Analysis of Different Taxation Systems
| ✓ Paper Type: Free Assignment | ✓ Study Level: University / Undergraduate |
| ✓ Wordcount: 6605 words | ✓ Published: 05 Oct 2021 |
Part of: Tax
Table of Contents
M1. Critically analyze and compare taxation systems in different countries.
P2. Explore and explain the implications of taxation liabilities for unincorporated organizations.
P3. Explore and explain taxation liabilities for both private and public companies.
P4. Evaluate the impact of key legal and ethical constraints on different organizations.
Introduction
Tax is economic charge which is levied on a taxpayer by the state or a country’s legislation for fulfilling the funds necessary for the various public expenditures. The structure of Taxation of a country is the set of rules and regulations made by that country to collect public taxes. The main purpose of tax collection is to increase government revenue for the development and welfare of the country. Secondary objectives of collecting tax is for the improvement the economic condition of the common people, to encourage them to produce basic needs and to discourage production of harmful issues and to maintain economic equality in order to discourage import trade and finally to protect the industries of the countries
In this assignment we are going to discuss about the different taxation systems, taxation liabilities of different types of organization, ethical issues regarding the taxation, the calculation of taxation for the incorporated organization and that of the unincorporated organization, and other related things about the taxation
P1. Analyze taxation systems and consider taxation legislation that will have given implications on national taxation using the information given to you by your line manager.
After the financial crisis, in numerous countries the government still has a strong necessity for cash. Whether it is the funding of stimulus programs for the economy, or generally prepared for the interval behind the fallen economy, indirectly proves the first choice for revenue collection for many years (Helmuth Cremer, 2001). And they will continue to be with this trend that can be explained with greater supporters of indirect tax instead of the direct taxes (such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF), Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) and the European Commission. Many international studies have found that there has minimal impact on the increase in Value Added Tax (VAT), when there is a negative impact on the growth of corporate income tax (Acosta et al, 2012). Indirect taxes, which are produced by the consumer according to their definitions and do not depend on profit, are less affected by this change. So it is clear that there are two tax provisions:
i) Direct tax: Direct tax is applied to the public’s income, or money and organization’s profit. Household income comes in the form of employment income and the interest on the savings and the dividends from the rights of the shares. Some returns are taxed directly by regulators, some people are charged on annual tax basis, which is usually mandatory for admission. Theoretically, such taxes are essential, because households and organizations are forced to declare their full-income to the government and accordingly they have to pay accordingly. Some of the types of Direct Taxes:
(ii) Indirect taxes: Indirect taxes are those whose burden is transferred to others so that they can pay this tax to the government, cannot bear the full burden, but pass it to others entirely or partially. Indirect taxes are imposed on production and sale, and small or large portion of indirect taxes are sent to customers (Arnold et al, 2011).
Some of the examples of indirect taxed:

Commentators do not always use the terms ‘direct taxation’ and ‘indirect tax’. However, there is a widespread agreement that UK has ‘direct tax’ like income tax or corporation tax, which is directly applied to taxpayers through some evaluation methods.
On the contrary, the UK’s Value Added Tax (VAT) as ‘indirect taxes’, taxpayers who indirectly give government; That is, the person who carries (the customer) to the retailer, then sends it to the government (Keen et al, 2010).
Depending on the amount of tax dependent on the government, therefore, it provides a great measure of security against the unexpected revenues of the tax regime. However, this ‘vision’ reduces itself from the expectation of profit, which can be seen to increase the revenue without increasing the political expenditure of the rate increase (Keen et al, 2010).
In the indirect tax category, governments can limit instability by imposing indirect taxes on goods or products, which are comparatively unethical claims; therefore, for example, tax on the food could generate an estimated revenue refund than tax on luxury products.
M1. Critically analyze and compare taxation systems in different countries.
