Marketing Strategy for Harrods to Launch its first store in China
| ✓ Paper Type: Free Assignment | ✓ Study Level: University / Undergraduate |
| ✓ Wordcount: 2816 words | ✓ Published: 12 Aug 2019 |
Executive Summary
The following essay incorporates the marketing strategy for the luxury department store Harrods to launch its first store in China and launch a new product. The purpose of this report is to support the establishment of Harrod’s marketing objectives and amalgamate the use of social media platform and promotional activities in order to enhance their brand reputation and achieve these objectives. The plan includes company and competitor analysis using competitor analysis framework and SWOT analysis. Further, using concepts such as STP, Boston Matrix and Customer Relationship Management this report will illustrate how Harrods can achieve the proposed marketing objectives with great success.
Company
Harrods is one of the largest and most iconic department stores in the world, established in 1849 by Charles Henry Harrod (BBC News, 2010). With more than a million square feet of retail space, Harrods sells luxury and everyday products across seven floors and 330 departments. The store itself was bought by Qatar Holdings, part of the Qatar Investment Authority for a reported fee of £1.5 billion in May 2010 (Financial Times, 2018).
Competitor Analysis
Competitive analysis is a field of strategic research that specialises in the collection and review of information about rival firms (Leo, 1982). Harrods main competitors includes the like of Selfridges and John Lewis. Using the competitor analysis framework Harrods can identify key objectives and strategy of its main competitors and use it to gain competitive advantage. The competitor analysis framework is based on four key aspects of a competitor: competitor objectives, assumptions, strategy and capabilities (Porter, 1997). Firstly, knowledge of competitor objectives provides a better prediction of the competitors reaction to different competitive moves (Leo, 1982). In 2014, Selfridges invested over £300 million to revamp its London store in order to provide better customer shopping experience which Harrods is well known for. This allowed Selfridges to increase their total revenues to £1.4 billion in 2016 (Carnish, 2016).
Secondly, competitor assumptions can help Harrods to define the next move that the competitors will consider. For example, John Lewis has recently reported plunge in their profits due to major consumer shift to online shopping (Kollewe, 2018). This means that Harrods can assume that John Lewis’s next move will be investing more in e-commerce and social media presence. By anticipating competitors assumptions Harrods can gain key advantage by doing what their competitors failed to do so (Kotler and Armstrong, 2013). Thirdly, knowledge of competitor’s strategy is vital for Harrods. However, there can be a key difference in what the competitor says and what it does. To identify what a competitor is saying about its strategy can be revealed in their annual shareholder reports (Porter, 1997). On the other hand, what the competitor actually is doing can be identified through their tangible actions such as capital investments and strategic partnerships (Porter, 1997). For example, Selfridges have invested on online shopping platform to make shopping more convenient for their customers.
The final key component of the competitive analysis framework examines the competitor’s resources and capabilities. In any competitive situations resources and capabilities determines a firm’s ability to respond effectively (Leo, 1982). This can be analysed by conducting financial analysis or SWOT analysis. In terms of Harrods competitors, Selfridges can be considered as Harrods main rival as both Harrods and Selfridges market share has increased by 40% over the last four years (Retail Data, 2017). Further, other firms such as House of Fraser recently went through severe financial loss and had to close many of their stores showing that House of Fraser is less capable to compete with the likes of Harrods and Selfridges (Financial Times, 2017).
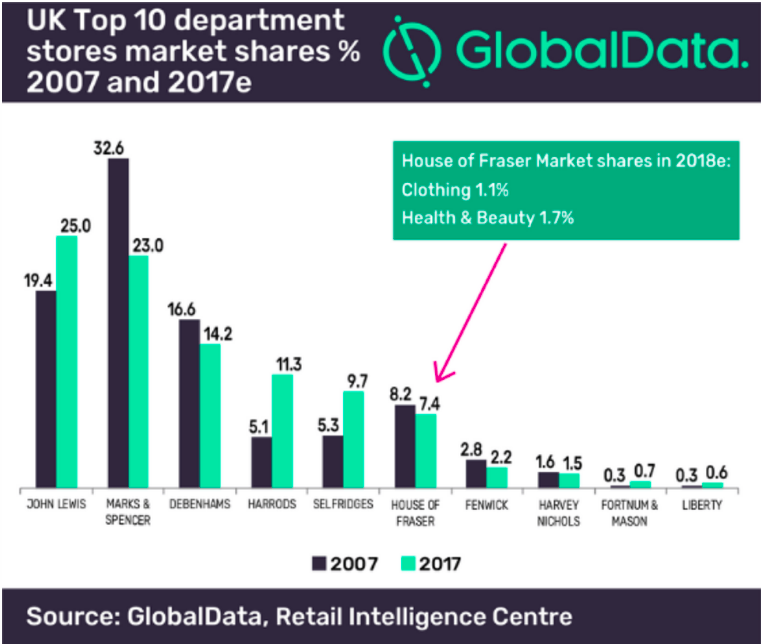
Figure 1 shows increase in market share of Harrods from 5.3% in 2007 to 11.3% in 2017. House of Fraser market share has fell from 8.2% to 7.4%.
