Challenges faced by the Institutions in Emerging Markets
| ✓ Paper Type: Free Assignment | ✓ Study Level: University / Undergraduate |
| ✓ Wordcount: 2669 words | ✓ Published: 12 Aug 2019 |
Abstract
This paper is mainly based on the issues and challenges that are faced by the institutions in the emerging markets. The emerging markets are rapidly growing markets of the world and these markets are mainly depending upon certain institutions in order to have better control over its operations. The institutions like banks play an important role in the development of the emerging markets. The banks are the main institutions which helps the investors and companies with the lending options. The growth of a emerging country is mainly depending upon the operations of banks as they control the market liquidity through the policies.
This paper is mainly discusses the political influence on the government banks in the emerging countries. The political systems in the emerging countries might change from country to country but the political motive remains the same. The political parties generally the ruling governments try to control the banking institutions in order to favour the market conditions for the ruling governments. There are several evidences collected in this paper regarding the political influence on the banking companies and especially on the government banks.
The research found that the political parties and the ruling governments put pressure on the government banks especially during the election periods. There are several instances where the political influences tries to control the banking policies in order to get better prospectus in front of the people. The political influence is not certainly bad but at times this could be dangerous. One has to consider the situation and interference in the banking rules and regulations can be reduced by the political parties and the banks should be given utmost autonomy over the operations.
Introduction
Politicians and banks: political influences on government owned banks in emerging markets one of the influential publication journal of financial economics. This publication has been cited more than 1047 times according to google scholar. This publication influenced many scholars, mangers and policymakers worldwide.in this paper author study the political influences on government banks in emerging markets and trends to lending by those banks in election and non election years. He shows that government ownership has not impact on economic growth of a country. There is a difference in pattern of ownership of banking firm in emerging and developed economies more the developed nation less the control on government in banking and vice a versa. Effects of government control may be not much visible in economic growth of a country but, the government banks fulfils the agenda of financial inclusion in a country to bring the each and every person of country into main stream banking which is important for economic growth (Burgerss & Pande, 2005). Political institution in emerging markets affect the government owned banks and control macroeconomic factors.
The banking sector is one of the dynamic industry which has seen ups and downs over the years. The banking industry is developed a lot due to the attention given by the governments and authorities in different countries. The emerging markets are particularly interested in the banking industry of the countries due to the importance and relevance of this industry. The growth and development of industries and markets in the emerging market economies generally depends on the banking industry. Banking companies are the architectures of development in the emerging markets.
The emerging markets which are volatile rely on the banking industry to bring the stability into the economy. The banking companies decide the liquidity position of the emerging markets along with many other financial decisions. So influencing the banking industry through various means is common not only in the emerging markets but also in the other markets in the world. The major idea of the forces those influence the banking companies is to get long terms benefits from the banks.
Most of the emerging countries have two types of banks. The first one is the private sector banks which are owned and managed by the private shareholders. The second category of banks are government sector banks. Government sector banks are owned and managed by the governments of countries. But the ownership of banks is quiet different in some of the countries like India where the ownership of public sector banks is also with the private shareholders.
The government owned banks are more influential in an emerging economy due to the liquidity that the bank carries. The government banks are generally controlled by the ruling governments and acts normally as per the directions of the ruling parties. The decisions of the government owned banks are generally based on political lobbies which would be controlling these banks. We can see the influence of political motives in the decisions of government banks in various periods.
This paper tries to work out the issues regarding the political influence on the government banks during various period. Although government-owned banks increase their lending in election years, the share of loans as a fraction of total assets is not any greater in government-owned banks across the electoral cycle on average. In reality, perhaps more strikingly, the share of government securities in bank property is ready 50% greater in government owned banks in rising markets than it’s miles in private banks. one of the essential arguments in want of government ownership of banks has been their capability to finance viable projects that non-public banks cannot or will now not finance. yet the proof suggests that government-owned banks in rising markets finance the government itself to a greater degree than do personal banks.
The evidence provided here extends the insights from single-country research on banking. Clarkeand Cull (2002) argue that governors who belonged to a fiscally conservative birthday celebration have been more likely to denationalize banks in Argentina. Sapienza (2004) reveals that the hobby rates charged by authorities-owned banks in Italy mirror the nearby power of the party that controls the financial institution. Mian (2003a) compares private and government-owned banks in Pakistan and demonstrates the differences in incentives and supervision.