Personal impact on any taxpayer is obvious: the level of tax in the country of the residence determines how much you earn, how much you take home and how much you want to pay, how you can afford it affect the neighborhood. You can live in the wonderful things you can buy and possibilities of getting the property
A few mostly prosperous and the wealthy people can only go to a new country because it offers fewer tax rates. But the taxation level may be quite different. This is the reason that we compare comparatively lower tax rates to the world’s most prevalent destinations
Income Tax in different countries
This tax is based on the personal income. This is the tax on earned money through self-employment, pension or other investments. We are going to discuss about two country’s taxation system:
The following table provides a brief description of the income tax rate in furthermost prevalent destination:
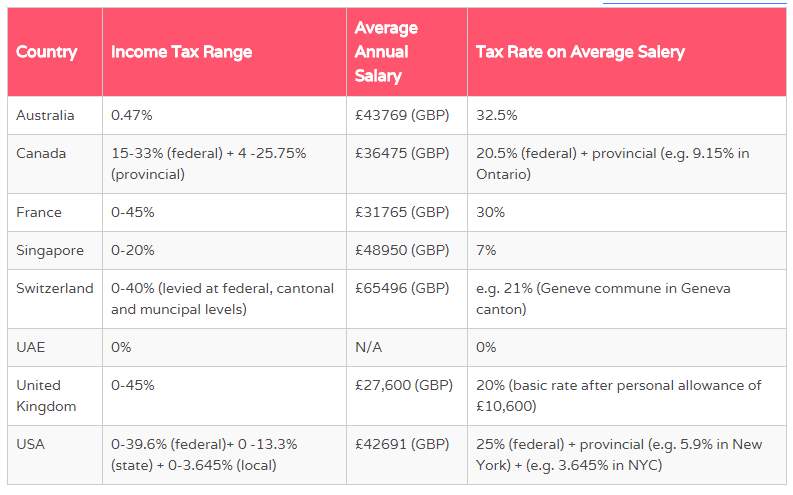
The table does not show the payroll deductions such as National Insurance (UK) or Medicare’s contributions (Australia)
Tax in Canada
Taxes in Canada are taken at federal and provincial levels.
Income tax: The federal government and the provincial government both impose the income tax in the full taxable income of the person. At the federal level, CAD 11,038 is a personal allowance; after which the tax rates ranges from 15% to 29%. The provincial tax rates are between 4% and 25.75%, where each province has its individual scale. Half of the capital gains are calculated as income – half exempted (OECD, 2006).
Sales tax
These are collected by the federal government (5% of goods and services tax) and provinces (provincial sales tax, between 2% to 12%). Two taxes for simplicity are often combined in single-ranked Harmonized Sales Tax (HST).
Property tax
When these two forms come, both municipal governments take it: a property tax which is given to property owners and is based on property value; by making a property transfer which is paid by the property purchased by the people and which usually takes 0.5% and the purchase price takes 2%.
Taxes in France
France has its precise and special tax system. That as follows:
Rate of Income tax
Regardless of the patriotism of France, a limit has been imposed on income related to income acknowledged in 2012, 2013 and 2014. It is 3% extra for a person, where the amount of income is $ 250,000 and in each family for € 500,000 in each family) and for every person € 4,000 for € 500,000; If the amount of 3% income for the family is more than € 1,000,000 in each part, 4% in spite of family status.
Accidental taxable income is to avoid the high rate of household income, but there is a high income, but many members of the family are divided into several parts of the family.
The total income is divided by division. The rate of income tax scale is applicable to the following figure and due to income tax, it has increased the number of shares.
D1. Provide supported and justified recommendations for developing effective tax systems and legislation that meet key principles in a global context.
Single tax structure cannot meet the needs of each country. The best system for any country should consider its economic structure, the ability to manage taxes, the requirements of its universal service and many other things (Auten et al, 2002). Yet, one way to look at what the tax policy can be considered is the tax available all over the world. In recent years tax levels and structures, and methods of taxation have changed, their review has been made in recent years on the basis of data collected from 168 countries, which represent each region of the world.
There is a need to reduce the unnecessary costs of taxes for a good tax policy. To reduce costs, the experience offers three general rules: First, the tax base should be as comprehensive as possible. For example, a wide-based spending tax will still discourage the effort to work, but if the product or service is all or most tax-deductible, this tax product will reduce the cost of the cost (Blomquist et al, 2009). Certain factors like gasoline, tobacco products and alcohol may be taxed at relatively high rates due to regulatory factors or are relatively responsible for the demand of these products. Tax base for income tax should be as extensive as possible, treating all income, whether it is any difference in the source, is equally possible.