SWOT Analysis of Harrods
Strengths
Harrods attracts consumers from all over the world and the Chinese are Harrods main consumer, spending over £200 million on high end fashion and accessories in 2016 (The Economist, 2014). This accounted for over 10% of Harrods £2 billion annual revenue in 2016 (Hancock, 2017). Further, being one store rather than multiple chains allows Harrods to generate higher exclusivity meaning excellent brand reputation and therefore increase in awareness amongst consumers. In addition, Harrods provide rewards scheme for their customers which includes of discounts and promotions allowing Harrods not only to keep their existing customers but also attracting new customers. This is beneficial for Harrods as keeping customers happy can lead to greater sales on the short run and healthy profit on the long run.
Weaknesses
Harrods is well known for selling range of luxury brands such as Gucci and Louis Vuitton, but Harrods does not have their own specific luxury products or services. This means that majority of the revenues made by Harrods could go back to the individual brands such as Gucci itself. Another major issue is that not all customers that visit Harrods necessarily spend money to buy the products as they are expensive. This shows that Harrods main consumers are wealthy individuals and less of consumers with lower income (The Economist, 2014).
Opportunities
Harrods operates as a single store which provides higher exclusivity but there are opportunities for Harrods to expand and open more stores overseas. For example, expansion into emerging economies such as China can help Harrods to increase customer base and potentially increase sales from rising middle class individuals in China who have greater disposable income (The Economist, 2014). Other opportunities for Harrods are, to increase social media presence and invest in sustainability in order to improve brand image.
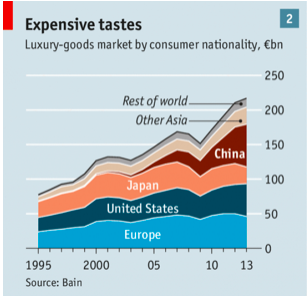
Figure 2 shows, Chinese nationals spent over 150 billion in 2013 illustrating their taste for expensive items.
Threats
The department stores industry is highly saturated however, the main threat to Harrods is increase in e-commerce and online sellers that have low operating costs but have the ability to reach customers world-wide giving them a competitive advantage over Harrods. Higher maintenance costs and costs of training and paying wages can lead to greater costs for Harrods as oppose to online sellers who can avoid these costs. Further other threats include of economic factors such as Brexit uncertainty and higher inflation which can potentially affect the future of Harrods.
Marketing Strategy and Strategy Formulation – STP
As mentioned above on the opportunities section of the SWOT analysis Harrods have plenty to do in order to maintain competitive advantage over their rivals.
Marketing Objectives
- To open up new stores in China, Harrods main consumer are the Chinese who spent over £200 million on luxury goods and accessories in 2016 (Tom Hancock, 2017).
- Another main objective for Harrods is to launch their own luxury product rather than just selling items owned by other brands. Launching their own products can help Harrods to create new ways of making revenues and enhance the brand itself. In addition, use social media extensively to create awareness of the launch of their new product in order to boost sales and increase the brands online presence.
Strategy Development
Segmenting
Harrods target market segment is a combination of socio demographic and geographic segmentations. Socio demographic varies differently in different geographic locations (Kotler and Armstrong, 2013). The typical consumers for Harrods are high class individuals who have sufficient disposable income and are on the top of the social hierarchy. However, in China due to the recent surge in growth of middle-class society, it provides Harrods the perfect opportunity to quickly tap into the market as the Chinese middle-class consumers seek western made luxury goods. In addition, buyers from China will be up to date with the latest technology and means of social media such as Instagram and WeChat to follow the latest fashion trends and interact with the brand at the same time.
In terms of the UK stores, the main store is located in central London where wealthy individuals are primarily the main customers of Harrods. In contrast to China and the growth of middles class, the UK economy is relatively different as UK has not seen an increase in rise of middle class, consumers within the UK do not have enough disposable income to spend on luxury items (The Economist, 2014). This illustrates the difference in socio demographic and consumer lifestyle in different geographic locations. Further, there are other alternative approaches to segment the market, for instance Harrods can target their very best consumers for sales and growth to become ‘super consumers’ (The Economist, 2014). This could be done if Harrods can successfully penetrate and establish their brand in the Chinese market.
