOWN THE FULL $650 COST OF THE IPHONE 5. Retrieved from Digital Trends: http://www.digitaltrends.com/mobile/iphone-cost-what-apple-is-paying/
- Ritchie, R. (2014, August 22). History of iPhone: Apple reinvents the phone. Retrieved from imore: http://www.imore.com/history-iphone-original
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
CollectionsContent relating to: "Microeconomics"
Microeconomics is the field of study that focuses on the decision making of individuals and businesses, including how resources are allocated and the impact that decisions can make.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this assignment and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