Secondly, tax rates should be set as low as possible, requiring revenues to fund government operations. This is the reason that tax efficiency is generated by their influence on relative prices, and this effect is related to the direct tax rate. The distortion of the tax generally increases in accordance with the tax rate proportionately, resulting in the tax rate doubling, increasing its skill cost by four times (Gray et al, 2001). From a point of viewpoint, it is better to increase the revenue by dividing the segments into segments and applying different rates in each segment, using a single rate on broader basis. In practice, degree training should be equally equal to Equity Logic for post-graduate program.
Third, with a strong perspective, it is particularly important to pay attention to production taxes. Taxation on production affects business spaces, changes in production methods, changes in forms organized by business and even more. Typically taxes are needed for most of the development and transnational countries. Firstly, making countries with limited administrative skills make it easier and less expensive to collect excise and sales tax. Secondly, taxes represent the cost of providing services to the public (Khan, 2001), businesses should spend on tax for those services. Finally, the countries must make corporate income to avoid tax in the corporation and to avoid collecting taxes from the foreign-owned company, avoiding taxation by the shareholder level tax.
Task 2: Determine taxation liabilities for unincorporated organizations and individuals. (LO2, P2, M2, D2)
P2. Explore and explain the implications of taxation liabilities for unincorporated organizations.
Before going deep into this matter, tell us what is the incomplete organization. An ‘incomplete organization’ organization (for example, a voluntary group or a sports club) established through a contract between a groups of people who come together for any reason other than profit. If the company starts business and earns profit, then you have to pay corporation tax and submit company tax returns as a limited company. This framework is not ideal for membership, short-term goals, low income and small groups of employee recruitment or property acquisition (Feldstein, 1995). Most voluntary organizations start with an unsupported organization and can be in this way, especially if they are small
Similarly, we do not have to register an incomplete association which will be registered in a company or charity organization, and there is no cost for it.
The main responsibility of the unorganized association is to subscribe and the organization can have a fund / entrepreneur, but it is very important, but these guidelines highlight the legal obligation of corporation tax.
On choosing legal forms, there are many options for unsupported organizations. Some of them are briefly discussed:
The most common form of an unsupported organization in the social sector is an unsupported organization. There is no law for the control of this organization or specially managed parliament, but if there is a large number of contractual relations among members of an institution; the governing document of the organization (which is often called ‘the Constitution’) provides the terms of the agreement. If a member or member breaks the contract (for example, if the governing body works in a way that is in conflict with the governing document) members can apply in court so that they can remain in their contract. The terms of this agreement should be written to avoid debate about its contents (Blow et al, 2002).
Parliament (for corporate bodies); If there is a ‘complete power’ to control the documents, then it has not been mentioned, so if there is no absolute force then you have to write it in to govern the documents if you want to include it.
If the company starts business and earns profit, then you have to pay corporation tax and submit company tax returns as a limited company.
An example of an unsupported organization is a registered charity organization.
A registered charity organization is an organization which is motivated to make donations and public benefits. Chartered objectives have been set for public benefit in the Charity Act 2006. The organization established for donation in England and Wales will have to register with charity commission if its income is more than £ 5000 annually (Bond, 2006).
Personal tax
For the UK government, personal income tax is the biggest source of revenue. The second largest source is the national insurance contribution, by adding the third value (VAT) and the fourth largest corporation tax. Income tax was first introduced during the Napoleonic war and it was permanently restored in 1842 (Goodman et al, 2006).
UK Income Tax-main features
Personal income tax laws are governed by the Income Tax Act 2007 and other functions. The rate of income of a person depends on how much income is earned on their personal income in the tax year. Current tax year runs from April 6, 2016 to April 5, 2017. Most people’s personal allowance is £ 11,000 per year. Tax-free allowance for all these UK residents is £ 2 per personal allowance, which earns £ 100,000 in earnings. This means that the earned income is £ 120,000 or above, then the personal income is zero (HR treasury, 2002).
For foreign entrepreneurs like ‘UBER’, it is important to remember that only self-employed businessmen, business partners and company managers’ partners have to self-assess and register for tax returns. Once registered, usually a letter is received from HM Revenue and Customs in April or May, which is to send tax return on 31st January.