Positioning
‘Effective positioning involves an understanding of homogeneous products sold by competitors and the benefits that are obtained by your target market’ (Kotler and Armstrong, 2013). Harrods is a high-end department store that prides itself on selling luxurious goods and providing customers a unique shopping experience. The majority of the products sold in Harrods are similar to other department stores such as Selfridges, however it communicates itself as providing better customer shopping experience and being highly exclusive (shown in figure 1) because of its single store. Higher exclusivity and strong customer loyalty are a key differential advantage for Harrods as they are set to enter the Chinese market and launch their own product (Leo, 1982). 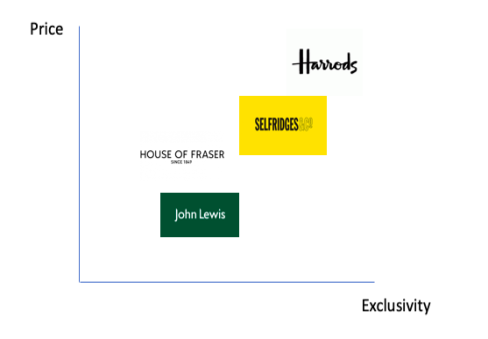
Figure 3 shows, perceptual map of department stores
Branding
‘Brands are valuable and enduring assets as long as they are kept in good shape and continue to offer consumers the values they require’ (Murphy, 1988). One of the aims of launching Harrods first store in China is to allow consumers to experience the brand meaning internal branding should be carefully planned and executed. The design of the stores will reflect on Harrods core values with a theme of luxury, stylish and sheer size in nature. Using the store aesthetics and layout as a brand application is potent due to its potential power in differentiating Harrods from competitors. Providing element of exclusivity leads to unique shopping experience for customers which Harrods thrives for. Further employees’ performance within the organisation is critical in terms of executing internal branding objectives, meaning that employee training and motivation is vital in order to represent everything the brand stands for (Oktay, 2017).
In addition, focusing on developing brand externally will be implemented through using social media platform and Harrods website. Social media platform helps company to enhance its brand image and credibility by meeting the audience’s needs through dialogic or interactive exchanges (Kim and Ko, 2010). Utilizing use of social media and other external communications can generate excitement and awareness before pre-launch of Harrods new products as well as new stores in China. This will help Harrods to reach out new customers and generate sales, whilst strengthening brand loyalty with existing customers.
Tactics
Product
Using Boston Matrix framework, we can analyse portfolio of products sold by Harrods and identify which product has potential to increase market share and help Harrods to achieve market growth. Each product is categorised into four categories: Stars, Cash cows, Question marks and Dogs (Consulting Group, 2016). Stars are high growth products with lot of potential in the market and high market value. Example being luxury fashion products sold in Harrods. However, star products require great levels of investment to sustain growth which can be costly for firms. Cash cows are products with lower levels of market growth but have higher market share. Example include of necessities products such as food that are sold in Harrods. Cash cows requires low level of investment but generates strong cash flows. Question marks are products that have relatively low market share but operate in high growth markets. In order for them to be successful it will require substantial level of investment and management expertise.
Finally, Dogs are products that operate in low growth market and have low levels of market share. These products are not worth investing in and are usually sold or closed. In order to avoid products that are categorised as ‘DOG’, Harrods needs to conduct a market research and identify the gap in the market and come up with products that will fulfil customer needs and demands.

Figure 4 shows Boston Matrix model
Price
All products sold by Harrods will be the same price both online and in stores. Prices for products sold in Harrods are generally higher compared to other stores such as House of Fraser and John Lewis. Although products are expensive, shopping in Harrods is exclusive and the customer experience is greater compared to shopping elsewhere. Higher exclusivity and providing better customer experience could be used as a source competitive advantage for Harrods (Leo, 1982). Further, for the new products that are set to be launched by Harrods, price skimming strategy can be implemented. Using this strategy will help Harrods to charge higher prices to its customers as Harrods has a strong brand reputation and existing customers are loyal to the brand. After, the price can be lowered in order to avoid competition from new competitors. Further, this pricing strategy can help Harrods to cover up costs that are involved in R&D of the new product (Prasad, 1997).