Kane(1996) and Kroszner and Strahan (1999) have a look at the role of politics in designing financial institution regulation, whilst Brown and Dinc (2004) show that the implementation of current law is also politically driven. Perotti and von Thadden (2003) show how the distribution of human and monetary capital can have an effect on the emergence of financial institution or marketplace dominance thru the political system. Pagano and Volpin (2004) have a look at the position of the electoral device inside the stage of minority protection. several current papers study the role of political connections in finance. Fisman (2001) indicates how the information approximately Suharto’s deteriorating fitness adversely affected thevalueof corporations with robust connections to him. Johnson and Mitton (2003) show that capital controls in Malaysia provided rents to politically related firms. Faccio (2004) unearths in a cross country examine that firms with political connections have simpler get entry to debt financing and revel in decrease taxation.
This paper has various sections which focuses towards the logical conclusions about the research topic. The paper discusses the methodology used to understand the research topic and various analytical techniques used for understanding the topic in a better way. The paper concludes with recommendations and major findings about the research topic.
Banking in the Emerging Markets
Government banks finance projects those are critical for economic development, private banks may not finance those projects but government ownership of banks has no evidence that it foster any GDP growth rather opposite is true. Politician use these government owned banks to fulfill their own agenda to remain in power (La porta et al, 2002).the reason is that economic growth offered by those projects may be offset by subsequent increase in bad loans which force government to infuse more capital in government owned banks which ultimately leads to less money spend for infrastructure development. In Pakistan Between 1962 and 2002 political connected firms borrow 45% more and have 50% more rate of default this trend hamper GDP growth rate by 0.3 to 1.9% every year (Khawja and Mian, 2005 ).
State owned banks plays important role in controlling macroeconomic factors in an economy and also stabilize credit because of followings reasons; first state’s principle internalize the benefits of more stable macro economic environment. Therefore credit stabilization is part of objective function of state-banks. Second to do with the fact that during recession depositors think that their deposit is safe with public banks than private banks (possibly because of deposit insurance), hence government owned banks enjoy more stable deposit base, make them able to smooth credit. Third, lower cyclicality is due to “Lazy” behaviour of managers of state banks. Final reason is that as political influence on state owned banks to increase lending in electoral cycle as author of this paper already stated.(Micco and Panizza, 2006).
In developed countries more than 90% of population has bank account or they are part of formal financial system, while in developing countries mainly low-income people has little or no access to formal financial system. Therefore those people has to depended on own source or informal source of finance which is very costly. Only 20 to 30 people are part of formal financial system in emerging economies. Recent report shows that countries with large population deprive of formal financial system face high poverty and inequality (Thorat , 2008)”.
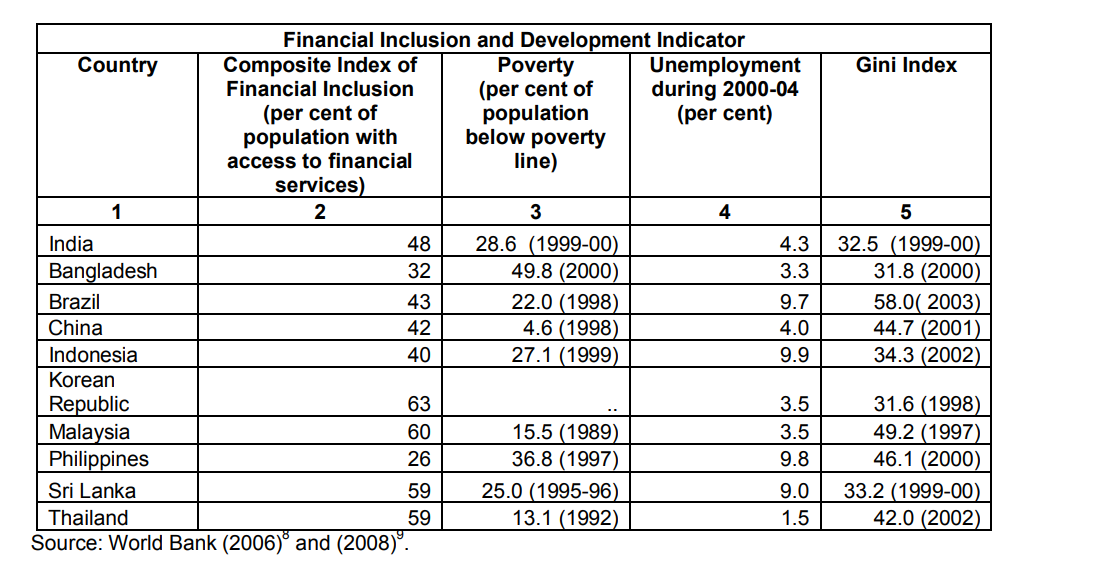
Source: Throat, 2008
Government banks offer banking services at free of cost to poor and most low income group of emerging markets such as no frill account and incentive to encourage people to use debit and creditcards to fil the gap of institutional voids. where as private banks are profits driven and charge for their services large people of emerging markets may not able to afford.Government owned banks may not helping in economic growth but financial inclusion and access to credit and financial system is very important for a country to reduce poverty and income inequality (Claessen and Perotti, 2005).