Income tax is earned at the rate of earned rate, high rate of income tax rate of the application. If the governing document does not say that the ruling party will be the employer of any employee, who are actually ensuring employee’s employment, they are outstanding, national insurance and private (Jones, 2008)
Some personal taxes are as follows:

M2. Apply recognized models and formulae to interpret data appropriately to Calculate and determine taxation liabilities for unincorporated organizations
Income tax should be applied on certain types of income of some types of entity. Regrettably, theoretically the taxpayers have no consensus on the right unit. There are many legal, economic, social and natural bodies that Congress can choose: individuals (normal), family units, families (together living), sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, trusts, property, government, religious parties, non-profit organizations, and other voluntary or co-operative societies.
Notwithstanding disagreements, which are the right choice among these or other organizations, the Congress has shown that reality, only some companies are responsible for paying taxes. According to the code, the individual, most corporations, and fiduciary (property and trust) are taxable institutions. Other organizations, such as sole proprietorship, partnership and so-called ‘S’ corporations do not have to pay taxes in any taxable income. Instead, the taxable income of these units is allocated to their owners, who take responsibility for paying any taxes (O Dea et al, 2007).
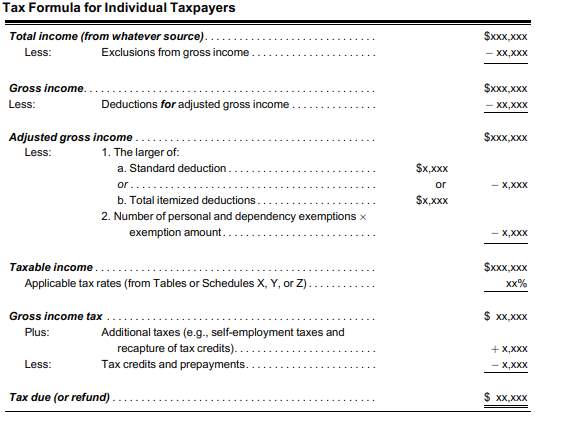
Calculating income tax liability is usually complex, only a few simple mathematical calculations are required. These steps, shown as 255 tax sources, are shown

D2. Investigate taxation liabilities and use appropriate application models and formulae to interpret and analyze data correctly.
Calculating tax liability is not a very difficult task. After all, the calculation is not anything but simple mathematical calculations. Apart from this, the rules provided by the Internal Revenue Service play a very important role in real calculation. To calculate tax liability, you should understand some of the ideas that you know (Wakefield, 2009). To pay tax liability to any person or corporation, legally mandatory total financial amount can be called.
Process
Compensation of tax liability for the corporation can be a difficult matter and should be done with the help of a certified chartered accountant. However, for private or private returns, these values are relatively easy to count.
Phase 1
Internal Revenue Service Officer Interface is the IRS portal. This interface is capable of resolving all potential tax-related questions. Another qualification for this interface is that it provides the director look for tax. Most of these work as form calculators. To calculate personal or separate tax liability, you need to download two documents, i.e. IRS Form 1040 and Form 1040 guide. The form is one that should be filed and used as a reference for instructions (Bromberg et al, 2003).
The next step is to calculate your total income for the year.
If you are a recruiting person, you can refer to the W-2 form issued by your employer. In addition, to accommodate more coordination, you need to keep an eye on the 10 99 filing.
The next step is to start calculating your permanent property income. Adjusted total income is calculated by legal adjustments and tax deductions from your general gross income (total of your total income).
This form will specify a specific financial person who changes every year, the number of claims you have claimed, the total value of your discount for the result. The value is deducted from your income and you will receive your taxable income.
In the last step, you can calculate your total taxable income. For this, apply tax rates applicable in taxable rates in taxable rates (specific to the tax bracket for which you qualify). This gives you your tax liability which you need to pay to the IRS.
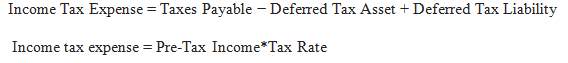
Task 3: Determine taxation liabilities for incorporated organizations. You may consider Uber and one more transport organization operating within the UK. (LO3, P3, M3)
A company can enter into an agreement with a corporate body to take part in its own right, property and matters. It enjoys limited liability. Businesses involved in the approach of law are considered legal acts. UBER is a corporate organization. This concept, known as limited liability, suggests that UBER will be held responsible for its own taxes, debts and the other consequences. Because of this, the owner-shareholder will not only lose the company’s investment, they will lose the investment amount of the company.