Promotion
Within the past decades, many firms have adopted customer focus notion through a formal programme of Customer Relationship Management – CRM (Jones and Ranchhod, 2007). One of the CRM tactic that many firms have considered is to establish customer loyalty program. These programmes aim to increase sales revenue and build a closer bond between the brand and its customers (Kim and Ko, 2010). Harrods can use these tactics to boost sales, profits and maintain strong brand presence amongst customers. Therefore, on the day of the product launch and the openings of new stores in, the first 150 customers that visit the stores and shop online will receive 30% discount codes and free Harrods merchandise. Furthermore, every customer that shops in Harrods on the opening first week will receive a loyalty card with more than 50 points which can be spent later online or in store.
Budget
The total estimated cost of opening a store in China, R&D of new products and other promotional activities are approximately at £957.35 million. A breakdown of the budget is shown in figure 3 below.
| Budget | Cost (£) |
| Store design | 3 million |
| Promotional packages | 1 million |
| Advertising | 1.3 million |
| R&D and new product line | 250 million |
| Construction of the store | 700 million |
| Operating costs | 1.2 million |
| Other overheads | 850,000 |
| Total | 957,350,000 million |
Evaluation and Control
In order to monitor the effectiveness of the promotional strategies and the launch of new product and stores, various monitoring strategies will be implemented before and after the launch of the product and the store. Firstly, social media impressions, key trends and statistics will be analysed using analytical systems to get clear information on what promotional campaigns have been the most effective. Further, sales made in stores and online will be recorded and examined to assess and inform future promotional campaigns. Lastly Harrods will perform marketing audits to identify any potential problems and rectify it in order to meet the company’s marketing objective.
References
- BBC News. (2010). History of Harrods department store. [online] Available at: https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/10103783 [Accessed 13 Oct. 2018].
- Carnish, C. (2016). Selfridges profits dip despite rise in sales | Financial Times. [online] Ft.com. Available at: https://www.ft.com/content/306878c2-9c4d-11e6-a6e4-8b8e77dd083a [Accessed 13 Nov. 2018].
- Consulting Group, B. (2016). Modification of the Boston Consulting Group matrix in the strategic management of an enterprise. Technology audit and production reserves, 1(3(27), p.96.
- England, A. (2018). Qatar spends £3bn as vote of confidence in post-Brexit Britain | Financial Times. [online] Ft.com. Available at: https://www.ft.com/content/9b5230fc-94a2-11e8-b747-fb1e803ee64e [Accessed 5 Oct. 2018].
- Hancock, T. (2017). Chinese nationals overtake Brits to become Harrods’ biggest spenders | Financial Times. [online] Ft.com. Available at: https://www.ft.com/content/9ea19ee2-d101-11e7-b781-794ce08b24dc [Accessed 11 Oct. 2018].
- Hancock, T. (2017). Chinese nationals overtake Brits to become Harrods’ biggest spenders | Financial Times. [online] Ft.com. Available at: https://www.ft.com/content/9ea19ee2-d101-11e7-b781-794ce08b24dc [Accessed 11 Oct. 2018].
- Jones, S. and Ranchhod, A. (2007). Marketing strategies through customer attention: beyond technology-enabled Customer Relationship Management. International Journal of Electronic Customer Relationship Management, 1(3), p.279.
- Kim, A. and Ko, E. (2010). Impacts of Luxury Fashion Brand’s Social Media Marketing on Customer Relationship and Purchase Intention. Journal of Global Fashion Marketing, 1(3), pp.164-171.
- Kollewe, J. (2018). Five reasons why John Lewis profits have dived. [online] the Guardian. Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/business/2018/sep/13/five-reasons-why-john-lewis-profits-have-dived [Accessed 9 Nov. 2018].
- Kotler, P. and Armstrong, G. (2013). Principles of marketing. 6th ed. Pearson.
- Leo, J. (1982). Competitive strategy: Techniques for analysing industries and competitors. Industrial Marketing Management, 11(4), pp.318-319.
- Murphy, J. (1988). BRANDING. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 6(4), pp.4-8.
- Oktay, F. (2017). An Examination on the Impact of Internal and External Environment Strategies Oncorporate Branding. IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 19(04), pp.42-54.
- Porter, M. (1997). COMPETITIVE STRATEGY. Measuring Business Excellence, 1(2), pp.12-17.
- Prasad, B. (1997). Analysis of pricing strategies for new product introduction. Pricing Strategy and Practice, 5(4), pp.132-141.
- Retail, G., Retail, G. and Retail, G. (2017). Harrods and Selfridges are winning department store market share. [online] Verdict. Available at: https://www.verdict.co.uk/harrods-department-store-market-share/ [Accessed 11 Oct. 2018].
- The Economist. (2014). Doing it their way. [online] Available at: https://www.economist.com/briefing/2014/01/23/doing-it-their-way [Accessed 20 Oct. 2018].
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this assignment and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