There is a second side of coin too we can understand this by studying behaviour of government in banking system in India in past 10 years. As recently government launched many financial inclusion policies to connect rural people to mainstream financial system which is successful mission up to some extent but at the same time many big corporate houses became defaulters on biggest public banks all houses has political connection that’s why they were getting preferential treatment despite being defaulter. But, ultimately this worsen the condition of public banks and government has to infuse more capitals into government banks.
As most of developed economies are free markets base economies and macroeconomic factors are predictable and people are with high income. In contrast people of emerging markets are with low income or poor and most of markets are mixed or state owned economies and business environment is unpredictable so government ownership of banks is inevitable part. It is also true that as the country develop income of people grows government ownership in firm keep of reducing.
It is also reported that the increased lending not only happen in emerging markets but also occur in developed economies in the time of election as per one research done in German saving banks from 1994 to 2006 and over the period of 1250 local election and also banks in economically weak areas are less prone to political influence (Yortglu, 2018 ).At same time lending by state banks in high income countries with good governance is less pro cyclical than lending by private banks. Lending by state banks in high-income economies is countercyclical (Bertay et al, 2012). Here it is understandable that lending by government owned banks in high income countries is depend on business cycle whereas lending in emerging markets is somewhere influenced by electoral cycle .
It also true for common man getting a loan from government is nor easy as compared to get a loan from private banks. Private Banks can lend a person more than his worth but government owned banks strictly follow rule and helps controlling the private debt, this is one the reason why emerging markets were less affected by sup-prime crisis as compared to developed economies in 2008.
Question is arising that why political institution largely affect the government owned banks in emerging markets. We have identified some of the reasons first most influential businessman in these countries join politics at some point or person already in politics create his business empire by his malpractices for their own interest law maker influence state banks. Secondly some board of director in the banks may appoint by ruling political party for their interest. Third, institutions are full of corruption their own interest is over and above nation’s interest. Last but not least low level of education in emerging markets makes people less aware and politician easily fool them.
However, government owned banks increase lending in election years as compared to private banks as author of this paper has showed in original paper but author has not showed the relationship and rationale behind the government ownership in banking sector in emerging markets.
As original has done study of cross- country, bank level politically motivated lending at government owned banks in emerging markets.In this paper further adding to original author we will study about how political actions in macroeconomic and business cycle effects institutions in emerging markets, Political Institution’s role in banking in emerging markets, is there rationale behind or political intention behind to keep control of major banks in emerging markets and finally study the robustness of the results to potential macroeconomic changes in election years. Five distinct macroeconomic variables are studied: GDP per capita, GDP growth rate, government budget surplus (or deficit), inflation rate, and exchange rate. We will be comparing the actions of government owned banks with actions of private banks around general election in major emerging economies over the period of 1994 to 2008.
Methodology
The emerging markets are volatile and the institutions operating in these countries are also volatile due to the nature of the market. The institutions in the emerging markets sometimes face problems due to the influences of the ruling governments. The institutions especially like banks are under serious threats in various occasions due to the influences of political forces who tries to control the institutions. For a long term sustainability this is not a good sign for the banks in the emerging markets. There are several scholars who has analyzed these issues through multiple articles and publications.
The methodology used in this paper is collected from various secondary sources. The secondary sources are mostly collected from the web sources and journals published related to this topic. There are several articles those are published related to the emerging markets are taken into consideration in order to have a better understanding of the topic. The articles are analyzed and required information is tabulated in this paper. Other than these secondary research sources our team has provided their understanding about the topic as well. So the paper is mostly the combination of primary and secondary sources.
The collected information from different sources is analyzed in this paper. The analysis and discussion focuses on the conclusion of the topic. There are few statistics those are collected from various sources in order to have better understanding about the topic. The discussion is generally concentrated on the collected data with few personal inputs. The conclusions and findings are reported after analyzing all the possible data available in various sources. Before summarizing the data related to the selected research topic let us first discuss the conceptual aspects of the topic.
Mapping of the research idea
The research question is all about the political influence on the government banks in the emerging markets. The emerging markets are mostly depending on the governmental banks in order to fund the developmental works in various countries. The idea is mapped based on the different related matters to the main issue. The basic concept of political influence is further mapped with the three important aspects of corruption rates in the countries. The main three divisions are highly corrupted countries, low corrupted countries and no corruption country. The political influence in the no corruption country would be much lower compared to other countries which are highly corrupted.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this assignment and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