Corporations also provide benefits on other types of businesses, which can increase through equity rather than loans. As a result of dividend payments, as well as optional, ubera does not have to pay for your investment share investment. Other business structures depend on a higher amount of debt, which should always be paid with interest.
Money operating business, the ability to raise money, large amounts of corporations much faster than other types of business.
Often unique psychological car corporate manager can decide unethical for the growth of revenue and profit continuously in the form of a loyal, long-term outsourcing staff, as a percentage of profit margins added or consumed and in addition to the natural environment. Some practices involved in external stakeholders (Bromberg et al, 2003). They have not paid taxes, have made immoral decisions and have done some illegal acts like paying taxes
There are four types of incorporated structures for voluntary organizations

Now we will be discussing about the taxation liabilities of both the private and the public companies and the models and the formulas for the determination of the taxation liabilities in the
P3. Explore and explain taxation liabilities for both private and public companies.
For at least one voluntary association, which is responsible for those shares of the transfer limit of its members, two of a private limited company have allowed it or invite a company whose securities exchanges do not have debentures. For subscribing to their shares, the public is restricted to the general public, the business is done and the color bought by any person can be sold.
Private limited company and tax:
When you set up a limited company, personal and business money is completely kept separate (as opposed to trade routes only). Contrary to life as a paid employee, you are now paying your income taxes by registering the responsibility of supervising your obligations, and at the time of making sure that there is no accountability of the HMRC (Bradford et al, 2004). Uber is a private limited company and for this reason it will be under the following tax system:
Value Added Tax (VAT)
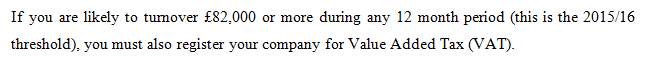
In fact, you collect VAT from HMRC, but add the existing move to your invoice (standard rate 20%). Once you have deducted VAT spent in VAT category, you pay HMRC balance.
PAYE / National Insurance Contributions
Your primary job (or your accountant) is likely to put your company’s payroll. If you and any other employee are deducted on the salary, income tax and National Insurance Contribution (NIC) source, and HMRC is paid on monthly or quarterly basis.
Public companies and tax
Instead of a public company, there are many tax requirements and rules that a non-governmental company cannot think first, there are some resources which should not be implemented after the publication of your company. It needs to be prepared before the public offer. Those who are not fully prepared for infection may lose face or face in case of more serious cases (De Vries et al, 2002).
Pre-IPO timeframe represents the ideal opportunity to raise tax issues. The first step is to review your company’s tax status and status review of individual taxpayers. This will enable you to provide directions in areas where you can make or profit in public, as well as ensure that your company’s tax is effectively protected.
Prior to the IPO, stock capital restructuring, corporate groups may need to be consolidated or reconstituted or the property should be shared or contributed.
M3. Apply recognized models and formulae to interpret data and determine taxation liabilities, including late payment interest penalties, for incorporated organizations.
Calculating your taxable income and tax liability as a small business can be a little challenging. Most small businesses are established as a limited liability company (LLC) or partnership, or any other type of pass-unit. In the pass unit, the owner of the income business is “passed” and the tax revenues of the person are recovered.
1. Set your total income. According to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
2. Reduce any cost to your business from your total income throughout your whole year
3. Apply your tax-appropriate tax rate based on the amount used for taxable income and method (single, married filing separately, etc.). This number will be your tax liability.
Calculating tax liability is not really a very difficult task. After all, counting is nothing but a few simple mathematical calculations. In addition, the rules set by the Internal Revenue Service play an important role in real calculation. To know how to calculate tax liability, you have to understand some ideas.
Important notice
Tax liability is understood as a total monetary amount, which is obliged by the government or corporation to pay the government. The same period is used in the context of undefined taxes which are further improved in the next fiscal year. So, it can be said in terms of the total tax amount paid to the organization, departments, and organizations in this term. This total figure consists mainly of the total amount of tax, which is paid for the current year and those who were not given earlier. In some cases, you have to calculate different federal tax and state taxes. In addition, in some cases, the collection agency may also inform the rate of interest paid on the total unauthorized taxes of previous interests.
For the late payment of Tax in the case of UBER:
Due to late tax treasures on tax is a lot because of the drain. It can also provide unexpected benefits for rivals and opponents. Interest on Late Payment (ILP) Charge: Fine for late payment; It ensures that those who pay timely payday loans will not be available for business; Encourage taxpayers to pay time in the future
This directive connects interest and interest payments with normal charging to late payments, with complaints of interest and debt of direct debit systems. It includes a brief note of interest rates released under the PayPal system.
In the last 12 months, the ILP should be regularly raised in all cases obtained by the ILP.
The interest process on late payments (PLPLP) is based on the pre-defined rules, to identify the ILP issues. Uber will come under this. Managers or team leaders run PAILP queries using case selection database. Questions can be run for warning letter, ILP fee or both. In most cases, a letter is automatically generated and this letter is signed by the printed and relevant caseworker. The PayPal system will create ‘closed’ job items in the automatic case so that it can be indicated whether a warning letter is issued or is being offered to the ISI or fees. The manager or team leader can allocate any case, which should be reviewed by the ICM team and the case maker will then decide if a warning letter or interest rate should be issued (Jones, 2008).
The interest is charged on a daily basis so that it can accurately reflect the payment accuracy. Therefore, to avoid high interest rates, it is necessary to pay their tax liability as soon as possible for the best interests of the customer.
Task 4: Evaluate the impact on organizations of the legal and ethical constraints associated with taxation responsibilities. You may consider the current state of affairs at Uber and other international organizations to evaluate the impact that taxation responsibilities have had on them. (LO4, P4, M4, D3)
P4. Evaluate the impact of key legal and ethical constraints on different organizations.
For the last decade, the globalization process has ruined the relevance of the bases of the areas for social, economic and political activities, processes and relationships. Commercially, it became a regional destination; growing corporations in foreign markets were suddenly new and diverse, sometimes facing ethical contradictions. The moral values given in the accepted market can be questioned immediately after the corporation entered the foreign market (Blow et al, 2002). In many countries, this power is greatly reduced due to poverty, poor education, limited access to information, corruption and an inefficient political environment.
Frequent Empathy: The host of the corrupt state officials (to get government benefits), disrespect for human rights, promote financial position of the company, and fraud information (information on the basis of dissemination) provides false information. Use of harmful workers, informational theft, industrial espionage, waste of natural resources, sexual discrimination, deliberate pollution etc.
The regions represent ethical issues of contemporary managers for real ethical dilemma, as they are producing, at least one short period, organizing economic activities in a conflict (to assess the costs and benefits of business measures) (Jones, 2008).
The challenge of international business is that ethics can be a deficiency, unless it is simple irrelevant. Many business people think that there are only two options in the business: behaving
Continuous or unsuccessful, and they argue that the existence of the company will not jeopardize competitors for their ethical conduct in order to fulfill a moral obligation. In my opinion, it is dramatic for both competition and competition in domestic and international markets, claiming that opponents are designed to destroy all opponents. The decision is not very dependent on whether it is very serious, most of the business existence, so the company is to protect immoral because it is the most important ethical conflict that the risk nature is changing, international managers have to face cases of corruption, respectively, There is a government clerk opportunity some business providers provide this action, local labor recruiting agencies, and organizational This increase has increased in capacity and level of life.
One of the most developed or undeveloped countries, which led to the opinion, are a daily aspect of that, in such countries, government money is an integral part of a successful business. Many multinational corporations implementing these practices are determined by their rivals that they practice them and they do not want to be left behind.
Ethical values vary between society, company and nation. People have different ethical values. In more developed countries in the United States, UK cases like bribery are considered to be great and illegal and illegal.
However, there are many bribe cases in less developed countries. In developed countries, while seeing most employees in developing countries, their employees are neglected on high consideration (Bradford et al, 2004).
M4. Critically evaluate the impacts of key legal and ethical constraints on application to different organizations, providing supporting conclusions and recommendations.
Each revenue authority has a different environment under which they manage their taxpayer system. Regional policies vary in relation to their policies and legal environment and their administrative practice and culture. Therefore, a standard method for tax administration is not practical and preferred in a particular example.
Documents that make the OCD guide series should be remembered.
Growth or underdeveloped countries, the situation is complicated that these institutions serve some ethical rules for the investigation of any organization. For this reason, many multinationals enjoy serious business ethical policies or serious violations in the external market. This happened in the case of recovering. The main attraction of successful work, due to the behavior of their ethical support for business ethics and cultural relativity, and local economic practices, attitudes and maintenance, they (Blow, 2002) business ethics. Success of the market is often dominated by suspicious practices. UBER is doing this. UBER did not pay the taxes for a long time and was doing some suspicious activities under some of its subsidiaries. As a result the TFL found UBER as guilty and cancelled its license and did not renew that. If they want to continue that business they will have to be in the discussion with TFL and will have to pay the taxes with the late fees following the ethical issues.
In my eyes, an organization has to adopt “long-term” ethical conduct without thinking otherwise. Therefore, any unethical behavior of the organization will represent the continuous source of cost; it will hide its activity from interested partners. In addition, any “secret” represents a weak PIN of the organization, which is weak before competitors. Obviously, the agency’s expression became more vulnerable, it became more risky for competitive attacks.
Regardless of the time, the organizations’ efforts to hide the shape are displayed in their unethical approach, they are widely published and widely (often by the media or its competitors).
It is an international agency to give immoral practices special effects to unethical practices in a particular developed market, where very strong restrictions are defined in the law.
In short, on the other hand, market develops in most cases, and the use of community managers on the false front with various unethical business practices, business and weird people are inactive and quiet.
“Peace” clearly sent a negative message to the public, of course, passed through any other ethical standards and principles captured in the activities of the organization and declared greater and more. On the other hand, we believe that in the developed countries, where trade fair games are very important and in this way large international corporations can not be taken to reduce some unethical practices of publication, by a series of customers and business partners Any restrictions beyond those people should be left.
An organization that respects suspicious transactions now wants to run a search to get rid of long goals and objectives, which can be centered on those who do not care about them. This company is losing its resources, and it is due to the fact that it came, and neglected to see past ethics (Blomquist et al, 2009).
This type of behavior does not leave the organization with the support of its internal forces and employees, who do not rely on it and its managers. Ethics of an organization can be considered morally from this point of view. An investor should not start any business unless he is interested in the policy, from the beginning, its meaning has failed.
For a long time, the organization went inside and it would be invisible to face a significant reduction of financial loss or even the lack of negative images of both markets that day.
Unfortunately, one ethical behavior does not provide more skills in organizing or organizing activities.
From the perspective of the opposition, respect for business ethical principles can be of significant benefit to the contemporary organization.
Therefore, firstly, in the case of unethical behavior of competition and potential abuse of its employees, company security is provided to promote ethical behavior.
Ethical behavior of employees related to more accurate, economic and social environment
D3. Provide supporting and justified recommendations for responding to and minimising the impact of legal and ethical constraints for a range of international examples.
We have to keep in mind that the origins of large international corporations have happened in developed countries, where trade fair games are extremely important and thus organizations lose some of the unethical behavior, even beyond the legal limitations, they will be released by a series of customers and business partners.
Nike’s situation is well-known, because in 1997, after the release of some unforeseen works of the corporation in New York, his image was quite bad. The American people easily find Nike sports shoes for children, for which American parents pay $ 100 and $ 180, Nike produces only $ 5. Completely surprising happens when some Pakistani and Indonesian children are supplied $ 2 billion each month to the Nike logo.
Those who first saw it were teenagers Bronx, who started a protest in front of Nike-town. About 200 teenagers were rescued in front of old Nike Sports Shoes security agents. A 13-year-old girl said to the national television channel, “Nike, we made you, we’ll break you!” (Warren and Viez, 2004, page 22)
After this incident, Nike opens the greed of the manager public and kills the corporation’s image, which has not been repaired yet.
This is an international agency to make unethical practices special effects on fame, especially in the developed market, where the law has very strong sanctions defined. In addition, rumors about the organization’s reputation or its vulnerability can determine sales constraints and customers can choose different providers (Auten et al, 2002).
Among the worst cases there are companies that do not violate the ethical business principles, but in such practices, they violate the fundamental rights of their consumers in front of the law.
Also, if the company is not at least immoral, many times customers are competing efficiently. In this way, chewing gum for brushing teeth is an example of immoral gem; in fact the false brain only corrupts the tooth and makes the stomach ill and the causes of the presence of some facial microbial cultures in artificial digestion
The issue of unethical intervention of customers is made based on this subject that a large part of the organization’s people are able to find out what can happen by these companies and they think that they, their family and friends can be treated properly (Keen et al, 2010).
Conclusion
Taxation is very important in any country’s revenue growth. These are spent to fulfill the necessity of the general people. The legislation makes the tax rate for the entities that comes under the tax policy of the country. Every entity should pay the tax so that it can be reimbursed to them. The organizations should follow the ethics in paying the taxes.
References
Acosta-Ormaechea, Santiago and Jiae Yoo, 2012, “Tax Composition and Growth: A Broad Cross-Country Perspective,” IMF Working Paper /12/257.
Arnold, Jens B., Bert Brys, Christopher Heady, Åsa Johansson, Cyrille Schwellnus and Laura Vartia, 2011, “Tax Policy for Economic Recovery and Growth,’” Economic Journal, Vol. 121, pp. F59-F80.
Auten, Gerald E., Holger Sieg, and Charles T. Clotfelter. 2002. “Charitable Giving, Income, and Taxes: An Analysis of Panel Data.” American Economic Review 92 (1): 371–82.
Blomquist, Sören, and Håkan Selin. 2009. “Hourly Wage Rate and Taxable Labor Income Responsiveness to Changes in Marginal Tax Rates.” Uppsala University Department of Economics Working Paper 2009-1.
Blow, L., Hawkins, M., Klemm, A., and McCrae, J. (2002), Budget 2002: Business Tax Changes, Briefing Note 24, London: Institute for Fiscal Studie
Bromberg. A. R. and L. E. Ribstein. 2003. Limited Liability Partnerships, the Revised Uniform Partnership Act, and the Uniform Limited Partnership Act.
Bradford, Steven C. 2004. Does Size Matter? An Economic Analysis of Small Business Exemptions from Regulation. Journal of Small and Emerging Business Law, 8(1): 1–37.
Bond, S. (2006), ‘Company Taxation’, in Chote, R., Emmerson, C., Harrison, R., and Miles, D. (eds.), The IFS Green Budget: January 2006, London: Institute for Fiscal Studies,
Brown, Michael , Linda K. Treviño , and David A. Harrison . 2005. Ethical Leadership: A Social Learning Perspective for Construct Development and Testing. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 97(2): 117–34.
De Vries , Michiel S . 2002. Can You Afford Honesty? A Comparative Analysis of Ethos and Ethics in Local Government. Administration & Society 34(3): 309–34.
Feldman, Martha S. , Anne M. Khademian , Helen Ingram , and Anne S. Schneider . 2006. Ways of Knowing and Inclusive Management Practices. Special issue, Public Administration Review 66: 89–99.
Gray, J. and Chapman, E (2001) Evaluation of Revenue Projects Synthesis Report Volume 1, Evaluation Report EV636 (London: Department for International Development).
Goodman, A., and Leicester, A. (2006), Household Spending in Britain: What Can It Teach Us About Poverty?, Bristol: The Policy Press.
HM Treasury (2002), ‘Tax Benefit Reference Manual 2002–03 Edition’.
Helmuth Cremer, Direct versus Indirect Taxation: The Design of the Tax Structure Revisited, 2001.
Jones, F. (2008), ‘The Effects of Taxes and Benefits on Household Income, 2006/07’, Economic and Labour Market Review, 2, 37–47, London: Office for National Statistics
Khan, M. (2001) “Agricultural taxation in developing countries: a survey of issues and policy” Agricultural Economics, vol. 24, pp. 315-328.
Keen, Michael, and Ben Lockwood, 2010, “The Value-Added Tax: Its Causes and Consequences,” Journal of Development Economics, Vol. 92, pp. 138–51.
Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development, 2006, The Challenge of Capacity Development – Working Towards Good Practice, (Paris: OECD).
O’Dea, C., Phillips, D., and Vink, A. (2007), A Survey of the UK Benefit System, Briefing Note 13, London: Institute for Fiscal Studies,
Wakefield, M. (2009), How Much Do We Tax the Return to Saving?, Briefing Note 82, London: Institute for Fiscal Studies,
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
CollectionsContent relating to: "Tax"
Tax is the name given to a payment or other financial charge that taxpayers must pay. Governments impose taxes to generate money to put towards government spending, and anybody found to be evading tax will face legal punishment.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this assignment and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


